Cyanuric fluoride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,4,6-trifluoro-1,3,5-triazine | |
| Other names
trifluorotriazine, 2,4,6-trifluoro-s-triazine, cyanuryl fluoride embox | |
| Identifiers | |
| 675-14-9 | |
| ChemSpider | 12143 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 12664 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3F3N3 | |
| Molar mass | 135.047 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.574 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −38 °C (−36 °F; 235 K) |
| Boiling point | 74 °C (165 °F; 347 K) |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R24, R26, R35 |
| S-phrases | S26, S28, S36/37/39, S45 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
cyanuric acid, cyanuric chloride, cyanuric bromide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cyanuric fluoride or 2,4,6-trifluoro-1,3,5-triazine is a chemical compound with the formula (CNF)3. It is a colourless, pungent liquid. It has been used as a precursor for fibre-reactive dyes, as a specific reagent for tyrosine residues in enzymes, and as a fluorinating agent.[1]
Preparation and reactions
Cyanuric fluoride is prepared by fluorinating cyanuric chloride. The fluorinating agent may be SbF3Cl2,[2] KSO2F,[3] or NaF.[4][5]
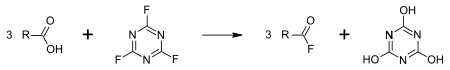
Cyanuric fluoride is used for the mild and direct conversion of carboxylic acids to acyl fluorides:[6]
Other fluorinating methods are less direct and may be incompatible with some functional groups.[7]
Cyanuric fluoride hydrolyses easily to cyanuric acid and it reacts more readily with nucleophiles than cyanuric chloride.[3] Pyrolysis of cyanuric fluoride at 1300 °C is a way to prepare cyanogen fluoride:[8]
- (CNF)3 → 3 CNF.
References
- ↑ "Fluorinated aromatic compounds". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology 11. Wiley-Interscience. 1994. p. 608.
- ↑ Abe F. Maxwell, John S. Fry & Lucius A. Bigelow (1958). "The Indirect Fluorination of Cyanuric Chloride". Journal of American Chemical Society 80 (3): 548. doi:10.1021/ja01536a010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Daniel W. Grisley, Jr, E. W. Gluesenkamp & S. Allen Heininger (1958). "Reactions of Nucleophilic Reagents with Cyanuric Fluoride and Cyanuric Chloride". Journal of Organic Chemistry 23 (11): 1802. doi:10.1021/jo01105a620.
- ↑ C. W. Tullock & D. D. Coffman (1960). "Synthesis of Fluorides by Metathesis with Sodium Fluoride". Journal of Organic Chemistry 25 (11): 2016. doi:10.1021/jo01081a050.
- ↑ Steffen Groß, Stephan Laabs, Andreas Scherrmann, Alexander Sudau, Nong Zhang & Udo Nubbemeyer (2000). "Improved Syntheses of Cyanuric Fluoride and Carboxylic Acid Fluorides". Journal für Praktische Chemie 342 (7): 711. doi:10.1002/1521-3897(200009)342:7<711::AID-PRAC711>3.0.CO;2-M.
- ↑ George A. Olah, Masatomo Nojima & Istvan Kerekes (1973). "Synthetic Methods and Reactions; IV. Fluorination of Carboxylic Acids with Cyanuric Fluoride". Synthesis 1973 (08): 487. doi:10.1055/s-1973-22238.
- ↑ Barda, David A. (2005). "Cyanuric Fluoride". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. p. 77. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00043.
- ↑ F. S. Fawcett & R. D. Lipscomb (1964). "Cyanogen Fluoride: Synthesis and Properties". Journal of American Chemical Society 86 (13): 2576. doi:10.1021/ja01067a011.