Critical infrastructure protection
Critical infrastructure protection (CIP) is a concept that relates to the preparedness and response to serious incidents that involve the critical infrastructure of a region or nation.
The American Presidential directive PDD-63 of May 1998 set up a national program of "Critical Infrastructure Protection".[1]
In Europe the equivalent "European Programme for Critical Infrastructure Protection" (EPCIP) refers to the doctrine or specific programs created as a result of the European Commission's directive EU COM(2006) 786 which designates European critical infrastructure that, in case of fault, incident, or attack, could impact both the country where it is hosted and at least one other European Member State. Member states are obliged to adopt the 2006 directive into their national statutes.
History of the U.S. CIP
The U.S. CIP is a national program to ensure the security of vulnerable and interconnected infrastructures of the United States. In May 1998, President Bill Clinton issued Presidential directive PDD-63 on the subject of Critical Infrastructure Protection.[1] This recognized certain parts of the national infrastructure as critical to the national and economic security of the United States and the well-being of its citizenry, and required steps to be taken to protect it.
This was updated on December 17, 2003, by President Bush through Homeland Security Presidential Directive HSPD-7 for Critical Infrastructure Identification, Prioritization, and Protection.[2] The directive describes the United States has having some critical infrastructure that is "so vital to the United States that the incapacity or destruction of such systems and assets would have a debilitating impact on security, national economic security, national public health or safety."[2]
Overview
The systems and networks that make up the infrastructure of society are often taken for granted, yet a disruption to just one of those systems can have dire consequences across other sectors.
Take, for example, a computer virus that disrupts the distribution of natural gas across a region. This could lead to a consequential reduction in electrical power generation, which in turn leads to the forced shutdown of computerized controls and communications. Road traffic, air traffic, and rail transportation might then become affected. Emergency services might also be hampered.
An entire region can become debilitated because some critical elements in the infrastructure become disabled through natural disaster. While potentially in contravention of the Geneva Conventions,[3] military forces have also recognized that it can cripple an enemy's ability to resist by attacking key elements of its civilian and military infrastructure.
The federal government has developed a standardized description of critical infrastructure, in order to facilitate monitoring and preparation for disabling events. The government requires private industry in each critical economic sector to:
- Assess its vulnerabilities to both physical or cyber attacks
- Plan to eliminate significant vulnerabilities
- Develop systems to identify and prevent attempted attacks
- Alert, contain and rebuff attacks and then, with the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), to rebuild essential capabilities in the aftermath
Infrastructure sectors
CIP defines sectors and organizational responsibilities in a standard way:
- Banking and finance: - The Department of the Treasury is responsible for coordinating the protection of not just systems but also maintaining public confidence, through industry initiatives such as the Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center[4] (ISAC)
- Transportation: - The Department of Transportation is responsible for protecting the road, rail, air, and water transportation infrastructure, including computer-controlled just-in-time delivery systems, optimization of distribution through hubs, and traffic and operations centers that are consolidated into key locations, and regulation of the transport of hazardous materials.
- Power: - The Department of Energy oversees energy supplies including electricity, oil, and gas, and works with the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for the protection of nuclear materials and power. Note that CIP in this sector is different from energy security, which is the politics and economics of supply. Additionally, operating under the auspices of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), a non-profit organization that defines and enforces reliability standards for the bulk power system.
- Information and communications: - Overseen by the Department of Commerce, most areas of life rely on telecommunications and information technology.

- Federal and municipal services: - Overseen jointly by Federal and State agencies. They guarantee continuity of government at the federal, state, and local levels to meet for provision of essential services.
- Emergency services: - Overseen by the Health and Human Services, this includes emergency health services and public health
- Fire departments: - Overseen by the Federal Emergency Management Agency FEMA.
- Law enforcement agencies: - Overseen jointly by the Department of Justice and the Federal Bureau of Investigation to ensure the orderly running of activities during times of threat or crises.
- Public works: - Overseen by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. This includes safe water systems and drainage.
In 2003 the remit was expanded to include:
- Agriculture and food, with the Department of Agriculture overseeing the safe supply of meat, poultry, and egg products.
- National monuments and icons, under the Department of the Interior
With much of the critical infrastructure privately owned, the Department of Defense (DoD) depends on commercial infrastructure to support its normal operations. The Department of State and the Central Intelligence Agency are also involved in foreign affairs and intelligence analysis with friendly countries.
In May 2007 the DHS completed its sector-specific plans (SSP) for coordinating and dealing with critical events.[5] the Continuity of government (COG) in time of a catastrophic event can be used to preserve the government as seen fit by the president, at which point the welfare of the government can be placed above the welfare of the citizenry of the United States ensuring that the government is preserved to rebuild the economy and country when it is deemed safe to return to the surface of the United States of America.
Significance
On March 9, 1999, Deputy Defense Secretary John Hamre warned the United States Congress of a cyber terrorist "electronic Pearl Harbor" saying, "It is not going to be against Navy ships sitting in a Navy shipyard. It is going to be against commercial infrastructure". Later this fear was qualified by President Clinton after reports of actual cyber terrorist attacks in 2000: "I think it was an alarm. I don't think it was Pearl Harbor. We lost our Pacific fleet at Pearl Harbor. I don't think the analogous loss was that great.[6]"
There are many examples of computer systems that have been hacked or victims of extortion. One such example occurred in September 1995 where a Russian national allegedly masterminded the break-in of Citicorp's electronic funds transfer system and was ordered to stand trial in the United States. A gang of hackers under his leadership had breached Citicorp's security 40 times during 1994. They were able to transfer $12 million from customer accounts and withdraw an estimated $400,000.
