Conus ermineus
| Conus ermineus | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Apertural and abapertural views of shell of Conus ermineus Born, I. von, 1778 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| (unranked): | clade Caenogastropoda clade Hypsogastropoda clade Neogastropoda |
| Superfamily: | Conoidea |
| Family: | Conidae |
| Subfamily: | Coninae |
| Genus: | Conus |
| Species: | C. ermineus |
| Binomial name | |
| Conus ermineus Born, 1778  Conus ermineus Born, I. von, 1778 | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Conus aspersus G. B. Sowerby II, 1833 | |
Conus ermineus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Conidae, the cone snails and their allies.[1]
Like all species within the genus Conus, these snails are predatory and venomous. They are capable of "stinging" humans, therefore live ones should be handled carefully or not at all.
Description
The maximum recorded shell length is 103 mm.[2]
Conantokin-E is a toxin derived from the venom of Conus ermineus.
It is a fishing eating species. Utilizes specialized hollow harpoon like radula tooth to harpoon small fish and paralyze them with venom to facilitate swallowing.
Habitat
Minimum recorded depth is 0 m.[2] Maximum recorded depth is 101 m.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Conus ermineus Born, 1778. Retrieved through: World Register of Marine Species on 27 March 2010.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Welch J. J. (2010). "The "Island Rule" and Deep-Sea Gastropods: Re-Examining the Evidence". PLoS ONE 5(1): e8776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008776.
Gallery
-
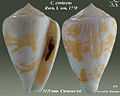
Conus ermineus Born, I. von, 1778
-

Conus ermineus Born, I. von, 1778
-

Conus ermineus Born, I. von, 1778