Decimal mark
| Numeral systems |
|---|
| Hindu–Arabic |
| East Asian |
| Alphabetic |
| Former |
| Positional systems by base |
| Non-standard positional numeral systems |
| List of numeral systems |
A decimal mark is a symbol used to separate the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form.
Different countries officially designate different symbols for the decimal mark. The choice of symbol for the decimal mark also affects the choice of symbol for the thousands separator used in digit grouping, so the latter is also treated in this article.
In mathematics the decimal mark is a type of radix point, a term that also applies to number systems with bases other than ten.
History
In the Middle Ages, before printing, a bar ( ¯ ) over the units digit was used to separate the integral part of a number from its fractional part, e.g. 9995 (meaning, 99.95 in decimal point format). This practice derived from the decimal system used in Indian mathematics[1] and was popularized by the Persian mathematician Al-Khwarizmi,[2] when Latin translation of his work on the Indian numerals introduced the decimal positional number system to the Western world. His Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing presented the first systematic solution of linear and quadratic equations in Arabic. A similar notation remains in common use as an underbar to superscript digits, especially for monetary values without a decimal mark, e.g. 9995. Later, a separator (a short, roughly vertical, ink stroke) between the units and tenths position became the norm among Arab mathematicians, e.g. 99ˌ95. When this character was typeset, it was convenient to use the existing comma (99,95) or full stop (99.95) instead.
Gerbert of Aurillac marked triples of columns with an arc (called a "Pythagorean arc") when using his Hindu–Arabic numeral-based abacus in the 10th century. Fibonacci followed this convention when writing numbers such as in his influential work Liber Abaci in the 13th century.[3]
In France, the full stop was already in use in printing to make Roman numerals more readable, so the comma was chosen. Many other countries, such as Italy, also chose to use the comma to mark the decimal units position.[4] It has been made standard by the ISO for international blueprints. However, English-speaking countries took the comma to separate sequences of three digits.
In the United States, the full stop or period (.) was used as the standard decimal mark.

In the nations of the British Empire, although the full stop could be used in typewritten material and its use was not banned, the interpunct (also known as the decimal point, point, or mid-dot) was preferred for the decimal mark in printing technologies that could accommodate it, e.g. 99·95.[6] However, as the mid-dot was already in common use in the mathematics world to indicate multiplication, the SI rejected its use as the decimal mark. During the beginning of British metrication in the late 1960s, and with impending currency decimalisation, there was widespread debate in the United Kingdom as to whether the decimal comma or decimal point should be preferred; the British Standards Institution and some sectors of industry advocated the comma, and the Decimal Currency Board advocated for the point. In the event, the point was decided on by the Ministry of Technology in 1968.[7]
When South Africa adopted the metric system, it adopted the comma as its decimal mark,[8] although a number of house styles, including some English-language newspapers, such as The Sunday Times continue to use the full stop.
The three most spoken international auxiliary languages, Ido, Esperanto, and Interlingua all use the comma as the decimal mark. Interlingua has used the comma as its decimal mark since the publication of the Interlingua Grammar in 1951.[9] Esperanto also uses the comma as its official decimal mark, while thousands are separated by non-breaking spaces: 12 345 678,9. Ido's Kompleta Gramatiko Detaloza di la Linguo Internaciona Ido (Complete Detailed Grammar of the International Language Ido) officially states that commas are used for the decimal mark while full stops are used to separate thousands, millions, etc. So the number 12,345,678.90123 (in American notation) for instance, would be written 12.345.678,90123 in Ido. The 1931 grammar of Volapük by Arie de Jong uses the comma as its decimal mark, and (somewhat unusually) uses the middle dot as the thousands separator (12·345·678,90123).[10]
In 1958, disputes between European and American delegates over the correct representation of the decimal mark nearly stalled the development of the ALGOL computer programming language.[11] ALGOL ended up allowing different decimal marks, but most computer languages and standard data formats (e.g. C, Java, Fortran, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)) specify a dot.
The 22nd General Conference on Weights and Measures declared in 2003 that "the symbol for the decimal marker shall be either the point on the line or the comma on the line". It further reaffirmed that "numbers may be divided in groups of three in order to facilitate reading; neither dots nor commas are ever inserted in the spaces between groups"[12] e.g. 1 000 000 000. This usage has therefore been recommended by technical organizations, such as the United States' National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Digit grouping
For ease of reading, numbers with many digits may be divided into groups using a delimiter.[13] In some countries, these "digit group separators" are only employed to the left of the decimal mark; in others, they are also used to separate numbers with a long fractional part. An important reason for grouping is that it allows rapid judgement of the number of digits, via subitizing (telling at a glance) rather than counting – contrast 1,000,000,000 with 1000000000 for a short billion.
