Combinatory categorial grammar
Combinatory categorial grammar (CCG) is an efficiently parsable, yet linguistically expressive grammar formalism. It has a transparent interface between surface syntax and underlying semantic representation, including predicate-argument structure, quantification and information structure. The formalism generates constituency-based structures (as opposed to dependency-based ones) and is therefore a type of phrase structure grammar (as opposed to a dependency grammar).
CCG relies on combinatory logic, which has the same expressive power as the lambda calculus, but builds its expressions differently. The first linguistic and psycholinguistic arguments for basing the grammar on combinators were put forth by Steedman and Szabolcsi. More recent prominent proponents of the approach are Jacobson and Baldridge.
For example, the combinator B (the compositor) is useful in creating long-distance dependencies, as in "Who do you think Mary is talking about?" and the combinator W (the duplicator) is useful as the lexical interpretation of reflexive pronouns, as in "Mary talks about herself". Together with I (the identity mapping) and C (the permutator) these form a set of primitive, non-interdefinable combinators. Jacobson interprets personal pronouns as the combinator I, and their binding is aided by a complex combinator Z, as in "Mary lost her way". Z is definable using W and B.
Parts of the Formalism
The CCG formalism defines a number of combinators (application, composition, and type-raising being the most common). These operate on syntactically-typed lexical items, by means of Natural deduction style proofs. The goal of the proof is to find some way of applying the combinators to a sequence of lexical items until no lexical item is unused in the proof. The resulting type after the proof is complete is the type of the whole expression. Thus, proving that some sequence of words is a sentence of some language amounts to proving that the words reduce to the type S.
Syntactic Types
The syntactic type of a lexical item can be either a primitive type, such as S, N, or NP, or complex, such as S\NP, or NP/N.
The complex types, schematizable as X/Y and X\Y, denote functor types that take an argument of type Y and return an object of type X. A forward slash denotes that the argument should appear to the right, while a backslash denotes that the argument should appear on the left. Any type can stand in for the X and Y here, making syntactic types in CCG a recursive type system.
Application Combinators
The application combinators, often denoted by > for forward application and < for backward application, apply a lexical item with a functor type to an argument with an appropriate type. The definition of application is given as:

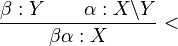
Composition Combinators
The composition combinators, often denoted by 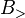 for forward composition and
for forward composition and 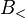 for backward composition, are similar to function composition from mathematics, and can be defined as follows:
for backward composition, are similar to function composition from mathematics, and can be defined as follows:
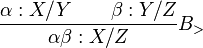
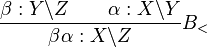
Type-raising Combinators
The type-raising combinators, often denoted as 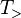 for forward type-raising and
for forward type-raising and 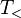 for backward type-raising, take argument types (usually primitive types) to functor types, which take as their argument the functors that, before type-raising, would have taken them as arguments.
for backward type-raising, take argument types (usually primitive types) to functor types, which take as their argument the functors that, before type-raising, would have taken them as arguments.
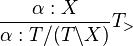
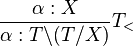
Example
The sentence "the dog bit John" has a number of different possible proofs. Below are a few of them. The variety of proofs demonstrates the fact that in CCG, sentences don't have a single structure, as in other models of grammar.
Let the types of these lexical items be
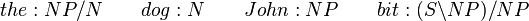
We can perform the simplest proof (changing notation slightly for brevity) as:
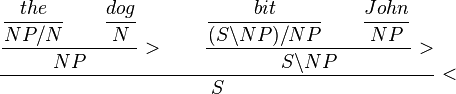
Opting to type-raise and compose some, we could get a fully incremental, left-to-right proof. The ability to construct such a proof is an argument for the psycholinguistic plausibility of CCG, because listeners do in fact construct partial interpretations (syntactic and semantic) of utterances before they have been completed.
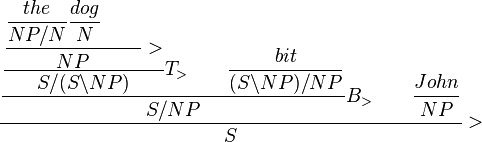
Formal properties
CCGs are known to be able to generate the language 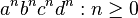 (which is an indexed language). Examples of this are unfortunately too complicated to provide here, but can be found in Vijay-Shanker and Weir (1994).[1]
(which is an indexed language). Examples of this are unfortunately too complicated to provide here, but can be found in Vijay-Shanker and Weir (1994).[1]
Equivalencies
Vijay-Shanker and Weir (1994)[1] demonstrates that Linear Indexed Grammars, Combinatory Categorial Grammars, Tree-adjoining Grammars, and Head Grammars are weakly equivalent formalisms, in that they all define the same string languages.
See also
References
- Baldridge, Jason (2002), "Lexically Specified Derivational Control in Combinatory Categorial Grammar." PhD Dissertation. Univ. of Edinburgh.
- Curry, Haskell B. and Richard Feys (1958), Combinatory Logic, Vol. 1. North-Holland.
- Jacobson, Pauline (1999), “Towards a variable-free semantics.” Linguistics and Philosophy 22, 1999. 117–184
- Steedman, Mark (1987), “Combinatory grammars and parasitic gaps”. Natural Language and Linguistic Theory 5, 403–439.
- Steedman, Mark (1996), Surface Structure and Interpretation. The MIT Press.
- Steedman, Mark (2000), The Syntactic Process. The MIT Press.
- Szabolcsi, Anna (1989), "Bound variables in syntax (are there any?)." Semantics and Contextual Expression, ed. by Bartsch, van Benthem, and van Emde Boas. Foris, 294–318.
- Szabolcsi, Anna (1992), "Combinatory grammar and projection from the lexicon." Lexical Matters. CSLI Lecture Notes 24, ed. by Sag and Szabolcsi. Stanford, CSLI Publications. 241–269.
- Szabolcsi, Anna (2003), “Binding on the fly: Cross-sentential anaphora in variable-free semantics”. Resource Sensitivity in Binding and Anaphora, ed. by Kruijff and Oehrle. Kluwer, 215–229.
Further reading
- Michael Moortgat, Categorial Type Logics, Chapter Two in J. van Benthem and A. ter Meulen (eds.) Handbook of Logic and Language. Elsevier, 1997, ISBN 0-262-22053-9
- http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/steedman/papers/ccg/SteedmanBaldridgeNTSyntax.pdf
External links
- The Combinatory Categorial Grammar Site
- The ACL CCG wiki page (likely to be more up-to-date than this one)