Collinsite
| Collinsite | |
|---|---|
|
Crystals of collinsite from the Rapid Creek area of northern Yukon, Canada | |
| General | |
| Category | Phosphate mineral |
| Formula (repeating unit) | Ca2(Mg,Fe2+)(PO4)2·2H2O |
| Strunz classification | 08.CG.05 |
| Dana classification | 40.2.2.3 |
| Crystal symmetry |
Pinacoidal H-M group: 1 Space group: P1 |
| Unit cell |
a = 5.734(1) Å b = 6.780(1) Å c = 5.441(1) Å α = 97.29° β = 108.56° γ = 107.28° Z = 1[1] |
| Identification | |
| Crystal system | Triclinic |
| Cleavage | Fair on {001} and {010} |
| Tenacity | Brittle[1] |
| Mohs scale hardness | 3 to 3.5 |
| Luster | Subvitreous, silky if fibrous[1] |
| Streak | White[1] |
| Diaphaneity | Translucent |
| Specific gravity | 2.99 |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (+) |
| Refractive index |
nα = 1.632 nβ = 1.642 nγ = 1.657 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.025 |
| 2V angle | 80° (measured) |
| Dispersion | r < v strong |
| Ultraviolet fluorescence | Non-fluorescent[2] |
| Solubility | Readily soluble in acids |
| References | [3] |
Collinsite is a mineral with formula Ca2(Mg,Fe2+)(PO4)2·2H2O. It was discovered in British Columbia, Canada, and formally described in 1927. It was named in honor of William Henry Collins (1878–1937), director of the Geological Survey of Canada. There are three varieties of the mineral: magnesian collinsite, zincian collinsite, and strontian collinsite. The crystal structure consists of polyhedral chains linked by weak hydrogen bonds.
Description

Collinsite is translucent and brown, chocolate-black, light brown, yellowish white, white, or colorless.[1] It is colorless in thin section[1] and light yellow-brown to colorless in transmitted light.[3] The zincian variety of collinsite is pale blue.[1] The mineral can occur with fibrous habit, as globular aggregates of crystals, as concentrically layered botryoidal masses, or as bladed or prismatic crystals up to 2 cm (0.79 in).[1]
Collinsite is a member of the fairfieldite group.[1] Hillite is the zinc analogue of collinsite[4] and collinsite is the magnesium analogue of messelite[5]
Varieties
There are three varieties of collinsite:
- magnesian collinsite, Ca2Mg(PO4)2·2H2O[6]
- zincian collinsite, Ca2(Mg,Zn2+)(PO4)2·2H2O[7]
- strontian collinsite, (Ca,Sr)2(Mg,Fe2+)(PO4)2·2H2O[7]
Magnesian collinsite was described from South Dakota in 1972,[6] zincian collinsite was described from South Australia in 1973,[8] and strontian collinsite was described from Russia as early as 1965.[9] The replacement of calcium by strontium that occurs in strontian collinsite is atypical of collinsite.[10]
Structure
The crystal structure of collinsite was determined using essentially pure magnesian collinsite, Ca2Mg(PO4)2·2H2O, and published in 1974.[11] It consists of chains of corner-sharing (MgΦ6) octahedra and (PO4) tetrahedra. Four of the Mg ligands link to (PO4) groups and the other two to water molecules. Two of the ligands in the (PO4) group link to (MgΦ6) octahedra and the other two link to calcium atoms and act as hydrogen bond acceptors. Weak hydrogen bonds link chains together and force separation between them.[12] The separation gives room for interstitial, eight-coordinated calcium between chains.[12][13]
History
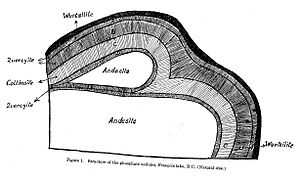
Collinsite was discovered prior to 1927 near François Lake, British Columbia.[14] In a 4-to-12-inch-wide vein (10 to 30 cm), phosphorite nodules were discovered that consisted of a fragment of andesite enclosed by concentric layers of phosphate minerals coated in wurtzilite.[14] The phosphate layers were composed of a mineral named quercyite (since determined to be improperly classified)[15] and the new mineral collinsite.[16] The François Lake collinsite was light-brown and consisted of sub-centimeter blades.[16]
Collinsite was named in honor of William Henry Collins (1878–1937) who, at the time, was director of the Geological Survey of Canada.[3][16] The mineral was described by Eugene Poitevin in 1927 in a publication of the Geological Survey.[17] With the analysis performed by E. A. Thompson, Poitevin identified the formula as Ca2(Mg,Fe2+)(PO4)2·2½H2O.[18] Since no crystals of collinsite were found, the only crystallographic information determined was the angle between cleavages.[19]
In 1940, C. W. Wolfe reexamined the mineral species.[19] With analysis performed by F. A. Gonyer, Wolfe identified the formula of collinsite was Ca2(Mg,Fe2+)(PO4)2·2H2O, containing less water than Poitevin indicated.[18] Wolfe also questioned the four cleavages found by Poitevin, since he could identify only two fair cleavages from six fibrous crystals.[19]
When the IMA was founded, messelite was grandfathered as a valid mineral species.[3]
Occurrence
Collinsite has been found in Australia, Austria, Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Germany, Namibia, Norway, Romania, Russia, South Africa, Spain, and the United States.[3] The mineral formed as an incrustation of other minerals by weathering. It occurs in association with bitumen, bobierrite, carbonate rich fluoroapatite, cryptomelane, dolomite, Fe–Mn oxides, kovdorskite, parahopeite, and scholzite.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Anthony, John W.; Bideaux, Richard A.; Bladh, Kenneth W.; Nichols, Monte C. (eds.). "Collinsite". Handbook of Mineralogy. Chantilly, VA: Mineralogical Society of America.