The groups created by the delimiters tend to follow the use of the local language, which varies. In European languages, large numbers are read in groups of thousands and the delimiter (which occurs every three digits when it is used) may be called a "thousands separator". In East Asian cultures, particularly China, Japan, and Korea, large numbers are read in groups of myriads (10,000s) but the delimiter commonly separates every three digits. The Indian numbering system is somewhat more complex: it groups the rightmost three digits in a similar manner to European languages but then groups every two digits thereafter: 1.5 million would accordingly be written 15,00,000 and read as "15 lakh".
The convention for digit group separators varies but usually seeks to distinguish the delimiter from the decimal mark. Typically, English-speaking countries employ commas as the delimiter—10,000—and other European countries employ periods or spaces: 10.000 or 10 000. Because of the confusion that can result in international documents, the withdrawn SI/ISO 31-0 standard advocates the use of spaces[14] and the International Bureau of Weights and Measures and International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry advocate the use of a "thin space" in "groups of three".[15][16] Within the United States, the American Medical Association's widely followed AMA Manual of Style also calls for a thin space.[13] In some online encoding environments (for example, ASCII-only) a thin space is not practical or available, in which case a regular word space or no delimiter are the alternatives. The Metrication Board proposed this system for the United Kingdom and, while it is not universally adopted, it is standard within the country's construction industry.
Data versus mask
Digit group separators can occur either as part of the data or as a mask through which the data is displayed. This is an example of the separation of presentation and content. In many computing contexts, it is preferred to omit digit group separators from the data and instead overlay them as a mask (an input mask or an output mask). Common examples include spreadsheets and databases in which currency values are entered without such marks but are displayed with them inserted. Similarly, phone numbers can have hyphens or spaces as a mask rather than as data.
In some programming languages, it is possible to group the digits in the program's source code to make it easier to read; see Integer literal: Digit separators. Ada, D, Java, Perl and Ruby use the underscore (_) character for this purpose. All these languages allow writing seven hundred million as 700_000_000. C++14 allows the use of the apostrophe (') for digit grouping and therefore seven hundred million can be represented as 700'000'000.
Exceptions to digit grouping
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures states that "when there are only four digits before or after the decimal marker, it is customary not to use a space to isolate a single digit".[15] Likewise, some manuals of style state that thousands separators should not be used in normal text for numbers from 1000 to 9999 inclusive where no decimal fractional part is shown (in other words, for four-digit whole numbers), whereas others use thousands separators, and others use both. For example, APA style stipulates a thousands separator for "most figures of 1,000 or more" except for page numbers, binary digits, temperatures, etc.
There are always common-sense exceptions to digit grouping, such as years, postal codes and ID numbers of predefined nongrouped format, which style guides usually point out.
In non-base-10 numbering systems
In binary (base-2), a full space can be used between groups of four digits, corresponding to a nibble, or equivalently to a hexadecimal digit. Similarly, in hexadecimal (base-16), full spaces are usually used to group digits into twos, making each group correspond to a byte.
In binary (base-2), a full space can be used between groups of three digits, corresponding to an octal digit.
Influence of calculators and computers
In countries with a decimal comma, the decimal point is also common as the "international" notation because of the influence of devices, such as electronic calculators, which use the decimal point. Most computer operating systems allow selection of the decimal mark and programs that have been carefully internationalized will follow this, but some programs ignore it and a few are even broken by it.
Hindu–Arabic numeral system
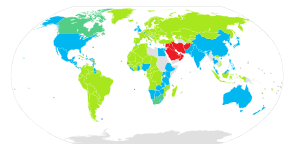
Countries using Arabic numerals with decimal point
Countries where a dot "." is used as decimal mark include:
- Australia
- Botswana
- British West Indies
- Brunei
- Canada (when using English)
- China, People's Republic of
- Dominican Republic
- Egypt
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Hong Kong
- India
- Ireland
- Israel
- Japan
- Kenya
- Korea (both North and South)
- Lebanon
- Luxembourg (uses both marks officially)
- Macau (in Chinese and English text)
- Malaysia
- Malta
- Mexico
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Panama
- Philippines
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Switzerland
- Taiwan
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- Uganda
- United Kingdom
- United States (including insular areas)
- Zimbabwe
Countries using Arabic numerals with decimal comma
Countries where a comma "," is used as decimal mark include:
- Albania
- Andorra
- Angola
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Bulgaria
- Cameroon
- Canada (when using French)
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia (comma used officially, but both forms are in use)
- Cuba
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- East Timor
- Ecuador
- Estonia
- Faroes
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Georgia
- Greece
- Greenland
- Hungary (comma is official but both are used)
- Iceland
- Indonesia
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg (uses both marks officially)
- Macau (in Portuguese text)
- Macedonia
- Moldova
- Mongolia
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- The Netherlands
- Norway
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- South Africa
- Spain
- Switzerland
- Sweden
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- Uruguay
- Uzbekistan
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
Other numeral systems
Unicode defines a decimal separator key symbol (⎖ in hex U+2396, decimal 9110) which looks similar to the apostrophe. This symbol is from ISO/IEC 9995 and is intended for use on a keyboard to indicate a key that performs decimal separation.
