Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Decamethyl-1,3,5,7,9,2,4,6,8,10-pentaoxapentasilecane | |
| Other names
Cyclopentamethicone Cyclic dimethylsiloxane pentamer | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1800166 | |
| 541-02-6 | |
| ChemSpider | 10451 |
| EC number | 208-764-9 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| MeSH | Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane |
| PubChem | 10913 |
| RTECS number | GY5945200 |
| |
| UNII | 0THT5PCI0R |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C10H30O5Si5 |
| Molar mass | 370.77 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 0.958 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | −47 °C; −53 °F; 226 K |
| Boiling point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) |
| 17.03±0.72 ppb (23 °C) [1] | |
| Vapor pressure | 20.4±1.1 Pa (25 °C) [2] |
| Viscosity | 3.74 cP |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S23, S24/25 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 73 °C (163 °F; 346 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related Organosilicon compounds |
Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
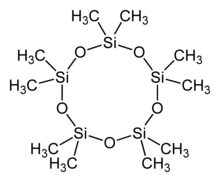
Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane (D5) is an organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]5. Is is a colorless liquid with a low vapor pressure. The compound is classified as a cyclomethicone. Such fluids are commonly used in cosmetics such as deodorants, sunblocks, hair sprays and skin care products. It is becoming more common in hair conditioners, as it makes the hair easier to brush without breakage. It is also used as part of silicone based personal lubricants. D5 is considered an emollient.
Production
Commercially D5, is produced by cracking polysiloxanes. The silicone polymer equilibrated in the presence of strong base to give the pentamer:
- n/5 [(CH3)2SiO]n → n [(CH3)2SiO]5
The tetramer octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane is also generated. These two cyclic species are separated from the polymer by distillation.[3]
Environment
D5 and D4 have attracted attention because they are pervasive. Although never acutely toxic, the cyclic siloxanes do affect aquatic life and some mammals.[4]
References
- ↑ Sudarsanan Varaprath, Cecil L. Frye, Jerry Hamelink (1996). "Aqueous solubility of permethylsiloxanes (silicones)". Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 15 (8): 1263–1265. doi:10.1002/etc.5620150803.
- ↑ Ying Duan Lei, Frank Wania, Dan Mathers (2010). "Temperature-Dependent Vapor Pressure of Selected Cyclic and Linear Polydimethylsiloxane Oligomers". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 55 (12): 5868–5873. doi:10.1021/je100835n.
- ↑ Moretto, Hans-Heinrich; Schulze, Manfred; Wagner, Gebhard (2005). "Silicones". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a24_057.
- ↑ Wang, De-Gao; Norwood, Warren; Alaee, Mehran; Byer, Jonathan D.; Brimble, Samantha "Review of recent advances in research on the toxicity, detection, occurrence and fate of cyclic volatile methyl siloxanes in the environment" Chemosphere 2013, volume 93, pages 711–725. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.041