In the past, the systems and networks of the infrastructure elements were physically and logically independent and separate. They had little interaction or connection with each other or other sectors of the infrastructure. With advances in technology, the systems within each sector became automated, and interlinked through computers and communications facilities. As a result, the flow of electricity, oil, gas, and telecommunications throughout the country are linked—albeit sometimes indirectly—but the resulting linkages blur traditional security borders.
While this increased reliance on interlinked capabilities helps make the economy and nation more efficient and perhaps stronger, it also makes the country more vulnerable to disruption and attack. This interdependent and interrelated infrastructure is more vulnerable to physical and cyber disruptions because it has become a complex system with single points of failure. In the past an incident that would have been an isolated failure can now cause widespread disruption because of cascading effects.[7] As an example, capabilities within the information and communication sector have enabled the United States to reshape its government and business processes, while becoming increasingly software driven. One catastrophic failure in this sector now has the potential bring down multiple systems including air traffic control, emergency services, banking, trains, electrical power, and dam control.
The elements of the infrastructure themselves are also considered possible targets of terrorism. Traditionally, critical infrastructure elements have been lucrative targets for anyone wanting to attack another country. Now, because the infrastructure has become a national lifeline, terrorists can achieve high economic and political value by attacking elements of it. Disrupting or even disabling the infrastructure may reduce the ability to defend the nation, erode public confidence in critical services, and reduce economic strength. Additionally, well chosen terrorist attacks can become easier and less costly than traditional warfare because of the interdependence of infrastructure elements. These infrastructure elements can become easier targets where there is a low probability of detection.
The elements of the infrastructure are also increasingly vulnerable to a dangerous mix of traditional and nontraditional types of threats. Traditional and non-traditional threats include equipment failures, human error, weather and natural causes, physical attacks, and cyber attacks. For each of these threats, the cascading effect caused by single points of failure has the potential to pose dire and far-reaching consequences.
Challenges
There are fears that the frequency and severity of critical infrastructure incidents will increase in the future.[8]
Although efforts are under way, there is no unified national capability to protect the interrelated aspects of the country's infrastructure. One reason for this is that a good understanding of the inter-relationships does not exist. There is also no consensus on how the elements of the infrastructure mesh together, or how each element functions and affects the others. Securing national infrastructure depends on understanding the relationships among its elements. Thus when one sector scheduled a three-week drill to mimic the effects of a pandemic flu, even though two-thirds of the participants claimed to have business continuity plans in place, barely half reported that their plan was moderately effective.[9]
Critical infrastructure protection requires the development of a national capability to identify and monitor the critical elements and to determine when and if the elements are under attack or are the victim of destructive natural occurrences. CIP is important because it is the link between risk management and infrastructure assurance. It provides the capability needed to eliminate potential vulnerabilities in the critical infrastructure.
CIP practitioners determine vulnerabilities and analyze alternatives in order to prepare for incidents. They focus on improving the capability to detect and warn of impending attacks on, and system failures within, the critical elements of the national infrastructure.
Organization and structure
PDD-63 mandated the formation of a national structure for critical infrastructure protection. To accomplish this one of the primary actions was to produce a National Infrastructure Assurance Plan, or NIAP, later renamed National Infrastructure Protection Plan or NIPP.
The different entities of the national CIP structure work together as a partnership between the government and the public sectors. Each department and agency of the federal government is responsible for protecting its portion of the government's critical infrastructure. In addition, there are grants made available through the Department of Homeland Security for municipal and private entities to use for CIP and security purposes. These include grants for emergency management, water security training, rail, transit and port security, metropolitan medical response, LEA terrorism prevention programs and the Urban Areas Security Initiative.[10]
PDD-63 identified certain functions related to critical infrastructure protection that must be performed chiefly by the federal government. These are national defense, foreign affairs, intelligence, and law enforcement. Each lead agency for these special functions appoints a senior official to serve as a functional coordinator for the federal government. In 2008 a mobile PDA-based Vulnerability Assessment Security Survey Tool (VASST) was introduced to speed physical security assessment of critical infrastructure by law enforcement to meet compliance requirements of PDD-63.[11]
National Infrastructure Assurance Plan / National Infrastructure Protection Plan
For each of the identified major sectors of the critical infrastructure, the federal government appointed a Sector Liaison Official from a designated Lead Agency. A private sector counterpart, a Sector Coordinator, was also identified. Together, the two sector representatives, one federal government and one corporate, were responsible for developing a sector NIAP.
In addition, each department and agency of the federal government was responsible for developing its own CIP plan for protecting its portion of the federal government's critical infrastructure. The federal department and agency plans were assimilated with the sector NIAPs to create one comprehensive National Infrastructure Assurance Plan. Additionally the national structure must ensure there is a national CIP program. This program includes responsibilities such as education and awareness, threat assessment and investigation, and research.
The process includes assessments of:
- Protection - Can be defined as the state of being defended, safeguarded, or shielded from injury, loss, or destruction from natural or unnatural forces.
- Vulnerability – The quality of being susceptible to attack or injury, warranted or unwarranted, by accident or by design.
- Risk – The possibility or likelihood of being attacked or injured.
- Mitigation – The ability to alleviate, reduce, or moderate a vulnerability, thus reducing or eliminating risk.
