Copper Island
| Copper Island | |
| Kuparisaari | |
| Region | |
| Official name: Northern Keweenaw Peninsula | |
| Country | United States |
|---|---|
| State | Michigan |
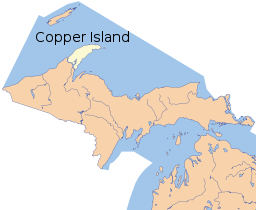 Copper Island is on Lake Superior, separated from the rest of the Keweenaw Peninsula by Portage Lake and the Keweenaw Waterway
| |
Copper Island is a local name given to the northern part of the Keweenaw Peninsula (projecting northeastward into Lake Superior at the western end of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, United States of America), separated from the rest of the Keweenaw Peninsula by Portage Lake and the Keweenaw Waterway.[1]
Geography
The area was "isolated" by dredging in 1859 and construction in the 1860s of a ship canal across an isthmus of the Keweenaw Peninsula from Portage Lake—on the east side of the Keweenaw Peninsula—to Lake Superior on the west. The ship canal is 100 feet (30 m) wide and 21 feet (6.4 m) deep. The resulting "island" was called Kuparisaari (meaning "Copper Island") by Finnish,[2] Irish,[3] and French/French Canadian[4] settlers in the area. However, neither the United States Geological Survey nor the state of Michigan identify this area as an island or use this name. Isle Royale is the largest naturally isolated island in Lake Superior; considered as an island, Copper Island would be the largest, with an area of around 554 square miles. It has a population around 21,500.
History
Historically, "Kuparisaari" ('Copper Island') was used to mean the Keweenaw north of Portage Lake, but more generically the copper country of the Upper Peninsula. Inhabitants of the area wryly claimed "that they were outside the American mainland. In practical usage, however, the term included towns such as Oskar, Atlantic, Baltic, South Range, Houghton, Dodgeville and Hurontown" all of which were south of Portage Lake. Nevertheless, "unquestionably" Finns in those locales considered themselves to be "Copper Islanders."[5] As the foregoing source indicates, "Copper Island" has sometimes been used as a sobriquet for Michigan's "copper country."
But in a larger sense, "Kuparisaari" was an amalgam of geographic location and cultural identity, particularly for the Finns. As one scholarly source notes:
Finnish immigration to Michigan’s copper district grew to become the most populous ethnic group with an enduring cultural identity. Kuparisaari, “copper island,” went beyond the Finnish immigrant identification of the island that comprises the northern half of the Keweenaw Peninsula to a symbolic island of landing, an Ellis Island. Michigan’s Copper Country is recognized as focal to Finnish immigration to America, the birthplace of many Finnish-American institutions religious, political and educational. This “island” includes both settlements in growing industrial urban communities like the Quincy, Calumet & Hecla and Champion mining {See, Copper Range Company} settlements, and cleared forestland for traditional Finnish agriculture as in Toivola, Tapiola, Elo, Pelkie, and Waasa; Finns settled north and south of the Portage Waterway that bisects the peninsula. Perhaps more than any other immigrant group, the Finnish communities in the district were bisected into divisions of politics and faith. The Finns who immigrated to the copper mining district held to a pietistic Laestadian (Apostolic) Lutheran belief, to the state-sanctioned Lutheranism of Finland (Suomi Synod) or rejected faith altogether. Within these divides of conscience of faith was a wide political spectrum: conservative to liberal adherents, resolute temperance advocates and active radical socialists. The social and economic conditions that emigrants left in northern Scandinavia and the Duchy of Finland influenced these allegiances and beliefs.[6]
Communities and transportation
The principal towns on the Copper Island end of Keweenaw Peninsula are Hancock and Calumet. The area is connected to the rest of the Upper Peninsula by the Portage Lake Lift Bridge, the latest in a series of bridges between Hancock and Houghton. The bridge crosses the Portage Canal.
