CoreOS
 | |
| OS family | Unix-like |
|---|---|
| Working state | In development |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | October 3, 2013[1] |
| Latest release | 660.0.0[2] / April 22, 2015 |
| Latest preview | 659.0.0[3] / April 21, 2015 |
| Marketing target | Servers and clusters |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux kernel) |
| License | Apache License 2.0[4][5] |
| Official website |
coreos |
CoreOS is an open source lightweight operating system based on the Linux kernel and designed for providing infrastructure to clustered deployments, while focusing on automation, ease of applications deployment, security, reliability and scalability. As an operating system, CoreOS provides only the minimal functionality required for deploying applications inside software containers, together with built-in mechanisms for service discovery and configuration sharing.[6][7][8][9]
CoreOS is a fork of Chrome OS, by the means of using its software development kit (SDK) freely available through Chromium OS as a base while adding new functionality and customizing it to support hardware used in servers.[8][10]:7:02 As of July 2014, CoreOS is actively developed, primarily by Alex Polvi, Brandon Philips and Michael Marineau,[7] with its major features (other than etcd and fleet) available as a stable release.[11][12][13]
Overview
CoreOS provides no package manager as a way for the distribution of applications, requiring instead all applications to run inside their containers. A single control host (CoreOS instance) runs multiple isolated Linux systems (containers), using Docker as an additional layer of abstraction and interface[14] to the underlying operating-system-level virtualization features of the Linux kernel. That way, resource partitioning is performed through multiple isolated userspace instances, instead of using a hypervisor and providing full-fledged virtual machines. This approach relies on the Linux kernel's cgroups functionality, which provides namespace isolation and abilities to limit, account and isolate resource usage (CPU, memory, disk I/O, etc.) for the collections of processes.[6][9][15]
CoreOS uses systemd as its primary init system, with tight integration between it and various CoreOS' internal mechanisms.[6][16]
Updates distribution
For additional security and reliability of operating system updates, CoreOS employs FastPatch as a dual-partition scheme for the read-only part of its installation, meaning that the updates are performed as a whole and installed onto a passive secondary boot partition, which becomes active upon reboot or kexec. This approach avoids possible issues arising from updating only certain parts of the operating system, ensures easy rollbacks to a known-to-be-stable version of the operating system, and allows each boot partition to be signed for additional security.[6][9][17] The root partition and its root file system are automatically resized to fill all available disk space upon reboots; while the root partition provides read-write storage space, the operating system itself is mounted read-only under /usr.[18][19]
To ensure that only a certain part of the cluster reboots at once when the operating system updates are applied, preserving that way the resources required for running deployed applications, CoreOS provides locksmith as a reboot manager. Using locksmith, it is possible to select between different update strategies that are determined by how the reboots are performed as the last step in applying updates; for example, it may be configured how many cluster members are allowed to reboot simultaneously. Internally, locksmith operates as the locksmithd daemon that runs on cluster members, while the locksmithctl command-line utility manages configuration parameters.[20][21] locksmith is written in the Go language and distributed under the terms of the Apache License 2.0.[22]
The updates distribution system employed by CoreOS is based on Google's open source Omaha project, which provides a mechanism for rolling out updates and the underlying request–response protocol based on XML.[23][24] Additionally, CoreOS provides CoreUpdate as a web-based dashboard for the management of cluster-wide updates. Operations available through CoreUpdate include assigning cluster members to different groups that share customized update policies, reviewing cluster-wide breakdowns of CoreOS versions, stopping and restarting updates, and reviewing recorded update logs. CoreUpdate also provides a HTTP-based API that allows its integration into third-party utilities or deployment systems.[17][25][26]
Cluster infrastructure
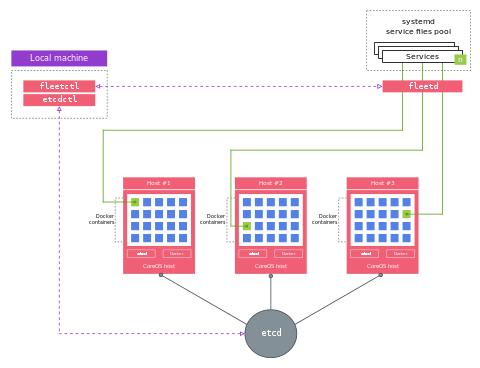