Controversy
There have been public criticisms of the mechanisms and implementation of some security initiatives and grants, with claims they are being led by the same companies who stand to benefit,[12] and that they are encouraging an unnecessary culture of fear. Commentators note that these initiatives started directly after the collapse of the Cold War, raising the concern that this was simply a diversion of the military-industrial complex away from a funding area which was shrinking and into a richer previously civilian arena.
Grants have been distributed across the different states even though the perceived risk is not evenly spread, leading to accusations of pork barrel politics that directs money and jobs towards marginal voting areas. The Urban Areas Security Initiative grant program has been particularly controversial, with the 2006 infrastructure list covering 77,000 assets, including a popcorn factory and a hot dog stand.[13] The 2007 criteria were reduced to 2,100 and now those facilities must make a much stronger case to become eligible for grants.[14] While well-intentioned, some of the results have also been questioned regarding claims of poorly designed and intrusive security theater that distracts attention and money from more pressing issues or creates damaging side effects.
An absence of comparative risk analysis and benefits tracking it has made it difficult to counter such allegations with authority. In order to better understand this, and ultimately direct effort more productively, a Risk Management and Analysis Office was recently created in the National Protection and Programs directorate at the Department of Homeland Security.
Department of Defense and CIP
The U.S. Department of Defense is responsible for protecting its portion of the government's critical infrastructure. But as part of the CIP program, DoD has responsibilities that traverse both the national and department-wide critical infrastructure.
PDD-63 identified the responsibilities DoD had for critical infrastructure protection. First, DoD had to identify its own critical assets and infrastructures and provide assurance through analysis, assessment, and remediation. DoD was also responsible for identifying and monitoring the national and international infrastructure requirements of industry and other government agencies, all of which needed to be included in the protection planning. DoD also addressed the assurance and protection of commercial assets and infrastructure services in DoD acquisitions. Other DoD responsibilities for CIP included assessing the potential impact on military operations that would result from the loss or compromise of infrastructure service. There were also requirements for monitoring DoD operations, detecting and responding to infrastructure incidents, and providing department indications and warnings as part of the national process. Ultimately, DoD was responsible for supporting national critical infrastructure protection.
In response to the requirements identified in PDD-63, DoD categorized its own critical assets by sector, in a manner similar to the national CIP organization. The DoD identified a slightly different list of infrastructure sectors for those areas that specifically required protection by DoD. DoD’s organizational structure for critical infrastructure protection reflects, complements, and effectively interacts with the national structure for CIP.
DoD sectors
There are ten defense critical infrastructure sectors that are protected by the DoD. These include:
- Financial Services - Defense financial services support activities related to officially appropriated funds. These activities include the disbursement of cash, receipt of funds, and acceptance of deposits for credit to officially designated Treasury general accounts. This sector also provides financial services to individuals and on-base organizations, including deposits, account maintenance, and safekeeping. The Defense Finance and Accounting Service is the lead component for the Financial Services sector.
- Transportation - The Defense Transportation System, or DTS, includes resources that support global DoD transportation needs. These include surface, sea, and lift assets; supporting infrastructure; personnel; and related systems. Transportation Command, or USTRANSCOM, is the single manager for DoD transportation.
- Public Works - Public works includes four distinct physical infrastructure sectors: electric power, oil, and natural gas, water and sewer; and emergency services, such as fire, medical, and hazardous material handling. This defense infrastructure sector is composed of networks and systems, principally for the distribution of the associated commodities. The Corps of Engineers is responsible for coordinating the assurance activities of the public works infrastructure sector.
- Global Information Grid Command Control, or GIG/C2 - The Global Information Grid Command Control, or GIG/C2, are two combined sectors that support overall asset assurance for CIP. The GIG is the globally interconnected set of personnel, information, and communication capabilities necessary to achieve information superiority. C2 includes assets, facilities, networks, and systems that support mission accomplishment. The Defense Information Systems Agency, or DISA, is the lead component responsible for Global Information Grid Command Control.
- Intelligence Surveillance, and Reconnaissance, or ISR - The Defense Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance infrastructure sector is composed of facilities, networks, and systems that support ISR activities such as intelligence production and fusion centers. The Defense Intelligence Agency, or DIA, is responsible for coordinating the assurance activities of this infrastructure sector.
- Health Affairs - The health care infrastructure consists of facilities and sites worldwide. Some are located at DoD installations; however, DoD also manages a larger system of non-DoD care facilities within its health care network. These health care facilities are linked by information systems. The Office of the Assistant Secretary of Defense, Heath Affairs is the designated lead component for this sector.
- Personnel - The defense personnel infrastructure sector includes a large number of assets hosted on component sites, a network of facilities, and information systems linking those sites and facilities. In addition to being responsible for its own assets, the personnel infrastructure sector also coordinates commercial services that support the personnel function. These services include recruitment, record keeping, and training. The Defense Human Resources Activity is the designated lead component for the Defense Personnel infrastructure sector.
- Space - The defense space infrastructure sector is composed of both space- and ground-based assets including launch, specialized logistics, and control systems. Facilities are located worldwide on both DoD-controlled and private sites. The Defense Space sector is led by the United States Strategic Command, or USSTRATCOM.
- Logistics - The defense logistics sector includes all activities, facilities, networks, and systems that support the provision of supplies and services to U.S. forces worldwide. Logistics includes the acquisition, storage, movement, distribution, and maintenance of material and supplies. This sector also includes the final disposition of material no longer needed by DoD. The Defense Logistics Agency, or DLA, is the lead component for the DoD Logistics infrastructure.