US 41 crosses this bridge. It enters Michigan at Menominee and goes north to it terminus just east of Copper Harbor at the far eastern tip of the peninsula.[7]
Modern usage of the name
A newspaper named Copper Island News was formerly published in Hancock, at least in the 1880s.[8] and an unrelated newspaper called the Copper Island Sentinel was published weekly in Calumet from 4 April 1978 to August 1986.[9][10]
Copper island is the core that the Keweenaw Water Trail wraps around. It is a designated loop route (which eliminates any need to use a shuttle or spot two vehicles) around and through the Keweenaw Peninsula for canoes and sea kayaks. The Keweenaw Waterway is central to it, crossing the peninsula.[11] Established in 1995, it was designated “A Superior Sports Port” by National Geographic Adventure Magazine. The trail "exemplifies the Keweenaw Peninsula in the most literal sense." The Lake Superior coast line—craggy, varied and forbidding—is claimed to be comparable to Isle Royale (sans the ferry). Uninhabited wilderness, parks, and nature preserves and parks offer counterpoint to sheltered harbors and towns, where paddlers find the option of civilization, including warm bed, hot meal and shower. The Copper Island grand tour takes an 'average paddler' six to eight days, but extra days should be planned "to compensate for being wind-bound." This circumnavigation is on its way to becoming "Michigan’s top paddling destination." Shorter trips are possible.[12]
The 'Copper Island Classic' is an ice hockey tournament contested annually between Hancock Central High School and Calumet High School.[13] Such local usage still persists, and there are many business in the area that use it.[14]
The Race for Copper Island (New York: Benziger Bros., 1905) is a novel written by Henry Sanislaus Spaulding (1865–1934) that involves the area.[15]
Alternate use
The phrase "Copper Island" was also used, especially in the 18th century, to describe a possibly mythical island in Lake Superior where there is an abundance of copper sitting on the surface of the land. While some scholars believe this was a reference to Isle Royale, the "island," because of its abundance of copper, could also have been the northern Keweenaw Peninsula.,[16] especially given the presence of vast quantities of native copper in the region.
See also
References
- ↑ Holmio, Armas K. E.; Ryynanen, Ellen M. (2001). History of the Finns in Michigan. Wayne State University Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-8143-2974-0. Retrieved 2008-09-24. See also, Portage Canal.
- ↑ Michigan Technical University, Kupperisian "Copper Island".
- ↑ New York University, From the Emerald Isle to the Copper Isle.
- ↑ DuLong,John P., Ph.D., French-Canadian Genealogical Research in Houghton County, Michigan: Tracing French Canadians in Michigan's Copper Country
- ↑ Holmio, Armas K. E.; Ryynanen, Ellen M. (2001). History of the Finns in Michigan. Wayne State University Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-8143-2974-0. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ↑ An Interior Ellis Island: Ethnic Diversity and the Peopling of Michigan’s Copper Country, Keweenaw Ethnic Groups -- The Finns. MTU Archives and Copper Country Historical Collection, J. Robert Van Pelt Library, Michigan Technological University.
- ↑ UP Transit: Find your way in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, USA
- ↑ Thurner, Arthur W. Strangers and Sojourners: A History of Michigan's Keweenaw Peninsula (Detroit, Michigan: Wayne State University Press, 1995) 408 pages, p. 359. ISBN 0-8143-2396-0, ISBN 978-0-8143-2396-0
- ↑ DuLong,John P., Ph.D., French-Canadian Genealogical Research in Houghton County, Michigan: Tracing French Canadians in Michigan's Copper Country.
- ↑ "Newspapers on Microfilm - Alphabetical by City". MTU Archives & Copper Country Historical Collections. Michigan Technological University. Retrieved 2008-09-24.
- ↑ Keweenaw Water Trail Society.
- ↑ "Keweenaw Water Trail". Keweenaw Convention & Visitors Bureau. 2008. Retrieved 2008-09-24.
- ↑ Copper Island Classic.
- ↑ See, e.g. Copper Island Cross Country Ski Club. and Michigan Association of Recreational Vehicles.
- ↑ Beasicker, Robert, Michigan in the Novel (1826-1996), An Annotated Bibliography (1996).
- ↑ The WPA Guide to Minnesota, p. 282.
Further reading
- An Interior Ellis Island: Ethnic Diversity and the Peopling of Michigan’s Copper Country, Keweenaw Ethnic Groups -- The Finns. MTU Archives and Copper Country Historical Collection, J. Robert Van Pelt Library, Michigan Technological University.
- Burt, Williams A., and Hubbard, Bela Reports on the Mineral Region of Lake Superior (Buffalo: L. Danforth, 1846), 113 pages.
- Thurner, Arthur W. Strangers and Sojourners - A History of Michigan's Keweenaw Peninsula (Detroit, Michigan, U.S.A.: Wayne State University Press, 1994) ISBN 0-8143-2396-0.
External links
- Exploring Houghton and Hancock in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
- In-group Finnish Place Names - Michigan
- Keweenaw Ethnic Groups - MTU Archives and Copper Country Historical Collections, J. Robert Van Pelt Library
- History of the Finns in Michigan, p76 ISBN 978-0-8143-2974-0
Coordinates: 46°19′05″N 83°58′04″W / 46.31800°N 83.96788°W