Close front unrounded vowel
| Close front unrounded vowel |
|---|
| i |
|---|
| IPA number |
301 |
|---|
| Encoding |
|---|
| Entity (decimal) |
i |
|---|
| Unicode (hex) |
U+0069 |
|---|
| X-SAMPA |
i |
|---|
| Kirshenbaum |
i |
|---|
| Braille |
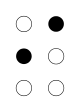 |
|---|
| Sound |
|---|
|
source · help |
The close front unrounded vowel, or high front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound that occurs in many spoken languages, represented in the International Phonetic Alphabet by the symbol i. It is similar to the vowel sound in the English word meet—and often called long-e in American English[1]—although in English this sound has additional length (usually being represented as /iː/) and is not normally pronounced as a pure vowel (it is a slight diphthong) – a purer [i] sound is heard in many other languages, such as French, in words like chic.
The close front unrounded vowel is the vocalic equivalent of the palatal approximant [j]. The two are almost identical featurally. They alternate with each other in certain languages, such as French, and in the diphthongs of some languages, [i̯] with the non-syllabic diacritic and [j] are used in different transcription systems to represent the same sound.
Languages that use the Latin script commonly use the letter ⟨i⟩ to represent this sound, though there are some exceptions: in English orthography that letter is usually associated with /aɪ/ (as in bite) or /ɪ/ (as in bit), and /iː/ is more commonly represented by ⟨e⟩, ⟨ea⟩, ⟨ee⟩, ⟨ie⟩ or ⟨ei⟩, as in the words scene, bean, meet, niece, conceive. Irish orthography reflects both etymology and whether preceding consonants are broad or slender, so such combinations as ⟨aí⟩, ⟨ei⟩, and ⟨aío⟩ all represent /iː/.
Features
- Its vowel height is close, also known as high, which means the tongue is positioned as close as possible to the roof of the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant.
- Its vowel backness is front, which means the tongue is positioned as far forward as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Note that rounded front vowels are often centralized, which means that often they are in fact near-front.
- It is unrounded, which means that the lips are not rounded.
Occurrence
References
Bibliography
- Allan, Robin; Holmes, Philip; Lundskær-Nielsen, Tom (2000), Danish: An Essential Grammar, London: Routledge, ISBN 0-19-824268-9
- Árnason, Kristján (2011), The Phonology of Icelandic and Faroese, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-922931-4
- Basbøll, Hans (2005), The Phonology of Danish, ISBN 0-203-97876-5
- Carbonell, Joan F.; Llisterri, Joaquim (1992), "Catalan", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 22 (1–2): 53–56, doi:10.1017/S0025100300004618, ISSN 0025-1003
- Cruz-Ferreira, Madalena (1995), "European Portuguese", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 25 (2): 90–94, doi:10.1017/S0025100300005223, ISSN 0025-1003
- Dum-Tragut, Jasmine (2009), Armenian: Modern Eastern Armenian, Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company
-
- Fougeron, Cecile; Smith, Caroline L (1993), "Illustrations of the IPA:French", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 23 (2): 73–76, doi:10.1017/S0025100300004874, ISSN 0025-1003
- Gilles, Peter; Trouvain, Jürgen (2013), "Luxembourgish" (PDF), Journal of the International Phonetic Association 43 (1): 67–74, doi:10.1017/S0025100312000278
- Grønnum, Nina (1998), "Illustrations of the IPA: Danish", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 28 (1 & 2): 99–105, doi:10.1017/s0025100300006290
- Grønnum, Nina (2003), Why are the Danes so hard to understand?
- Grønnum, Nina (2005), Fonetik og fonologi, Almen og Dansk (3rd ed.), Copenhagen: Akademisk Forlag, ISBN 87-500-3865-6
- Gussenhoven, Carlos (1992), "Dutch", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 22 (2): 45–47, doi:10.1017/S002510030000459X, ISSN 0025-1003
- Gussmann, Edmund (2011). "Getting your head around: the vowel system of Modern Icelandic" (PDF). Folia Scandinavica Posnaniensia 12: 71–90. ISBN 978-83-232-2296-5.
