Dimepheptanol
Dimepheptanol (INN; Amidol, Pangerin), also known as methadol or racemethadol, is a synthetic opioid analgesic related to methadone. It has similar effects to other opioids, including analgesia, sedation and euphoria, as well as side effects like itching, nausea and respiratory depression.
Dimepheptanol is a mixture of two isomers, alphamethadol (α-methadol) and betamethadol (β-methadol).[1] These are also available separately, and this drug has three separate entries in many national and international lists of illegal drugs, which refer to the racemic mixture dimepheptanol, and the two optical isomers.[1] Each of these isomers is itself a mixture of two isomers, and so there are in fact four isomers of dimepheptanol in total; L-α-methadol, D-α-methadol, L-β-methadol and D-β-methadol.[1]
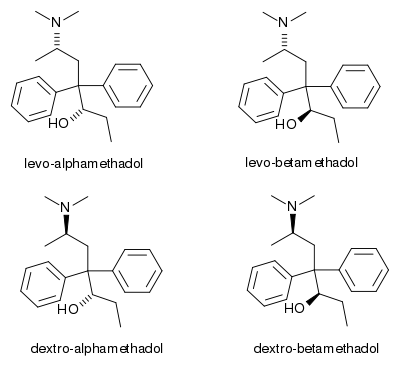
The isomer L-α-methadol is the active metabolite of the long-acting opioid substitute drug levomethadyl acetate (LAAM), and has been used much more widely than β-methadol or the racemic mixture of dimepheptanol.
Both in US Controlled Substances Act 1970 Schedule I, the two isomers both have annual manufacturing quotas of 2 grammes and the ACSCNs of 9605 for alphamethadol and 9609 for betamethadol.
See also
References
|
|---|
| | Opioids | |
|---|
| | Anilines | |
|---|
| | NSAIDs | |
|---|
| | Cannabinoids | |
|---|
| | Channelergics | |
|---|
| | Myorelaxants | |
|---|
| | Others | |
|---|
| |
| | |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- meninges
- cortex
- association fibers
- commissural fibers
- lateral ventricles
- basal ganglia
- diencephalon
- mesencephalon
- pons
- cerebellum
- medulla
- spinal cord
- Physiology
- Development
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Cerebral palsy
- Meningitis
- Demyelinating diseases
- Seizures and epilepsy
- Headache
- Stroke
- Sleep
- Congenital
- Injury
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Other
- Symptoms and signs
- head and neck
- eponymous
- lesions
- Tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- general anesthetics
- analgesics
- addiction
- epilepsy
- cholinergics
- migraine
- Parkinson's
- vertigo
- other
|
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Receptor
(ligands) | | MOR |
- PAMs: BMS-986121
- BMS-986122
|
|---|
| | DOR | |
|---|
| | KOR |
- Agonists: 6'-GNTI
- 8-CAC
- 18-MC
- 14-Methoxymetopon
- β-Chlornaltrexamine
- β-Funaltrexamine
- Adrenorphin (metorphamide)
- Akuuamicine
- Alazocine
- Allomatrine
- Asimadoline
- BAM-12P
- BAM-18P
- BAM-22P
- Big dynorphin
- Bremazocine
- BRL-52537
- Butorphanol
- BW-373U86
- Cebranopadol
- Ciprefadol
- CR845
- Cyclazocine
- Cyclorphan
- Cyprenorphine
- Diamorphine (heroin)
- Diacetylnalorphine
- Dihydroetorphine
- Dihydromorphine
- Dynorphin A
- Dynorphin B (rimorphin)
- Enadoline
- Eptazocine
- Erinacine E
- Ethylketazocine
- Etorphine
- FE 200665 (CR665)
- Fedotozine
- Fentanyl
- Gemazocine
- GR-89696
- GR-103545
- Hemorphin-4
- Herkinorin
- HS665
- Hydromorphone
- HZ-2
- Ibogaine
- ICI-199,441
- ICI-204,448
- Ketamine
- Ketazocine
- Laudanosine
- Leumorphin (dynorphin B-29)
- Levallorphan
- Levorphanol
- Lofentanil
- LPK-26
- Lufuradom
- Matrine
- MB-1C-OH
- Menthol
- Metazocine
- Metkefamide
- Mianserin
- Mirtazapine
- Morphine
- Moxazocine
- N-MPPP
- Nalbuphine
- NalBzOH
- Nalfurafine
- Nalmefene
- Nalorphine
- Naltriben
- Norbuprenorphine
- Norbuprenorphine-3-glucuronide
- O-Desmethyltramadol
- Oripavine
- Oxilorphan
- Oxycodone
- Pentazocine
- Pethidine (meperidine)
- Phenazocine
- Proxorphan
- RB-64
- Salvinorin A (salvia)
- Salvinorin B ethoxymethyl ether
- Salvinorin B methoxymethyl ether
- SKF-10047
- Spiradoline (U-62,066)
- Thienorphine
- Tifluadom
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, desipramine, imipramine, nortriptyline)
- U-50,488
- U-54,494A
- U-69,593
- Xorphanol
|
|---|
| | NOP |
- Antagonists: (Nphe1)Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
- AT-076
- BAN-ORL-24
- J-113397
- JTC-801
- LY-2940094
- NalBzOH
- Nociceptin (1-7)
- Nocistatin
- SB-612111
- SR-16430
- Thienorphine
- Trap-101
- UFP-101
|
|---|
| Unsorted /
unknown | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Enzyme
(inhibitors) | |
|---|
| | Others | |
|---|
| See also: Neuropeptidergics • Peptidergics |
|