- Defense Industrial Base - The Defense Industrial Base consists of DoD product and service providers from the private sector. The services and products provided constitute critical assets for DoD. The lead component for the Defense Industrial Base is the Defense Contract Management Agency. For those cases when infrastructure protection requirements affect more than one defense sector, DoD has set up special function components that support the implementation of CIP.
DoD special functions
The DoD CIP special function components interface with the equivalent national functional coordinators and coordinate all activities related to their function within DoD.
DoD’s special function components currently include seven areas of focus. They include the following components:
- Policy and Strategy - The Policy and Strategy Special Function Component provides the strategic planning required to prepare our Armed Forces for the 21st century. In part, it satisfies this responsibility through the development of the National Military Strategy. Within the area of policy development it is responsible for leading the Chairman's biennial review of the Unified Command Plan and developing Joint Staff positions on such key issues as the organization, roles and missions, and functions of the Armed Forces and the combatant commands.
- Intelligence Support - The CIP Intelligence Support Special Function Component provides intelligence support to DoD in protection of the Defense portion of the Federal Government Critical Infrastructure. Intelligence Support responsibilities also include supporting the Defense Warning System, Alert and Notification, and interfacing with the national intelligence community. The responsibilities of the Intelligence Support agencies include such activities as provisioning threat assessments; indications and warnings of potential attacks; advice and support to Sector CIAOs in the development of defense infrastructure sector monitoring and reporting; crisis management support; and counter-intelligence. This special function component is also tasked with the support to the DoD contingent of the NIPC related to intelligence and counter-intelligence.
- Industrial Policy - The Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition, Technology & Logistics ensures that an adequate defense industrial base exists and remains viable to meet current, future, and emergent national security requirements."
- Defense Security - The Defense Security Service provides to the Department of Defense and other Federal agencies an array of security products and services which are designed to deter and detect espionage
- Information Assurance - The Assistant Secretary of Defense for Networks and Information Integration, or ASD NII, is the principal OSD staff assistant for the development, oversight, and integration of DoD policies and programs relating to the strategy of information superiority for the Department of Defense. Information Assurance, or IA, is the component of Information Operations that assures DoD's operational readiness by providing for the continuous availability and reliability of information systems and networks. IA protects the DII against exploitation, degradation, and denial of service, while providing the means to efficiently reconstitute and reestablish vital capabilities following an attack.
- Research and Development - The Research and Development Special Function Component is responsible for information assurance and protection. The Office of Director, Defense Research and Engineering coordinates a CIP DoD research and development agenda. As well as reconciling the DoD agenda with the national R&D agenda.
- Education and Awareness - Although education and awareness may rightly be considered everyone's responsibility, a comprehensive education and awareness strategy was deemed essential for a successful DoD CIP program. The National Defense University, or NDU, provided advice and assistance in assessing DoD education and awareness requirements. The Education and Awareness Component also developed the CIAO Education Program. This component was tasked to assist in the development of any special education or training required for CIP crisis management personnel. Education and Awareness also supports both DoD and national CIP policy and strategy formulation and executive leadership development through periodic "infrastructure games".
DoD CIP lifecycle
As mandated by PDD-63, the DoD must protect its portion of the federal government's critical infrastructure. For DoD, this is the Defense Infrastructure or DI. Protecting the Defense Infrastructure is a complex task involving ten defense sectors.
It was deemed that it was nearly impossible to protect every critical asset at every location, therefore the focus was directed on protecting the critical Defense Infrastructure. The critical Defense Infrastructure is the critical assets essential to providing mission assurance.
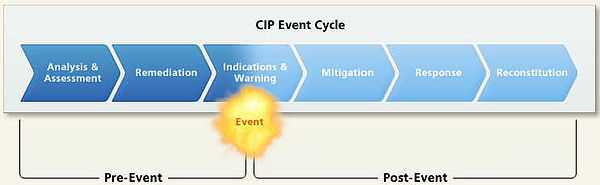
Six phases
The six phases of the DoD CIP life cycle build on one another to create a framework for a comprehensive solution for infrastructure assurance. The life cycle phases occur before, during, and after an event that may compromise or degrade the infrastructure. A synopsis of the six phases are:
- Analysis and Assessment (occurs before an event) - The Analysis and Assessment phase is the foundation and most important phase of the CIP life cycle. This phase identifies the assets absolutely critical to mission success and determines the assets’ vulnerabilities, as well as their interdependencies,[15] configurations, and characteristics. An assessment is then made of the operational impact of infrastructure loss or degradation. In addition, Proactive Cyber Defence may anticipate an attack against computers and networks. It applies equally well to all critical infrastructure sectors, as it involves interdicting and disrupting an attack or a threat’s preparation to attack, either preemptively or in self-defense.
- Remediation (occurs before an event) - The Remediation phase involves precautionary measures and actions taken before an event occurs to fix the known cyber and physical vulnerabilities that could cause an outage or compromise a National Defense Infrastructure, or NDI, or critical asset. For example, remediation actions may include education and awareness, operational process or procedural changes or system configuration and component changes.
- Indications and Warnings (occurs before and/or during an event) - The Indications and Warnings phase involves daily sector monitoring to assess the mission assurance capabilities of critical infrastructure assets and to determine if there are event indications to report. Indications are preparatory actions that indicate whether an infrastructure event is likely to occur or is planned. Indications are based on input at the tactical, operational, theater, and strategic level. At the tactical level, input comes from asset owners. At the operational level, input comes from the NDI sectors. At the theater level, input comes from regional assets such as allied intelligence, NATO, command intelligence, allied governments, and coalition forces. At the strategic level, input comes from intelligence, law-enforcement, and the private sector. Warning is the process of notifying asset owners of a possible threat or hazard.
