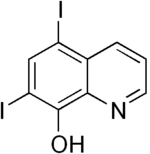
Diiodohydroxyquinoline
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5,7-diiodoquinolin-8-ol | |
| Other names
Diquinol, iodoxin, diiodoquin, amebaquin | |
| Identifiers | |
| ATC code | G01 |
| 83-73-8 | |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL86754 |
| ChemSpider | 3597 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| KEGG | D00581 |
| MeSH | Iodoquinol |
| PubChem | 3728 |
| |
| UNII | 63W7IE88K8 |
| Properties | |
| C9H5I2NO | |
| Molar mass | 396.951 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
The quinoline derivative diiodohydroxyquinoline (INN) or iodoquinol (USAN), can be used in the treatment of amoebiasis.[1]
It is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is used as a luminal amebicide. It acts by chelation of ferrous ions essential for metabolism.[2]
It was discovered by Adco Co. and introduced as diiodohydroxyquinoline.[3]
Susceptibility of Dientamoeba fragilis has been measured.[4]
Iodoquinol is an amebocide used against Entamoeba histolytica, and it is active against both cysts and trophozoites that are localized in the lumen of the intestine. It is considered the drug of choice for treating asymptomatic or moderate forms of amebiasis. The mechanism of action is unknown. Iodoquinol is used for diseases caused by moderate intestinal amebiasis.
References
- ↑ Ghaskadbi S, Vaidya VG (March 1989). "In vivo antimutagenic effect of ascorbic acid against mutagenicity of the common antiamebic drug diiodohydroxyquinoline". Mutat. Res. 222 (3): 219–22. doi:10.1016/0165-1218(89)90137-7. PMID 2493578.
- ↑ Gideon Online http://web.gideononline.com/web/therapy/index.php?type=drugs&code=20130&view=General. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Page 1312. http://books.google.co.in/books?id=TIu28TH_iAYC&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q&f=false
- ↑ Chan FT, Guan MX, Mackenzie AM, Diaz-Mitoma F (May 1994). "Susceptibility testing of Dientamoeba fragilis ATCC 30948 with iodoquinol, paromomycin, tetracycline, and metronidazole". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 38 (5): 1157–60. doi:10.1128/aac.38.5.1157. PMC 188168. PMID 8067755.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||