In the Arab world, where Eastern Arabic numerals are used for writing numbers, a different character is used to separate the integer and fractional parts of numbers. It is referred to as an Arabic decimal separator (٫) in Unicode. An Arabic thousands separator (٬) also exists.
In Persian, the decimal mark is called momayyez, which is written like a forward slash—there is a small difference between the "comma" character used in sentences and the momayyez (٫) used to separate sequences of three digits. To separate sequences of three digits, a comma or blank space may be used; however this is not a standard.[17][18][19]
In English Braille, the decimal point, ⠨, is distinct from both the comma, ⠂, and the period / full stop ⠲.
Examples of use
The following examples show the decimal mark and the thousands separator in various countries that use the Hindu–Arabic numeral system.
| Style | Countries |
|---|---|
| 1234567,89 | SI style (French version), Albania, Austria, Belgium, Bosnia, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada (French-speaking), Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latin Europe, Lithuania, Netherlands (non-currency numbers, see below), Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Ukraine |
| 1234567.89 | SI style (English version), Canada (English-speaking), China |
| 1,234,567.89 | Australia, Canada (English-speaking, unofficial), China, Hong Kong, Ireland, Israel, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, United Kingdom, United States |
| 1,234,567·89 | Ireland, Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, United Kingdom, United States (older, typically hand written) |
| 1.234.567,89 | Turkey, Austria, Brazil, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Indonesia, Italy, Netherlands (currency), Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovenia, Spain (older),[20] Sweden (not recommended) |
| 1˙234˙567,89 | Italy (handwriting) |
| 12,34,567.89 | India (see Indian Numbering System) |
| 1'234'567.89 | Switzerland (printed, computing, currency, international requisite, everyday use) |
| 1'234'567,89 | Switzerland (handwriting) |
| 1.234.567'89 | Spain (handwriting) |
| 123,4567.89 | China (alternative) |
- In Albania, Belgium, Bosnia, Estonia, France, Hungary, Poland, Slovakia and much of Latin Europe as well as French Canada: 1234567,89 (In Spain, in handwriting it is also common to use an upper comma: 1.234.567'89)
- In Brazil, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Indonesia, Italy, Netherlands, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovenia, Sweden and much of Europe: 1234567,89 or 1.234.567,89. In handwriting, 1˙234˙567,89 is also seen, but never in Brazil, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Slovenia or Sweden. In Italy a straight apostrophe is also used in handwriting: 1'234'567,89. In the Netherlands, the points thousands separator is preferred in currency amounts, and the space for other large numbers.
- In Germany and Austria, thousands separators were often denoted by alternating uses of comma and point, e.g. 1.234,567.890,12[21][22] for "one billion 234 million ..."
- In Switzerland: There are two cases. 1'234'567.89 is used for currency values. An apostrophe as thousands separator along with a "." as decimal mark. For other values the SI style 1234567,89 is used with a "," as decimal mark. The apostrophe is also the most common variety for non-currency values: 1'234'567,89, though this usage is officially discouraged.
- In Ireland, Israel, Japan, Korea (both), Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, the United Kingdom, and the United States: 1,234,567.89 or 1,234,567·89; the latter is generally found only in older, and especially handwritten, documents. Australia used this style up until the 1970s; now it uses the SI style.[23]
- In English Canada: There are two cases. The preferred method for currency values is $4,000.00 while for numeric values it is 1234567.89; however, commas are also sometimes used although no longer taught in school or used in official publications.[24]
- SI style: 1 234 567.89 or 1 234 567,89 (in their own publications the dot is used in the English version and the comma in the French version).
- In China, comma and space are used to mark digit groups because dot is used as decimal mark. There is no universal convention on digit grouping, so both thousands grouping and no digit grouping can be found. Although names for large numbers in Chinese are based on powers of 10,000 (万) (e.g. the next new word (亿) is for 108), grouping is never done for every 4 digits. Japan is similar, although when grouping by myriads numeral kanji are frequently used as separators: 1億2345万6789.