- Mitigation (occurs both before and during an event) - The Mitigation phase comprises actions taken before or during an event in response to warnings or incidents. DoD Critical Asset owners, NDI sectors, DoD installations, and military operators take these actions to minimize the operational impact of a critical asset’s loss or debilitation.
- Incident Response (occurs after an event) - Incident Response comprises the plans and activities taken to eliminate the cause or source of an infrastructure event.
- Reconstitution (occurs after an event) - The last phase of the CIP life cycle, involves actions taken to rebuild or restore a critical asset capability after it has been damaged or destroyed. This phase is the most challenging and least developed process.
Effective management of the CIP life cycle ensures that protection activities can be coordinated and reconciled among all DoD sectors. In many ways, DoD CIP, is risk management at its most imperative. Achieving success means obtaining mission assurance. Missing the mark can mean mission failure as well as human and material losses. For critical infrastructure protection, risk management requires leveraging resources to address the most critical infrastructure assets that are also the most vulnerable and that have the greatest threat exposure.
The most important part of the CIP lifecycle is Phase 1. Because it is crucial to target the right assets for infrastructure protection, determining these assets is the first phase in the CIP life cycle. This phase, Analysis and Assessment, is the key and foundation of the seven lifecycle activities. Without a solid foundation, the remaining CIP life cycle phases may be flawed, resulting in a CIP plan that fails to protect the critical infrastructure and, therefore, mission assurance.
Phase 1: Analysis and Assessment
Phase 1 determines what assets are important, and identifies their vulnerabilities, and dependencies so that decision makers have the information they need to make effective risk management choices.
The Defense Infrastructure, or DI, is organized into ten sectors. Each sector is composed of assets, such as systems, programs, people, equipment, or facilities. Assets may be simple, such as one facility within one geographic location, or complex, involving geographically dispersed links and nodes.
The Analysis and Assessment is made up of five steps that include activities that span and encompass the ten DI sectors and their assets.
- I. The first step in the Analysis and Assessment phase is to identify critical assets. An asset’s criticality is a function of both time and situation based on the asset’s operational or business value. For the DI, value depends on several factors: First, what military operations or services rely on an asset and how those dependencies change across time Next, how sensitive the operation is to the loss or compromise of the asset, in other words what is the maximum allowable down time if the asset is compromised. Finally, what the asset’s assurance profile is, in particular whether asset restoration or a switch to a backup can occur within the allowable down time. Through domain expertise and inspection, critical assets are identified and then reported to the CIP Program.
- II. The second step of the Analysis and Assessment phase is Defense Infrastructure characterization. This step maps and associates critical asset functions and relationships within a DI sector.
- III. The third step in the Analysis and Assessment phase is the Operational Impact Analysis. This step is accomplished through the development of operational dependency matrices and the application of operations research methods. Potential operational impacts and service-level requirements are then reflected in the asset’s criticality attributes and criticality index in the CIP program.
- IV. The fourth step is the Vulnerability Assessment. This step is accomplished through multiple channels. Through the CIP program, all critical assets have a baseline vulnerability index, which is calculated from inputs associated with the class of asset and geographic region such as the probability of natural disasters, criminal or national security events, and technological failures. Asset owners, host installations, the sector CIAO, or other DoD entities may provide asset operational readiness and emergency preparedness information.
- V. The fifth and final step in the Analysis and Assessment phase is Interdependency Analysis. Interdependency analysis seeks to map functions and relationships among DI sectors. As a result of the Interdependency Analysis, the criticality attributes for previously identified assets may be updated and additional critical assets may be identified to the CIP program. Multiple groups within the DoD CIP structure perform analysis and assessment activities. Translating the analysis and assessment process into concrete data requires specific activities, tasks, and tools.
Phase 1 example in the “Real World”
On August 24, 2001, the Director of the Joint Staff requested USPACOM to serve as the lead support Combatant Command for creating a CIP first-ever theater CIP Plan – known as the “CIP Appendix 16 Plan”. The following is how USPACOM approached the task. USPACOM focused the Analysis and Assessment phase by organizing its activities to answer three major questions:
- What is critical?
- Is it vulnerable?
- What can be done?
To answer the question, “What is critical?”, USPACOM outlined a three-step procedure:
- First, identify the project focus.
- Second, complete an operational analysis.
- Third, complete a Defense Infrastructure analysis.
To accomplish these steps, USPACOM adopted a methodology that focuses its CIP efforts on Tier 1 assets. Tier 1 assets are assets that could cause mission failure if they are compromised or damaged. The methodology UAPACOM adopted and modified is Mission Area Analysis, or MAA. The MAA links combatant command missions to infrastructure assets that are critical to a given Operations Plan, or OPLAN, Contingency Plan, or CONPLAN, or Crisis Action Plan. Typically, the MAA process determines the assessment site priorities. USPACOM modified the process and selected the CIP assessment sites and installations prior to conducting the MAA. The following is an illustration of the USPACOM MAA process:
- First, it identified the Mission Essential Requirements, or MERs, which are specific combatant commands or joint task force capabilities essential for execution of a warfighting plan. Then, they created an MER matrix for the specific command. For example, one MER may be to provide command, control, communications, and computers, or C4.