CoreOS provides etcd, a daemon that runs across all computers in a cluster and provides a dynamic configuration registry, allowing various configuration data to be easily and reliably shared between the cluster members. Since the key–value data stored within etcd is automatically distributed and replicated (with automated master election), all changes in stored data are reflected across the entire cluster, while the achieved redundancy prevents failures of single cluster members from causing data loss. Beside the configuration management, etcd also provides service discovery by allowing deployed applications to announce themselves and the services they offer. Communication with etcd is performed through an exposed API, which internally uses JSON on top of HTTP; the API may be used directly (through curl or wget, for example), or indirectly through etcdctl, which is a specialized command-line utility also supplied by CoreOS.[6][9][28][29][30]
CoreOS also provides so-called fleet functionality, based on the fleetd cluster manager daemon that controls CoreOS' separate systemd instances at the cluster level. By using fleetd, CoreOS creates a distributed init system that ties together separate systemd instances and a cluster-wide etcd deployment; internally, fleetd daemon communicates with local systemd instances over D-Bus, and with the etcd deployment through its exposed API. Using fleetd allows single or multiple containers to be deployed cluster-wide, with more advanced options including redundancy, failover, deployment to specific cluster members, dependencies between containers, and grouped deployment of containers. Command-line utility called fleetctl is used to configure and monitor this distributed init system; internally, it communicates with the fleetd daemon using a JSON-based API on top of HTTP, which may also be used directly. When used locally on a cluster member, fleetctl communicates with the local fleetd instance over a Unix domain socket; when used from an external host, SSH tunneling is used with authentication provided through public SSH keys.[31][32][33][34][35]
All of the above mentioned daemons and command-line utilities (etcd, etcdctl, fleetd and fleetctl) are written in the Go language and distributed under the terms of the Apache License 2.0.[5][36]
Deployment
When running on dedicated hardware, CoreOS can be either permanently installed to local storage, such as a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD),[37] or booted remotely over a network using Preboot Execution Environment (PXE) in general, or iPXE as one of its implementations.[38][39] CoreOS also supports deployments on various hardware virtualization platforms, including Amazon EC2, DigitalOcean, Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure, OpenStack, QEMU/KVM, Vagrant and VMware.[9][40][41][42]
CoreOS can also be deployed through its commercial distribution called Tectonic, which additionally integrates Google's Kubernetes as a cluster management utility. As of April 2015, Tectonic is planned to be offered as beta software to select customers.[43][44]
See also
- Application virtualization – software technology that encapsulates application software from the operating system on which it is executed
- Comparison of application virtualization software – various portable and scripting language virtual machines
- Comparison of platform virtualization software – various emulators and hypervisors, which emulate the whole physical computers
- LXC (Linux Containers) – an environment for running multiple isolated Linux systems (containers) on a single Linux control host
- Operating-system-level virtualization implementations – based on operating system kernel's support for multiple isolated userspace instances
- Software as a service (SaaS) – a software licensing and delivery model that hosts the software centrally and licenses it on a subscription basis
- Virtualization – a general concept of providing virtual versions of computer hardware platforms, operating systems, storage devices, etc.
References
- ↑ "coreos/manifest: Release v94.0.0 (CoreOS v94.0.0)". github.com. October 3, 2013. Retrieved September 22, 2014.
- ↑ "coreos/manifest: Release v660.0.0 (CoreOS v660.0.0)". github.com. April 22, 2015. Retrieved April 29, 2015.
- ↑ "coreos/manifest: Release v659.0.0 (CoreOS v659.0.0)". github.com. April 21, 2015. Retrieved April 29, 2015.
- ↑ "CoreOS Pilot Agreement". coreos.com. March 13, 2014. Retrieved March 26, 2014.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "coreos/etcd: etcd/LICENSE at master". github.com. July 31, 2013. Retrieved March 26, 2014.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Libby Clark (September 9, 2013). "Brandon Philips: How the CoreOS Linux Distro Uses Cgroups". Linux.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Cade Metz (August 21, 2013). "Linux Hackers Rebuild Internet From Silicon Valley Garage". Wired. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "CoreOS – a new approach to Linux-based server systems". itnews2day.com. August 22, 2013. Retrieved March 26, 2014.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 "CoreOS documentation: Using CoreOS". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ Brian Harrington (July 8, 2014). "CoreOS: Anatomy of a CoreOS update". youtube.com. Rackspace. Retrieved July 25, 2014.
