DAPK1
| Death-associated protein kinase 1 |
|---|
PDB rendering based on 1ig1. |
| Available structures |
| PDB |
Ortholog search: PDBe, RCSB |
| List of PDB id codes |
|
1IG1, 1JKK, 1JKL, 1JKS, 1JKT, 1P4F, 1WVW, 1WVX, 1WVY, 1YR5, 2W4J, 2W4K, 2X0G, 2XUU, 2XZS, 2Y0A, 2Y4P, 2Y4V, 2YAK, 3DFC, 3DGK, 3EH9, 3EHA, 3F5G, 3F5U, 3GU4, 3GU5, 3GU6, 3GU7, 3GU8, 3GUB, 3ZXT, 4B4L, 4PF4
|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Symbols | DAPK1 ; DAPK |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600831 MGI: 1916885 HomoloGene: 3626 IUPHAR: 2002 ChEMBL: 2558 GeneCards: DAPK1 Gene |
|---|
| EC number | 2.7.11.1 |
|---|
|
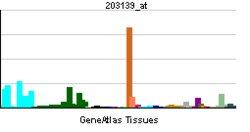
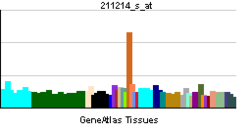
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
|
|
| More reference expression data |
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse | |
|---|
| Entrez | 1612 | 69635 | |
|---|
| Ensembl | ENSG00000196730 | ENSMUSG00000021559 | |
|---|
| UniProt | P53355 | Q80YE7 | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001288729 | NM_001285917 | |
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001275658 | NP_001272846 | |
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 9:
90.11 – 90.32 Mb | Chr 13:
60.6 – 60.76 Mb | |
|---|
| PubMed search | | | |
|---|
|
Death-associated protein kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DAPK1 gene.[1]
Death-associated protein kinase 1 is a positive mediator of gamma-interferon induced programmed cell death. DAPK1 encodes a structurally unique 160-kD calmodulin dependent serine-threonine kinase that carries 8 ankyrin repeats and 2 putative P-loop consensus sites. It is a tumor suppressor candidate.[2]
In melanocytic cells DAPK1 gene expression may be regulated by MITF.[3]
References
- ↑ Feinstein E, Druck T, Kastury K, Berissi H, Goodart SA, Overhauser J, Kimchi A, Huebner K (Feb 1996). "Assignment of DAP1 and DAPK--genes that positively mediate programmed cell death triggered by IFN-gamma--to chromosome regions 5p12.2 and 9q34.1, respectively". Genomics 29 (1): 305–7. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1255. PMID 8530096.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: DAPK1 death-associated protein kinase 1".
- ↑ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM et al. (2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21 (6): 665–76. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971.
Further reading
- Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H et al. (1995). "Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death.". Genes Dev. 9 (1): 15–30. doi:10.1101/gad.9.1.15. PMID 7828849.
- Inbal B, Shani G, Cohen O et al. (2000). "Death-associated protein kinase-related protein 1, a novel serine/threonine kinase involved in apoptosis.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (3): 1044–54. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.1044-1054.2000. PMC 85221. PMID 10629061.
- Jin Y, Blue EK, Dixon S et al. (2001). "Identification of a new form of death-associated protein kinase that promotes cell survival.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (43): 39667–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101886200. PMC 2823794. PMID 11485996.
- Shohat G, Spivak-Kroizman T, Cohen O et al. (2002). "The pro-apoptotic function of death-associated protein kinase is controlled by a unique inhibitory autophosphorylation-based mechanism.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (50): 47460–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105133200. PMID 11579085.
- Soria JC, Rodriguez M, Liu DD et al. (2002). "Aberrant promoter methylation of multiple genes in bronchial brush samples from former cigarette smokers.". Cancer Res. 62 (2): 351–5. PMID 11809677.
- Larramendy ML, Niini T, Elonen E et al. (2003). "Overexpression of translocation-associated fusion genes of FGFRI, MYC, NPMI, and DEK, but absence of the translocations in acute myeloid leukemia. A microarray analysis.". Haematologica 87 (6): 569–77. PMID 12031912.
