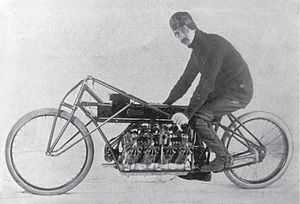
Curtiss V-8 motorcycle
 | |
| Manufacturer | Glenn Curtiss |
|---|---|
| Assembly | 1906 |
| Class | Speed record challenger |
| Engine | Curtiss B-8: 269 cu in (4,410 cc), dual carburetor, 90° F-head V-8[1][2] |
| Bore / stroke | 3.625 in × 3.25 in (92.1 mm × 82.6 mm)[1] |
| Top speed | 136 mph (219 km/h)[2] |
| Power | 40 hp (30 kW) @ 1,800 RPM[2][3] |
| Ignition type | Battery ignition, jump-spark |
| Transmission |
Direct drive Shaft and rear hub bevel |
| Frame type | Steel tubing |
| Brakes | Rear v brake[4] |
| Tires | 26 in (660 mm)[5] |
| Wheelbase | 64 in (1.6 m) |
| Dimensions |
L: 7 ft 10 in (2.4 m)[3] W: 2 ft 3 in (0.7 m)[3] H: 3 ft (0.9 m)[3] |
| Weight | 275 lb (125 kg)[3] (wet) |
| Fuel capacity | 2.5 US gal (9.5 l)[4] |
The Curtiss V-8 motorcycle was a 269 cu in (4,410 cc) V8 engine-powered motorcycle designed and built by aviation and motorcycling pioneer Glenn Curtiss that set an unofficial land speed record of 136.36 miles per hour (219.45 km/h) on January 24, 1907.[6][7] The air-cooled F-head engine was developed for use in dirigibles.[8][9][10]
Engine
The forty horsepower engine was the two carburetor version of the Curtiss Model B-8 aircraft powerplant, one of thirteen engines listed in the May 1908 "Aerial and Cycle Motors" catalog.[1] The engine weighed 150 lb (68 kg) and was offered for US$1,200 but it did not sell, in spite of the engine's notoriety from the speed record.[1] An eight carburetor version of the Model B-8 was used in the experimental AEA Red Wing and White Wing airplanes that flew in 1908.[1]
Legacy
Curtiss remained "the fastest man in the world," the title the newspapers gave him for going faster than any vehicle, on land, sea or air, until 1911,[11] when his absolute record was broken by the 141.7 mph (228.0 km/h) Blitzen Benz automobile.[12] No motorcycle surpassed the record until 1930.[13][14] Curtiss's success at racing strengthened his reputation as a leading maker of high-performance motorcycles and engines.[15]
It has been suggested that the literary character Tom Swift was based on Curtiss.[12][16] Tom Swift and His Motor Cycle, the first of over 100 books in the Tom Swift series, was published shortly after the V-8 record setting run.
The record setting V-8 motorcycle is now in the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum.[17] The Air and Space museum lent it to the Guggenheim for the 1998 The Art of the Motorcycle exhibition in New York.[18][9]
The Curtiss OX-5 aero engine, a successor of the V-8 motorcycle engine, powered several United States civilian and military aircraft. More than 10,000 were manufactured.[19]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 House, Kirk W. (2003), Hell-Rider to King of the Air: Glenn Curtiss' Life of Innovation, Warrendale, Pennsylvania: SAE International, pp. 57–60, ISBN 0-7680-0802-6, retrieved March 22, 2013
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Paul Garson (June 25, 2004), 1907 Curtiss V-8 / Faster Than a Speeding Bullet: Glenn H. Curtiss, Motorcycle.com
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Motorcycle, Curtiss V-8, Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 de Cet, Mirco (2002). The illustrated directory of motorcycles. MotorBooks/MBI Publishing Company. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-7603-1417-3.
- ↑ "Racing Outlook Good for Autos at Ormond", The New York Times, January 22, 1907 (dateline January 21) Check date values in:
|date=(help) - ↑ House 2003, p. 41.
- ↑ "The Fastest and Most Powerful American Motor Bicycle" (INTERNET ARCHIVE), Scientific American 96 (6), February 9, 1907: 128
- ↑ House 2003, p. 40.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Past Exhibitions | The Art of the Motorcycle (1868-1919 models), The Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation, 2009
- ↑ Trafford L-M. Doherty, Glenn H. Curtiss - 100 Years Ago, Glenn H. Curtiss Museum
- ↑ Roseberry 1972, p. 57.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Garson, Paul (September 15, 2010), "Top 10 Weirdest Custom Motorcycles; Dimensionally challenged motorcycle mavericks", Motorcycle.com
- ↑ Setright, L.J.K. (1979), The Guinness book of motorcycling facts and feats, Guinness Superlatives, ISBN 978-0-85112-200-7
- ↑ Hatfield, Jerry (2006), Standard Catalog of American Motorcycles 1898-1981, Krause Publications, p. 44, ISBN 978-0-87349-949-1
- ↑ Hatch 2007, p. 36.
- ↑ Dizer, John T (1982). Tom Swift & Company. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland Publishing. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-89950-024-9.
- ↑ "Curtiss V-8 Motorcycle." Smithsonian Air and Space Museum Collections. Retrieved: February 24, 2011.
- ↑ Statnekov, Daniel K.; Guggenheim Museum Staff (2001) [1998], Krens, Thomas; Drutt, Matthew, eds., The Art of the Motorcycle, Harry N. Abrams, p. 107, ISBN 0810969122
- ↑ Curtiss OX-5 V-8 Engine, Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum
Bibliography
- Hatch, Alden. Glenn Curtiss: Pioneer of Aviation. Guilford, Connecticut: The Lyons Press, 2007. ISBN 978-1-59921-145-9.
- Roseberry, C.R. Glenn Curtiss: Pioneer of Flight. Garden City, New York: Doubleday & Company, 1972. ISBN 0-8156-0264-2.
Further reading
- Vintage Motorcycles & Antique Motorcycles, Glenn H. Curtiss Museum
- Cameron, K., (April 2002), "Creative Power: Glenn Curtiss: Inventor, Manufacturer, Racer, Pilot.", Cycle World: 90–92
- Simanaitis, Dennis (Sep 1997), "Glenn Curtiss--fastest man alive!", Road & Track: 172–173
- Dr. John H. Lienhard (2002). "Curtiss' Motorcycles". The Engines of Our Ingenuity (Audio, with transcript). Episode 1693. University of Houston College of Engineering.
External links
 Media related to Curtiss V-8 motorcycle at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Curtiss V-8 motorcycle at Wikimedia Commons