D-alanine—D-serine ligase
| D-alanine—D-serine ligase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 6.3.2.35 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
D-alanine—D-serine ligase (EC 6.3.2.35, VanC, VanE, VanG) is an enzyme with system name D-alanine:D-serine ligase (ADP-forming).[1][2][3][4][5] This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
The product of this enzyme, D-alanyl-D-serine, can be incorporated into the peptidoglycan pentapeptide instead of the usual D-alanyl-D-alanine dipeptide.
References
- ↑ Dutka-Malen, S., Molinas, C., Arthur, M. and Courvalin, P. (1992). "Sequence of the vanC gene of Enterococcus gallinarum BM4174 encoding a D-alanine:D-alanine ligase-related protein necessary for vancomycin resistance". Gene 112: 53–58. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(92)90302-6. PMID 1551598.
- ↑ Park, I.S., Lin, C.H. and Walsh, C.T. (1997). "Bacterial resistance to vancomycin: overproduction, purification, and characterization of VanC2 from Enterococcus casseliflavus as a D-Ala-D-Ser ligase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 10040–10044. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.19.10040. PMID 9294159.
- ↑ Fines, M., Perichon, B., Reynolds, P., Sahm, D.F. and Courvalin, P. (1999). "VanE, a new type of acquired glycopeptide resistance in Enterococcus faecalis BM4405". Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43: 2161–2164. PMID 10471558.
- ↑ Depardieu, F., Bonora, M.G., Reynolds, P.E. and Courvalin, P. (2003). "The vanG glycopeptide resistance operon from Enterococcus faecalis revisited". Mol. Microbiol. 50: 931–948. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03737.x. PMID 14617152.
- ↑ Watanabe, S., Kobayashi, N., Quinones, D., Hayakawa, S., Nagashima, S., Uehara, N. and Watanabe, N. (2009). "Genetic diversity of the low-level vancomycin resistance gene vanC-2/vanC-3 and identification of a novel vanC subtype (vanC-4) in Enterococcus casseliflavus". Microb. Drug Resist. 15: 1–9. doi:10.1089/mdr.2009.0856. PMID 19216682.
External links
- D-alanine—D-serine ligase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
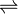 D-alanyl-D-serine + ADP +
D-alanyl-D-serine + ADP +