Conway notation (knot theory)
In knot theory, Conway notation, invented by John Horton Conway, is a way of describing knots that makes many of their properties clear. It composes a knot using certain operations on tangles to construct it.
Basic concepts
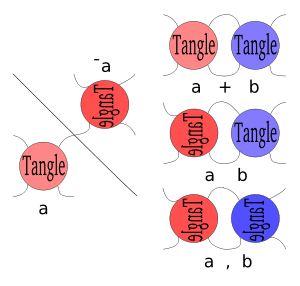
Tangles
In Conway notation, the tangles are generally algebraic 2-tangles. This means their tangle diagrams consist of 2 arcs and 4 points on the edge of the diagram; furthermore, they are built up from rational tangles using the Conway operations.
[The following seems to be attempting to describe only integer or 1/n rational tangles] Tangles consisting only of positive crossings are denoted by the number of crossings, or if there are only negative crossings it is denoted by a negative number. If the arcs are not crossed, or can be transformed to into an uncrossed position with the Reidemeister moves, it is called the 0 or ∞ tangle, depending on the orientation of the tangle.
Operations on tangles
If a tangle, a, is reflected on the NW-SE line, it is denoted by −a. (Note that this is different from a tangle with a negative number of crossings.)Tangles have three binary operations, sum, product, and ramification,[1] however all can be explained using tangle addition and negation. The tangle product, a b, is equivalent to −a+b. and ramification or a,b, is equivalent to −a+−b.
Advanced concepts
Rational tangles are equivalent if and only if their fractions are equal. An accessible proof of this fact is given in (Kauffman and Lambropoulou 2004). A number before an asterisk, *, denotes the polyhedron number; multiple asterisks indicate that multiple polyhedra of that number exist. [2]
See also
- Dowker notation
- Alexander–Briggs notation
References
- ↑ "Conway notation", mi.sanu.ac.rs.
- ↑ "Conway_Notation", The Knot Atlas.
Further reading
- Conway, J. H. "An Enumeration of Knots and Links, and Some of Their Algebraic Properties." In J. Leech (editor), Computational Problems in Abstract Algebra. Oxford, England. Pergamon Press, pp. 329-358, 1970. pdf available online
- Louis H. Kauffman, Sofia Lambropoulou: On the classification of rational tangles. Advances in Applied Mathematics, 33, No. 2 (2004), 199-237. preprint available at arxiv.org.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||