Dehydroalanine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
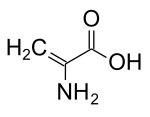
| IUPAC name
2-Aminoprop-2-enoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1948-56-7 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17123 |
| ChemSpider | 110510 |
| DrugBank | DB02688 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| KEGG | C02218 |
| PubChem | 123991 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 87.08 g/mol |
| Density | 1.222 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 251.2 °C (484.2 °F; 524.3 K) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Dehydroalanine (Cα,β-didehydroalanine, (alpha)-(beta)-di-dehydroalanine, or 2,3-didehydroalanine) is an uncommon unsaturated α-amino acid found in peptides of microbial origin.
Dehydroalanine (DHA) is also found in food proteins, including casein, that have been heated and/or treated with an alkali such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH). These treatments can dehydrate serine in the protein chain.
In food, DHA frequently alkylates lysine to yield the crosslinking aminoacid lysinoalanine (LAL). Lysinoalanine, N6-(DL-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-L-lysine, an unusual amino acid implicated as a renal toxic factor in laboratory rats (kidney damage), has been found in proteins of home-cooked and commercial foods and ingredients. Although it had been reported to occur in both edible and non-food proteins only after alkali treatment (such as occurs in soybean processing), it has also been identified in food proteins that had not been subjected to alkali. Lysinoalanine can also be generated in a variety of proteins when heated under non-alkaline conditions.
Many dehydroalanine-containing peptides are toxic or antibiotic and constitute parts of lantibiotics or microcystins.