Daunorubicin
 | |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
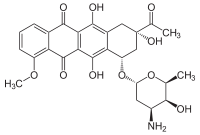
(8S,10S)-8-acetyl-10-[(2S,4S,5S,6S)- 4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-oxan- 2-yl]oxy-6,8,11-trihydroxy-1-methoxy- 9,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Cerubidine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682289 |
| |
| |
| Exclusively intravenous. Causes severe necrosis if administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Half-life | 26.7 hours (metabolite) |
| Excretion | Biliary and urinary |
| Identifiers | |
|
20830-81-3 | |
| L01DB02 | |
| PubChem | CID 30323 |
| DrugBank |
DB00694 |
| ChemSpider |
28163 |
| UNII |
ZS7284E0ZP |
| KEGG |
C01907 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:41977 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL178 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C27H29NO10 |
|
527.52 g/mol 563.99 g/mol (HCl salt) | |
|
SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
Daunorubicin or daunomycin (daunomycin cerubidine) is chemotherapeutic of the anthracycline family that is given as a treatment for some types of cancer. It is most commonly used to treat specific types of leukemia (acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia). It was initially isolated from Streptomyces peucetius.
A liposomal formulation of daunorubicin, liposomal daunorubicin, is marketed in the United States as DaunoXome.
History
In the 1950s, an Italian research company, Farmitalia Research Laboratories, began an organized effort to isolate anticancer compounds from soil-based microbes. A soil sample was isolated from the area surrounding the Castel del Monte, a 13th-century castle in Apulia. A new strain of Streptomyces peucetius which produced a red pigment was isolated, and an antibiotic was produced from this bacterium that was found to have good activity against murine tumors. Since a group of French researchers discovered the same compound at about the same time, the two teams named the compound daunorubicin, combining the name Dauni, a pre-Roman tribe that occupied the area of Italy where the compound was isolated, with the French word for ruby, rubis, describing the color.[1] Clinical trials began in the 1960s, and the drug saw success in treating acute leukemia and lymphoma. However, by 1967, it was recognized that daunorubicin could produce fatal cardiac toxicity.[2]
Uses
It slows or stops the growth of cancer cells in the body. Treatment is usually performed together with other chemotherapy drugs (such as cytarabine), and its administration depends on the type of tumor and the degree of response.
In addition to its major use in treating AML, daunorubicin is also used to treat neuroblastoma. Daunorubicin has been used with other chemotherapy agents to treat the blastic phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia.
Daunorubicin is also used as the starting material for semi-synthetic manufacturing of doxorubicin, epirubicin and idarubicin.
Mechanism of action
Similar to Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin interacts with DNA by intercalation and inhibition of macromolecular biosynthesis.[3][4] This inhibits the progression of the enzyme topoisomerase II, which relaxes supercoils in DNA for transcription. Daunorubicin stabilizes the topoisomerase II complex after it has broken the DNA chain for replication, preventing the DNA double helix from being resealed and thereby stopping the process of replication. On binding to DNA, daunomycin intercalates, with its daunosamine residue directed toward the minor groove. It has the highest preference for two adjacent G/C base pairs flanked on the 5' side by an A/T base pair. Daunomycin effectively binds to every 3 base pairs and induces a local unwinding angle of 8°, but negligible distortion of helical conformation.[5] It can also induce histone eviction from chromatin upon intercalation.[6]
Route of administration
Daunorubicin should only be administered in a rapid intravenous infusion. It should not be administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously, since it may cause extensive tissue necrosis. It should also never be administered intrathecally (into the spinal canal), as this will cause extensive damage to the nervous system and may lead to death. Daunorubicin has been used intravitreally (inside the eye) for the purposes of preventing proliferative vitreoretinopathy, a common complication following retinal detachment surgery, but has not been found to be effective and is not used for any other ophthalmic purposes at this time.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Weiss RB (December 1992). "The anthracyclines: will we ever find a better doxorubicin?". Seminars in Oncology 19 (6): 670–86. PMID 1462166.
- ↑ Tan C, Tasaka H, Yu KP, Murphy ML, Karnofsky DA (March 1967). "Daunomycin, an antitumor antibiotic, in the treatment of neoplastic disease. Clinical evaluation with special reference to childhood leukemia". Cancer 20 (3): 333–53. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(1967)20:3<333::AID-CNCR2820200302>3.0.CO;2-K. PMID 4290058.
- ↑ Fornari FA, Randolph JK, Yalowich JC, Ritke MK, Gewirtz DA (April 1994). "Interference by doxorubicin with DNA unwinding in MCF-7 breast tumor cells". Mol Pharmacol 45 (4): 649–56. PMID 8183243.
- ↑ Momparler RL, Karon M, Siegel SE, Avila F (August 1976). "Effect of adriamycin on DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis in cell-free systems and intact cells". Cancer Res 36 (8): 2891–5. PMID 1277199.
- ↑ G J Quigley, A H Wang, G Ughetto, G van der Marel, J H van Boom, and A Rich (December 1980). "Molecular structure of an anticancer drug-DNA complex: daunomycin plus d(CpGpTpApCpG)". PNAS 77 (12): 7204–7208. doi:10.1073/pnas.77.12.7204.
- ↑ Pang B, Qiao X, Janssen L, Velds A, Groothuis T, Kerkhoven R, Nieuwland M, Ovaa H, Rottenberg S, van Tellingen O, Janssen J, Huijgens P, Zwart W, Neefjes J (2013). "Drug-induced histone eviction from open chromatin contributes to the chemotherapeutic effects of doxorubicin". Nature Communications 4: 1908. doi:10.1038/ncomms2921. PMID 23715267.
- ↑ Mortensen, ME et al. (1992). "Inadvertent intrathecal injection of daunorubicin with fatal outcome". Med Pediatr Oncol 20 (3): 249–253. PMID 1574039.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||