- In South Asia, due to a numeral system using lakhs (lacs) (1,23,456 equal to 123 456) and crores (1,23,45,678 equal to 12 345 678), comma is used at levels of thousand, lakh and crore, for example, 10 million (1 crore) would be written as 1,00,00,000.
| South Asian Value | Value |
|---|---|
| One | 1 |
| Ten | 10 |
| Hundred | 100 |
| Thousand | 1,000 |
| Lakh | 100,000 |
| Crore | 10,000,000 |
| Arab | 1,000,000,000 |
| Kharab | 100,000,000,000 |
Unicode characters
Used with Western Arabic numerals (0123456789):
- U+0020 space (HTML
 ) - U+0027 ' apostrophe (HTML
'·') - U+002C , comma (HTML
,) - U+002E . full stop (HTML
.) - U+00B7 · middle dot (HTML
···) - U+2009 thin space (HTML
 · ) - U+202F narrow no-break space (HTML
 ) - U+02D9 ˙ dot above (HTML
˙)
Used with Eastern Arabic numerals (٠١٢٣٤٥٦٧٨٩):
- U+066B ٫ arabic decimal separator (HTML
٫) - U+066C ٬ arabic thousands separator (HTML
٬)
Used with keyboards:
- U+2396 ⎖ decimal separator key symbol (HTML
⎖) (resembles an apostrophe)
See also
References
- ↑ Reimer, L., and Reimer, W. Mathematicians Are People, Too: Stories from the Lives of Great Mathematicians, Vol. 2. 1995. pp. 22-22. Parsippany, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc. as Dale Seymor Publications. ISBN 0-86651-823-1.
- ↑ Khwarizmi, Abu Jafar Muhammad ibn Musa al-, Oxford Islamic Studies Online
- ↑ Devlin, Keith (2011). The Man of Numbers: Fibonacci's Arithmetic Revolution. New York: Walker & Company. pp. 44–45. ISBN 9780802779083.
- ↑ Enciclopedia Universal Santillana, 1996 by SANTILLANA S.A., Barcelona, Spain. ISBN 84-294-5129-3. Comma, def.2: "coma: MAT. Signo utilizado en los números no enteros para separar la parte entera de la parte decimal o fraccionaria; p.ej., 2,123."
- ↑ Thomas Henderson (1839-01-03). "On the Parallax of α Centauri" (PDF). Memoirs of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 11, p. 64. Retrieved 2015-03-26. Scan published by Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
- ↑ Reimer, L., and Reimer, W. Mathematicians Are People, Too: Stories from the Lives of Great Mathematicians, Vol. 1. 1990 p. 41. Parsippany, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc. as Dale Seymor Publications. ISBN 0-86651-509-7.
- ↑ "Victory on Points". Nature 218 (5137): 111. 1968. doi:10.1038/218111c0.
- ↑ Government Notice R. 1144, Government Gazette 4326, 5 July 1974
- ↑ Grammar of Interlingua: Parts of Speech – Numerals
- ↑ Gramat Volapüka. Cathair na Mart: Evertype. ISBN 978-1-904808-94-7
- ↑ Perlis, Alan, The American Side of the Development of ALGOL, ACM SIGPLAN Notices, August 1978.
- ↑ , Resolution 10.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Iverson, Cheryl, et al. (eds) (2007). AMA Manual of Style (10th ed.). Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. p. 793. ISBN 978-0-19-517633-9.
- ↑ "Decimals Score a Point on International Standards". 2006-11-22. Retrieved 2008-11-27.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 International Bureau of Weights and Measures. "Rules and style conventions for expressing values of quantities": "".
- ↑ "Guidelines for drafting IUPAC technical reports and recommendations". 2007. Retrieved 2008-11-27.
- ↑ Pournader, Roozbeh (2000-10-15). "Persian decimal separator". Unicode Mail List Archive. Unicode Consortium. Retrieved 2008-06-21.
- ↑ "The Decimal Numeral". Academic Grammar of New Persian. Archived from the original on 2006-06-20. Retrieved 2006-06-19.
- ↑ Descriptive Grammar of New Persian (archived)
- ↑ Diccionario panhispánico de dudas, when writing numbers more than four figures, these three will be grouped into three, starting from the right, and separating the groups by whitespace. (Exceptions: Never written with periods, commas or white separation numbers that refer to years, pages, verses, urban roads, postal codes, legal articles, decrees or laws.)
- ↑ Röll. "Enzyklopädie des Eisenbahnwesens". Retrieved 26 August 2014., entry "Union Pacific-Eisenbahn", largest numbers in table
- ↑ Röll. "Enzyklopädie des Eisenbahnwesens". Retrieved 26 August 2014., entry "Bilanz", sums in last table
- ↑ Steinle, Vicki. "Teaching and Learning about Decimals". Retrieved 20 April 2012.
- ↑ Government of Canada (2011-01-13). "Public Service Commission Style Guide". Retrieved 2013-09-25.