- ↑ Alex Polvi (July 25, 2014). "CoreOS Stable Release". coreos.com. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS Release Notes". coreos.com. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ↑ Blake Mizerany (April 14, 2014). "etcd – The Road to 1.0". coreos.com. Retrieved August 28, 2014.
- ↑ "Docker 0.9: Introducing execution drivers and libcontainer". docker.com. March 10, 2014. Retrieved January 20, 2015.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Using docker with CoreOS". coreos.com. Retrieved January 20, 2015.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Using systemd with CoreOS". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "CoreOS documentation: Updates & patches". coreos.com. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Adding disk space to your CoreOS machine". coreos.com. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ↑ Alex Polvi (March 27, 2014). "Major Update: btrfs, Docker 0.9, add users, writable /etc, and more!". coreos.com. Retrieved February 27, 2015.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Update strategies". coreos.com. Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ↑ "coreos/locksmith: locksmith/README.md at master". github.com. February 1, 2015. Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ↑ "coreos/locksmith: locksmith/LICENSE at master". github.com. January 19, 2014. Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ↑ "Omaha – software installer and auto-updater for Windows". code.google.com. Retrieved October 11, 2014.
- ↑ "Omaha Overview". omaha.googlecode.com. September 23, 2009. Retrieved October 11, 2014.
- ↑ "Package omaha". godoc.org. June 24, 2014. Retrieved July 4, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: CoreUpdate". coreos.com. Retrieved July 4, 2014.
- ↑ Mark Moudy (May 16, 2014). "CoreOS + Docker Development Environment Demo". github.com. Retrieved April 16, 2015.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Using etcd with CoreOS". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Getting started with etcd". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ Brandon Philips (January 15, 2014). "etcd @ GoSF". speakerdeck.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Launching containers with fleet". coreos.com. Retrieved April 3, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Using the client". coreos.com. Retrieved April 3, 2014.
- ↑ "coreos/fleet: fleet/README.md at master". github.com. February 18, 2014. Retrieved April 3, 2014.
- ↑ "coreos/fleet: fleet/Documentation/deployment-and-configuration.md at master (Deploying fleet)". github.com. April 14, 2015. Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ↑ "coreos/fleet: fleet/Documentation/api-v1.md (fleet API v1)". github.com. October 29, 2014. Retrieved April 17, 2015.
- ↑ "coreos/fleet: fleet/LICENSE at master". github.com. February 6, 2014. Retrieved April 3, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Installing CoreOS to disk". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Booting CoreOS via PXE". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ "CoreOS documentation: Booting CoreOS via iPXE". coreos.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ↑ Alex Crawford (September 5, 2014). "CoreOS Image Now Available On DigitalOcean". coreos.com. Retrieved September 5, 2014.
- ↑ Jack Clark (May 23, 2014). "Google brings futuristic Linux software CoreOS onto its cloud". The Register. Retrieved May 26, 2014.
- ↑ Alex Crawford (October 20, 2014). "CoreOS Now Available On Microsoft Azure". coreos.com. Retrieved October 22, 2014.
- ↑ Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols (April 6, 2015). "CoreOS is bringing Google's Kubernetes to the enterprise". ZDNet. Retrieved April 29, 2015.
- ↑ Ben Kepes (April 6, 2015). "CoreOS And Google Make Their Defensive Plays, Is Docker The Victim?". Forbes. Retrieved April 29, 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to CoreOS. |
- Official CoreOS and Tectonic websites
- CoreOS at DistroWatch
- First glimpse at CoreOS, September 3, 2013, by Sébastien Han
- CoreOS: Linux for the cloud and the datacenter, ZDNet, July 2, 2014, by Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols
- What's CoreOS? An existential threat to Linux vendors, InfoWorld, October 9, 2014, by Matt Asay
- CoreOS fleet architecture, August 26, 2014, by Brian Waldon et al.
- CoreOS is building a container runtime, Rocket, December 1, 2014, by Alex Polvi
- Running CoreOS on Google Compute Engine, May 23, 2014
- CoreOS moves from Btrfs to Ext4 + OverlayFS, Phoronix, January 18, 2015, by Michael Larabel
- CoreOS, etcd and fleet source code on GitHub
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||