- Second, it identified forces required for each MER. For example, the C4 MER is linked to a specific signal battalion. Third, it linked the forces to the necessary functions and tasks supporting the force. For example, the signal battalion is linked to the Communications and Civil Engineers functions and the task of managing the theater’s C4 information systems requirements.
- Third, it links assets to the functions supporting the tasks. The result is a mission area analysis of mission-critical assets.
USPACOM uses the MAA data it gathers to scope and focus its efforts on truly mission-critical assets to answer the next question in its process, Is it vulnerable?
The first step in answering this question is to complete an installation analysis. The next step is to complete a commercial infrastructure analysis. USPACOM relied upon two different DoD organizations for CIP assessments: Balanced Survivability Assessments, or BSAs, and Mission Assurance Assessments. The BSA is a two-week mission-focused assessment at a military installation or designated site. A Mission Assurance Assessment is unique because it uses an area assessment approach to focus on both commercial and military asset vulnerabilities and dependencies. The final step to determine vulnerabilities is to integrate the two analyses and assessments. With its critical assets and their vulnerabilities identified, USPACOM is ready to perform risk management activities to decide what can be done to protect the mission-critical assets.
Booz Allen Hamilton developed this process at PACOM.
Phase 2: Remediation
The first phase of the CIP life cycle, Analysis and Assessment, identified the critical assets of DoD sector infrastructures and the vulnerabilities or weaknesses of those critical assets.
The second phase is the Remediation phase. In the Remediation phase, the known weaknesses and vulnerabilities are addressed. Remediation actions are deliberate, precautionary measures designed to fix known virtual and physical vulnerabilities before an event occurs. The purpose of remediation is to improve the reliability, availability, and survivability of critical assets and infrastructures. Remediation actions apply to any type of vulnerability, regardless of its cause. They apply to acts of nature, technology failures, or deliberate malicious actions.
The cost of each remediation action depends on the nature of the vulnerability it addresses. The Defense Infrastructure Sector Assurance Plan that each infrastructure sector must develop, establishes the priorities and resources for remediation. Remediation requirements are determined by multiple factors. These are analysis and assessment, input from military planners and other DoD sectors, the National Infrastructure Assurance Plan and other plans, reports, and information on national infrastructure vulnerabilities and remediation, as well as intelligence estimates and assessments of threats.
Remediation requirements are also gathered through lessons learned from Defense Infrastructure sector monitoring and reporting and infrastructure protection operations and exercises. The CIP program tracks the status of remediation activities for critical assets. Remediation activities to protect the critical Defense Infrastructure cross multiple Department components.
Phase 3: Indications and warnings
The need to monitor activities and warn of potential threats to the United States is not new. From conventional assaults to potential nuclear attacks, the military has been at the forefront of monitoring and warning of potential dangers since the founding of the country. Protecting the security and well being of the United States, including the critical Defense Infrastructure, has now entered a new era. It has been deemed essential to have a coordinated ability to identify and warn of potential or actual incidents among critical infrastructure domains. The ability to detect and warn of infrastructure events is the third phase of the critical infrastructure protection life cycle, the Indications and Warnings phase.
Indications and warnings are actions or infrastructure conditions that signal an event is either”
- Likely,
- Planned or
- Underway.
Historically, DoD event indications have focused and relied on intelligence information about foreign developments. These event indications have been expanded to include all potential infrastructure disruption or degradation, regardless of its cause. DoD CIP indications are based on four levels of input:
- Tactical level input from DoD asset owners or installations
- Operational-level input from sector Chief Information Assurance Officers (CIAOs)
- Theater-level input from command and service intelligence and counter-intelligence activities.
- Strategic-level intelligence from the intelligence community, law enforcement, and the private sector
This fusion of traditional intelligence information with sector-specific information has been determined to be essential for meaningful CIP indications.
If an indication is detected, a warning notifying the appropriate asset owners of a possible or occurring event or hazard can be issued. The sector’s assurance plan determines what conditions and actions are monitored and reported for each Defense Infrastructure Sector. Each sector must develop a written Defense Sector Assurance Plan that includes a compendium of sector incidents for monitoring and reporting. The sector incident compendium is made up of three types of incidents:
- Nationally defined reportable incidents
- DoD defined reportable incidents, and
- Sector-defined reportable incidents.
DoD critical asset owners, installations, and sector CIAOs determine the DoD and sector-defined incidents. Each of the reportable incidents or classes of incidents must include the following components:
- Who should monitor the incident
- How soon the incident must be reported
- Which information elements the incident should contain
- How the incident reporting should be routed
- What follow-up actions are required
The National Infrastructure Protection Center (NIPC) is the primary national warning center for significant infrastructure attacks. Critical asset owners, DoD installations, and Sector CIAOs monitor the infrastructure daily. Indications of an infrastructure incident are reported to the National Military Command Center, or NMCC. If indications are on a computer network, they are also reported to the Joint Task Force Computer Network Operations (JTF-CNO). The NMCC and JTF-CNO assess the indications and pass them to the NIPC and appropriate DoD organizations. When the NIPC determines that an infrastructure event is likely to occur, is planned, or is under way, it issues a national warning. For DoD, the NIPC passes its warnings and alerts to the NMCC and JTF-CNO. These warnings and alerts are then passed to the DoD components. The warning may include guidance regarding additional protection measures DoD should take.
