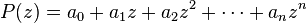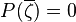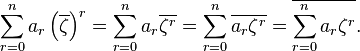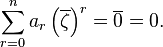Complex conjugate root theorem
In mathematics, the complex conjugate root theorem states that if P is a polynomial in one variable with real coefficients, and a + bi is a root of P with a and b real numbers, then its complex conjugate a − bi is also a root of P.[1]
It follows from this (and the fundamental theorem of algebra), that if the degree of a real polynomial is odd, it must have at least one real root.[2] That fact can also be proven by using the intermediate value theorem.
Examples and consequences
- The polynomial x2 + 1 = 0 has roots ±i.
- Any real square matrix of odd degree has at least one real eigenvalue. For example, if the matrix is orthogonal, then 1 or −1 is an eigenvalue.
- The polynomial
- has roots
- and thus can be factored as
- In computing the product of the last two factors, the imaginary parts cancel, and we get
- The non-real factors come in pairs which when multiplied give quadratic polynomials with real coefficients. Since every polynomial with complex coefficients can be factored into 1st-degree factors (that is one way of stating the fundamental theorem of algebra), it follows that every polynomial with real coefficients can be factored into factors of degree no higher than 2: just 1st-degree and quadratic factors.
Corollary on odd-degree polynomials
It follows from the present theorem and the fundamental theorem of algebra that if the degree of a real polynomial is odd, it must have at least one real root.[2]
This can be proved as follows.
- Since non-real complex roots come in conjugate pairs, there are an even number of them;
- But a polynomial of odd degree has an odd number of roots;
- Therefore some of them must be real.
This requires some care in the presence of multiple roots; but a complex root and its conjugate do have the same multiplicity (and this lemma is not hard to prove). It can also be worked around by considering only irreducible polynomials; any real polynomial of odd degree must have an irreducible factor of odd degree, which (having no multiple roots) must have a real root by the reasoning above.
This corollary can also be proved directly by using the intermediate value theorem.
Simple proof
One proof of the theorem is as follows:[2]
Consider the polynomial
where all ar are real. Suppose some complex number ζ is a root of P, that is P(ζ) = 0. It needs to be shown that
as well.
If P(ζ) = 0, then
which can be put as
Now
and given the properties of complex conjugation,
Since,
it follows that
That is,
Notes
- ↑ Anthony G. O'Farell and Gary McGuire (2002). "Complex numbers, 8.4.2 Complex roots of real polynomials". Maynooth Mathematical Olympiad Manual. Logic Press. p. 104. ISBN 0954426908. Preview available at Google books
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Alan Jeffrey (2005). "Analytic Functions". Complex Analysis and Applications. CRC Press. pp. 22–23. ISBN 158488553X.