- ↑ "Collinsite". Webmineral. Retrieved August 9, 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "Collinsite". Mindat. Retrieved August 8, 2012.
- ↑ Yakubovich et al. 2003, p. 981
- ↑ Foshag 1928, p. 202
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Bridge & Pryce 1974, p. 579
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Yakubovich et al. 2003, p. 227
- ↑ Bridge & Pryce 1974, p. 577
- ↑ Liferovich et al. 2001, p. 1082
- ↑ Yakubovich et al. 2003, p. 226
- ↑ Brotherton et al. 1974, p. 653
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Hawthorne 1998, p. 162
- ↑ Brotherton et al. 1974, p. 655
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Poitevin 1927, pp. 2–4
- ↑ "Quercyite". Mindat. Retrieved August 9, 2012.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Poitevin 1927, p. 5
- ↑ Poitevin 1927, p. 2
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Wolfe 1940, p. 747
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Wolfe 1940, p. 746
- Bibliography
- Bridge, P. J.; Pryce, M. W. (March 1974). "Magnesian collinsite from Milgun Station, Western Australia" (PDF). Mineralogical Magazine 39 (305): 557–559. doi:10.1180/minmag.1974.039.305.11.
- Brotherton, P. D.; Maslen, E. N.; Pryce, M. W.; White, A. H. (1974). "Crystal Structure of Collinsite". Australian Journal of Chemistry 27 (3): 653–656. doi:10.1071/CH9740653. (subscription required)
- Foshag, W. F. (May 1928). "New Mineral Names: Collinsite" (PDF). American Mineralogist 13 (5): 201–202.
- Hawthorne, Frank C. (April 1998). "Structure and chemistry of phosphate minerals" (PDF). Mineralogical Magazine 62 (2): 141–164. doi:10.1180/002646198547512.
- Liferovich, Ruslan P.; Pakhomovsky, Yakov A.; Bogdanova, Alla N.; Balaganskaya, Elena G.; Laajoki, Kauko V.O.; Gehör, Seppo; Chukanov, Nikita V. (August 2001). "Collinsite in hydrothermal assemblages related to carbonatites in the Kovdor Complex, northwestern Russia" (PDF). The Canadian Mineralogist 39 (4): 1081–1094. doi:10.2113/gscanmin.39.4.1081.
- Poitevin, Eugene (July 21, 1927). "A new Canadian occurrence of phosphorite from near Francois Lake, British Columbia" (PDF). Bulletin (Canada Department of Mines, Geological Survey) 46: 2–12.
- Wolfe, C. W. (December 1940). "Classification of minerals of the type A3(XO4)2·nH2O" (PDF). American Mineralogist 25 (12): 738–753.
- Yakubovich, Olga V.; Kabalov, Yu K.; Gavrilenko, Polina G.; Liferovich, Ruslan P.; Massa, Werner (2003). "Strontium in the Collinsite Structure: Rietveld Refinement". Crystallography Reports 48 (2): 226–232. doi:10.1134/1.1564200. (subscription required)
- Yakubovich, Olga V.; Massa, Werner; Liferovich, Ruslan P.; Gavrilenko, Polina G.; Bogdanova, Alla N.; Tuisku, Pekka (2003). "Hillite, a new member of the fairfieldite group: its description and crystal structure" (PDF). The Canadian Mineralogist 41: 981–988. doi:10.2113/gscanmin.41.4.981.
Further reading
- Herwig, Sasha; Hawthorne, Frank C. (October 2006). "The topology of hydrogen bonding in brandtite, collinsite and fairfieldite" (PDF). The Canadian Mineralogist 44 (5): 1181–1196. doi:10.2113/gscanmin.44.5.1181.
- Hill, R. J.; Milnes, A. R. (June 1974). "Phosphate minerals from Reaphook Hill, Flinders Ranges, South Australia" (PDF). Mineralogical Magazine 39 (306): 684–695. doi:10.1180/minmag.1974.039.306.06.
External links
![]() Media related to collinsite at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to collinsite at Wikimedia Commons