Phase 4: Mitigation
Phase 1 of the CIP life cycle provided a layer of protection by identifying and assessing critical assets and their vulnerabilities. Phase 2 provided another layer of protection by remediating or improving the identified deficiencies and weaknesses of an asset. Even with these protections and precautions, an infrastructure incident was still possible. When it does the Indications and Warnings phase goes into effect.
The Mitigation phase (Phase 4), is made up of preplanned coordinated actions in response to infrastructure warnings or incidents. Mitigation actions are taken before or during an infrastructure event. These actions are designed to minimize the operational impact of the loss of a critical asset, facilitate incident response, and quickly restore the infrastructure service.
A primary purpose of the Mitigation phase is to minimize the operational impact on other critical Defense Infrastructures and assets when a critical asset is lost or damaged. As an example, if there is a U.S. installation, Site A, located in a host nation. Site A is a tier 1 asset, meaning that if it fails, the Combatant Commands mission fails. Site A has mutual Global Information Grid Command Control (GIG/C2), information interdependencies with Sites B and C. In addition, other Defense Infrastructure sectors rely on Site A for mission capabilities. In this scenario, what could be the impact if the supply line to the commercial power plant that provides the installation’s primary power is accidentally severed. Because of all the interdependencies, losing this asset is more than the loss of just one site. It means the loss of other sector capabilities.
A possible mitigation action might be for Site A to go on backup power. An alternate action could be to pass complete control of Site A’s functionality to another site, where redundancy has been previously arranged. These actions would limit the impact of this incident on the other sites and related sectors. In addition to lessening the operational impact of a critical infrastructure event, the Mitigation phase of the CIP life cycle supports and complements two other life cycle phases. Mitigation actions aid in the emergency, investigation, and management activities of Phase 5, Incident Response. They also facilitate the reconstitution activities of Phase 6.
During the Mitigation phase, DoD critical asset owners, DoD installations, and Sector Chief Infrastructure Assurance Officers, or CIAOs, work with the National Military Command Center (NMCC) and the Joint Task Force-Computer Network Operations (JTF-CNO) to develop, train for, and exercise mitigation responses for various scenarios. When there is a warning, emergency, or infrastructure incident, the critical asset owners, installations, and Sector CIAOs initiate mitigation actions to sustain service to the DoD. They also provide mitigation status information to the NMCC and JTF-CNO. The NMCC monitors for consequences from an event within one Defense Infrastructure sector that are significant enough to affect other sectors. For events that cross two or more sectors, the NMCC advises on the prioritization and coordination of mitigation actions. When event threats or consequences continue to escalate, the NMCC directs mitigation actions by sector to ensure a coordinated response across the DoD. The NMCC and the JTF-CNO keep the National Infrastructure Protection Center, or NIPC, apprised of any significant mitigation activities.
Phase 5: Incident response
When an event affects the Defense Infrastructure, the Incident Response phase begins. Incident Response is the fifth phase of the CIP life cycle. The purpose of the Incident Response phase is to eliminate the cause or source of an infrastructure event. For example, during the 9/11 attacks on the World Trade Center and Pentagon, all non-military airplanes were grounded over the United States to prevent further incidents. Response activities included emergency measures, not from the asset owners or operators, but from dedicated third parties such as law enforcement, medical rescue, fire rescue, hazardous material or explosives handling, and investigative agencies. Response to Defense Infrastructure incidents can take one of two paths depending on whether or not the event affects a DoD computer network.
When incidents compromise a DoD computer network, the Joint Task Force-Computer Network Operations (JTF-CNO) directs the response activities. These activities are designed to stop the computer network attack, contain and mitigate damage to a DoD information network and then restore minimum required functionality. JTF-CNO also requests and coordinates any support or assistance from other Federal agencies and civilian organizations during incidents affecting a DoD network. When incidents impact any other DoD owned assets, installation commanders and critical asset owners follow traditional channels and procedures to coordinate responses. This includes notifying affected Sector Chief Infrastructure Assurance Officers, or CIAOs, in the initial notice and status reporting. Although third parties play a major role in the response to Defense Infrastructure events, DoD CIP personnel also have responsibilities to fulfill.
Phase 6: Reconstitution
After the source or cause of an infrastructure event is eliminated or contained, the infrastructure and its capabilities must be restored. Reconstitution is the last phase of the critical infrastructure protection. Reconstitution is probably the most challenging and least developed process of the life cycle. DoD critical asset owners have the major responsibility for reconstitution.
International Perspective Of Critical Infrastructure Protection
Internet is full of unprotected and unsafe devices, SCADA systems and computers making critical infrastructures vulnerable to cyber attacks.[16] Further, conflict of laws in cyberspace[17] is a major hurdle before global critical infrastructure protection efforts. There is no global cyber law[18] and cyber security treaty[19] that can be invoked for enforcing global cyber security issues.
