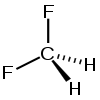
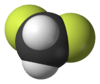Difluoromethane
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Difluoromethane[1] | |||
| Other names
Carbon fluoride hydride Methylene difluoride | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| Abbreviations | HFC-32 R-32 | ||
| 1730795 | |||
| 75-10-5 | |||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:47855 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL115186 | ||
| ChemSpider | 6105 | ||
| EC number | 200-839-4 | ||
| 259463 | |||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| MeSH | Difluoromethane | ||
| PubChem | 6345 | ||
| RTECS number | PA8537500 | ||
| |||
| UN number | 3252 | ||
| Properties | |||
| Molecular formula |
CH2F2 | ||
| Molar mass | 52.02 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 1.1 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −136 °C (−213 °F; 137 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −52 °C (−62 °F; 221 K) | ||
| log P | -0.611 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 1518.92 kPa (at 21.1 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| MSDS | External MSDS | ||
| EU classification | | ||
| R-phrases | R11 | ||
| S-phrases | S9, S16, S33 | ||
| NFPA 704 | |||
| 648 °C (1,198 °F; 921 K) | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. | |||
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas | ||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Difluoromethane, also called HFC-32 or R-32, is an organic compound of the dihalogenoalkane variety. It is based on methane, except that two of the four hydrogen atoms have been replaced by fluorine atoms. Hence the formula is CH2F2 instead of CH4 for normal methane.
Uses
Difluoromethane is a refrigerant that has zero ozone depletion potential. Difluoromethane in a zeotropic (50%/50%) m/m mixture with pentafluoroethane (R-125) is known as R-410A, a common replacement for various chlorofluorocarbons (aka Freon) in new refrigerant systems, especially for air-conditioning. The zeotropic mix of difluoromethane with pentafluoroethane (R-125) and tetrafluoroethane (R-134a) is known as R-407A through R-407E depending on the composition. Likewise the azeotropic (48.2%/51.8% m/m) mixture with chlorotrifluoromethane (R13). As a refrigerant difluoromethane is classified as A2L - slightly flammable [2009 ASHRAE Handbook]. Although it has zero ozone depletion potential, it has global warming potential 675 times that of carbon dioxide, based on a 100-year time frame [May 2010 TEAP XXI/9 Task Force Report].
References
- ↑ "Difluoromethane - Compound Summary". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center of Biotechnological Information.
External links
- Flammability Measurements of Difluoromethane in Air at 100 °C
- Difluoromethane at Gas Encyclopaedia
- IR absorption spectra
| ||||||||||||||||||||||