D
|

D (named dee /ˈdiː/[1]) is the fourth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.
History
| Egyptian hieroglyph door |
Phoenician daleth |
Greek Delta |
Etruscan D |
Roman D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
The Semitic letter Dâlet may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are various Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic,ConAncient Greek and Latin, the letter represented /d/; in the Etruscan alphabet the letter was superfluous but still retained (see letter B). The equivalent Greek letter is Delta, 'Δ'.
The minuscule (lower-case) form of 'd' consists of a loop and a tall vertical stroke. It developed by gradual variations on the majuscule (capital) form. In handwriting, it was common to start the arc to the left of the vertical stroke, resulting in a serif at the top of the arc. This serif was extended while the rest of the letter was reduced, resulting in an angled stroke and loop. The angled stroke slowly developed into a vertical stroke.
Usage

In nearly all languages that use the Latin alphabet and the International Phonetic Alphabet 'd' represents the voiced alveolar or voiced dental plosive /d/, but in the Vietnamese alphabet, it represents the sound /z/ (or /j/ in southern dialects). In Fijian it represents a prenasalized stop /nd/.[2] In some languages where voiceless unaspirated stops contrast with voiceless aspirated stops, 'd' represents an unaspirated /t/, while 't' represents an aspirated /tʰ/. Examples of such languages include Icelandic, Scottish Gaelic, Navajo, and the Pinyin transliteration of Mandarin.
The symbol "D" is used for 500 in Roman numerals.
Related letters and other similar characters
- Đ đ : Latin letter D with stroke
- Ɗ ɗ : Latin letter D with hook
- Ð ð : Latin letter Eth
- Δ δ : Greek letter Delta
- Д д : Cyrillic letter De
- ד : Hebrew letter Dalet
- ∂ : the partial derivative symbol,
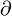
Computing codes
| Character | D | d | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER D | LATIN SMALL LETTER D | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 68 | U+0044 | 100 | U+0064 |
| UTF-8 | 68 | 44 | 100 | 64 |
| Numeric character reference | D | D | d | d |
| EBCDIC family | 196 | C4 | 132 | 84 |
| ASCII 1 | 68 | 44 | 100 | 64 |
- 1 Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Other representations
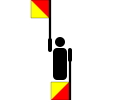
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Delta |
 |
 |
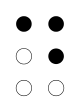 |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | Braille dots-145 |
In British Sign Language (BSL), the letter 'd' is indicated by signing with the right hand held with the index and thumb extended and slightly curved, and the tip of the thumb and finger held against the extended index of the left hand.
References
- ↑ "D" Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993); "dee", op. cit.
- ↑ Lynch, John (1998). Pacific languages: an introduction. University of Hawaii Press. p. 97. ISBN 0-8248-1898-9.
External links
 Media related to D at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to D at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of D at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of D at Wiktionary The dictionary definition of d at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of d at Wiktionary