International legal issues of cyber attacks[20] are really tricky and complicated in nature.[21] For instance, even if a cyber attack is traced back to a particular jurisdiction, authorship attribution for cyber crimes and cyber attacks has become a major problem for international law enforcement agencies.[22]
India
Critical infrastructure protection in India [23] is facing many problems and challenges. Indian cyber security initiatives are grossly deficient [24] and they need to be improved. For instance, critical infrastructures like automated power grids [25] are facing cyber security challenges.[26] Similar is the position regarding Indian satellites [27] and other critical infrastructures that require immediate attention of Indian government. There is also no critical ICT infrastructure protection policy in India.[28] It has now been realised that critical infrastructure protection in India is needed.[29]
Indian government has also discussed few good projects in this direction. For instance, a national critical information infrastructure protection centre (NCIPC) of India [30] has been proposed by Indian government and it may become functional very soon.[31] Similarly, hints have been given regarding formulation of a tri service cyber command for armed forces of India [32] and cyber crisis management plan of India.[33] NTRO would protect [34] critical infrastructures like thermal power in India.[35] A national cyber security policy of India 2013 (NCSP 2013) has also been prescribed by Indian government but it has not become functional till now.[36]
See also
- Richard A. Clarke, Former Special Advisor to the President for Counterterrorism, Cybersecurity, and Critical Infrastructure Protection
- Proactive Cyber Defence Proactive Cyber Defence in depth to protect critical information infrastructures
- Presidential Decision Directive 62
- ITU Global Cybersecurity Agenda
- North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC)
- Critical Foreign Dependencies Initiative
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Presidential directive PDD-63
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "December 17, 2003 Homeland Security Presidential Directive/Hspd-7". White House Archives. 17 December 2003. Retrieved 29 July 2014.
- ↑ Article 52 and 54 of the Protocol Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949, and relating to the Protection of Victims of International Armed Conflicts ("Geneva Conventions")
- ↑ Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center
- ↑ Department of Homeland Security - Sector-Specific Plans
- ↑ Federation of American Scientists February 15, 2000 Presidential remarks on Computer Security
- ↑ Austen Givens, "Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Is An Ominous Sign for Critical Infrastructure's Future", May 27, 2011.
- ↑ Paul J. Maliszewski, "Modeling Critical Vaccine Supply Location: Protecting Critical Infrastructure and Population in Central Florida" (2008)
- ↑ How Well Can Wall Street Handle Pandemic Flu? Drill Results Are Mixed Wall Street & Technology
- ↑ 2006 Catalog of Federal domestic assistance grants (CFDA), including security projects
- ↑ "Aegis Bleu Launches VASST, Vulnerability Assessment Security Survey Tool", PR Leap 11 September 2008.
- ↑ Elisa Williams, "Climate of Fear", Forbes magazine, 2 April 2002
- ↑ Eric Lipton, "Terror Target List", New York Times, July 12, 2006.
- ↑ Zack Phillips, "Security Theater," Government Executive, 1 August 2007.
- ↑ Critical Infrastructure Interdependency Wheel (CIIW) assessment tool
- ↑ "Internet Is Full Of Unprotected And Unsafe Devices, SCADA Systems And Computers". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 25 March 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Conflict Of Laws In Cyberspace, Internet And Computer Era". Conflict Of Laws In Cyberspace, Internet And Computer Era. 9 October 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "International Cyber Law Treaty Is Required". Perry4Law Organisation’s Blog – An Exclusive And Global Techno Legal Knowledge Base. 10 October 2012. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "International Cyber Security Treaty Is Required". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 9 January 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "International Legal Issues Of Cyber Attacks, Cyber Terrorism, Cyber Espionage, Cyber Warfare And Cyber Crimes". International And Indian Legal Issues Of Cyber Security. 11 March 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "International Legal Issues Of Cyber Attacks And Indian Perspective". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 22 March 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Cross Border Cyber Attacks, Authorship Attribution And Cyber Crimes Convictions". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 29 March 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Critical Infrastructure Protection In India: The Problems, Challenges And Solutions". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 6 January 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "India Is A Sitting Duck In The Cyberspace And Civil Liberties Protection Regime". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 2 July 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Cyber Security Of Automated Power Grids Of India". Global ICT Policies And Strategies And Indian Perspective. 23 November 2011. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Power Grids Cyber Security In India And Its Challenges". Global ICT Policies And Strategies And Indian Perspective. 7 August 2012. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Cyber Security Of Indian Satellites And Critical Infrastructure". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 23 February 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Critical ICT Infrastructure Protection Policy Of India". Global ICT Policies And Strategies And Indian Perspective. 3 June 2011. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Critical Infrastructure Protection In India Is Needed". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 23 February 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIPC) Of India". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 3 February 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "National Cyber Coordination Centre (NCCC) Of India May Become Functional". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 20 January 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Tri Service Cyber Command For Armed Forces Of India In Pipeline". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 15 January 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "Cyber Attacks Crisis Management Plan Of India". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 17 January 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "NTRO Would Protect The Critical ICT Infrastructures Of India". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 13 January 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "National Infrastructure Protection Plan In Thermal Power Sector Of India Proposed". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 8 March 2014. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
- ↑ "National Cyber Security Policy Of India 2013 (NCSP 2013)". Centre Of Excellence For Cyber Security Research And Development In India (CECSRDI). 26 December 2013. Retrieved 11 September 2014.
External links
- Anderson, K. "Intelligence-Based Threat Assessments for Information Networks and Infrastructures: A White Paper".
- Strategy to Secure Cyberspace
- Critical Infrastructure Protection Program, George Mason University
- "Critical Infrastructure: Homeland Security and Emergency Preparedness"
- Infracritical
- Centre for the Protection of National Infrastructure (United Kingdom)
- "Water Infrastructure Security Enhancements" draft national standards
- Terrorism & Public Utility Infrastructure Protection
- DoD IA Policy Chart - Build & Operate a Trusted GIG
- Critical Infrastructure Security: Assessment, Prevention, Detection, Response
- Critical Infrastructure Protection In India: The Problems, Challenges And Solutions
- Cyber Security Trends And Developments In India 2013
- Cyber Warfare Policy Of India
- NERC CIP Reliability Standards