- Hasegawa M, Nelson HH, Peters E et al. (2002). "Patterns of gene promoter methylation in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck.". Oncogene 21 (27): 4231–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205528. PMID 12082610.
- Jin Y, Blue EK, Dixon S et al. (2003). "A death-associated protein kinase (DAPK)-interacting protein, DIP-1, is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that promotes tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis and regulates the cellular levels of DAPK.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (49): 46980–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208585200. PMC 2824503. PMID 12351649.
- Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Yao CC, Chen RH (2002). "DAP-kinase induces apoptosis by suppressing integrin activity and disrupting matrix survival signals.". J. Cell Biol. 159 (1): 169–79. doi:10.1083/jcb.200204050. PMC 2173490. PMID 12370243.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Nakatsuka S, Takakuwa T, Tomita Y et al. (2003). "Hypermethylation of death-associated protein (DAP) kinase CpG island is frequent not only in B-cell but also in T- and natural killer (NK)/T-cell malignancies.". Cancer Sci. 94 (1): 87–91. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01357.x. PMID 12708480.
- Tian JH, Das S, Sheng ZH (2003). "Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of syntaxin-1A by the death-associated protein (DAP) kinase regulates its interaction with Munc18.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (28): 26265–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300492200. PMID 12730201.
- Gonzalez-Gomez P, Bello MJ, Alonso ME et al. (2004). "Frequent death-associated protein-kinase promoter hypermethylation in brain metastases of solid tumors.". Oncol. Rep. 10 (4): 1031–3. doi:10.3892/or.10.4.1031. PMID 12792765.
- Matsumoto H, Nagao M, Ogawa S et al. (2003). "Prognostic significance of death-associated protein-kinase expression in hepatocellular carcinomas.". Anticancer Res. 23 (2B): 1333–41. PMID 12820391.
- Henshall DC, Araki T, Schindler CK et al. (2003). "Expression of death-associated protein kinase and recruitment to the tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway following brief seizures.". J. Neurochem. 86 (5): 1260–70. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01934.x. PMID 12911633.
- Voso MT, Scardocci A, Guidi F et al. (2004). "Aberrant methylation of DAP-kinase in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes.". Blood 103 (2): 698–700. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-07-2249. PMID 14504087.
- Jin Y, Gallagher PJ (2004). "Antisense depletion of death-associated protein kinase promotes apoptosis.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (51): 51587–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309165200. PMC 2823796. PMID 14530257.
- Kim WS, Son HJ, Park JO et al. (2004). "Promoter methylation and down-regulation of DAPK is associated with gastric atrophy.". Int. J. Mol. Med. 12 (6): 827–30. doi:10.3892/ijmm.12.6.827. PMID 14612952.
- Bai T, Tanaka T, Yukawa K et al. (2004). "Reduced expression of death-associated protein kinase in human uterine and ovarian carcinoma cells.". Oncol. Rep. 11 (3): 661–5. doi:10.3892/or.11.3.661. PMID 14767518.
PDB gallery |
|---|
| | 1ig1: 1.8A X-Ray structure of ternary complex of a catalytic domain of death-associated protein kinase with ATP analogue and Mn. |
| 1jkk: 2.4A X-RAY STRUCTURE OF TERNARY COMPLEX OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE WITH ATP ANALOGUE AND MG. |
| 1jkl: 1.6A X-RAY STRUCTURE OF BINARY COMPLEX OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE WITH ATP ANALOGUE |
| 1jks: 1.5A X-RAY STRUCTURE OF APO FORM OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE |
| 1jkt: TETRAGONAL CRYSTAL FORM OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE |
| 1p4f: DEATH ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE CATALYTIC DOMAIN WITH BOUND INHIBITOR FRAGMENT |
| 1wvw: Crystal structures of kinase domain of DAP kinase in complex with small molecular inhibitors |
| 1wvx: Crystal structures of kinase domain of DAP kinase in complex with small molecular inhibitors |
| 1wvy: Crystal structures of kinase domain of DAP kinase in complex with small molecular inhibitors |
|
|
|
|
|---|
| | | | | | |
- Biochemistry overview
- Enzymes overview
- By EC number: 1.1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 10
- 11
- 13
- 14
- 15-18
- 2.1
- 3.1
- 4.1
- 5.1
- 6.1-3
|
|
|
|