Crotonic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(E)-but-2-enoic acid | |
| Other names
trans-2-butenoic acid beta-methylacrylic acid 3-methylacrylic acid (E)-2-butenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 107-93-7 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:41131 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1213528 |
| ChemSpider | 552744 |
| DrugBank | DB02074 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| PubChem | 637090 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.09 g/mol |
| Density | 1.02 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 70 to 73 °C (158 to 163 °F; 343 to 346 K) |
| Boiling point | 185 to 189 °C (365 to 372 °F; 458 to 462 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.69 [1] |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | SIRI.org |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
crotonate |
| Related carboxylic acids |
propionic acid acrylic acid butyric acid succinic acid malic acid tartaric acid fumaric acid pentanoic acid |
| Related compounds |
butanol butyraldehyde crotonaldehyde 2-butanone |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
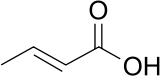
Crotonic acid, or trans-2-butenoic acid, is a short-chain unsaturated carboxylic acid, described by the formula CH3CH=CHCO2H. Crotonic acid is so named because it was erroneously thought to be a saponification product of croton oil. It crystallizes as needles from hot water.
Racemic threonine can be prepared from crotonic acid by alpha-functionalization using mercury(II) acetate.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Dawson, R. M. C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- ↑ Carter, H. E.; West, H. D. (1955). "dl-Threonine". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 3, p. 813
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.