- Haugen, Einar (1958). "The Phonemics of Modern Icelandic". Language 34 (1): 55–88. doi:10.2307/411276. JSTOR 411276.
- Iivonen, Antti; Harnud, Huhe (2005), "Acoustical comparison of the monophthong systems in Finnish, Mongolian and Udmurt", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 35 (1): 59–71, doi:10.1017/S002510030500191X, ISSN 0025-1003
- Jassem, Wiktor (2003), "Polish", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 33 (1): 103–107, doi:10.1017/S0025100303001191, ISSN 0025-1003
- Jones, Daniel; Ward, Dennis (1969), The Phonetics of Russian, Cambridge University Press
- Kohler, Klaus J. (1999), "German", Handbook of the International Phonetic Association: A guide to the use of the International Phonetic Alphabet, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 86–89, ISBN 0-521-65236-7
- Ladefoged, Peter; Johnson, Keith (2010), A Course in Phonetics (6th ed.), Boston, Massachusetts: Wadsworth Publishing, ISBN 978-1-4282-3126-9
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-19814-8.
- Mangold, Max (2005), Das Aussprachewörterbuch, Duden, ISBN 9783411040667
- Martínez-Celdrán, Eugenio; Fernández-Planas, Ana Ma.; Carrera-Sabaté, Josefina (2003), "Castilian Spanish", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 33 (2): 255–259, doi:10.1017/S0025100303001373, ISSN 0025-1003
- Merrill, Elizabeth (2008), "Tilquiapan Zapotec", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 38 (1): 107–114, doi:10.1017/S0025100308003344, ISSN 0025-1003
- Okada, Hideo (1991), "Japanese", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 21 (2): 94–96, doi:10.1017/S002510030000445X, ISSN 0025-1003
- Roach, Peter (2004), "British English: Received Pronunciation", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 34 (2): 239–245, doi:10.1017/S0025100304001768, ISSN 0025-1003
- Rogers, Derek; d'Arcangeli, Luciana (2004), "Italian", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 34 (1): 117–121, doi:10.1017/S0025100304001628, ISSN 0025-1003
- Rood, David S; Taylor, Allan R. (1996), "Sketch of Lakhota, a Siouan Language, Part I", Handbook of North American Indians 17: 440–482
- Shosted, Ryan K.; Chikovani, Vakhtang (2006), "Standard Georgian", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 36 (2): 255–264, doi:10.1017/S0025100306002659, ISSN 0025-1003
- Szende, Tamás (1994), "Illustrations of the IPA:Hungarian", Journal of the International Phonetic Alphabet 24 (2): 91–94, doi:10.1017/S0025100300005090, ISSN 0025-1003
- Tingsabadh, M.R. Kalaya; Abramson, Arthur S. (1993), "Thai", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 23 (1): 24–26, doi:10.1017/S0025100300004746, ISSN 0025-1003
- Thelwall, Robin (1990), "Illustrations of the IPA: Arabic", Journal of the International Phonetic Association 20 (2): 37–41, doi:10.1017/S0025100300004266, ISSN 0025-1003
- Traunmüller, Hartmut (1982), "Vokalismus in der westniederösterreichischen Mundart.", Zeitschrift für Dialektologie und Linguistik 2: 289–333, doi:10.1017/S0025100300006290
- Uldall, Hans Jørgen (1933), A Danish Phonetic Reader, The London phonetic readers, London: University of London Press
| |
|---|
| | IPA topics |
|---|
| | IPA | |
|---|
| | Phonetics | |
|---|
| | Special topics | |
|---|
| | Encodings | |
|---|
|
| | | |
|---|
|
| — These tables contain phonetic symbols, which may not display correctly in some browsers. [Help] |
| — Where symbols appear in pairs, left–right represent the voiceless–voiced consonants. |
| — Shaded areas denote pulmonic articulations judged to be impossible. |
| — Symbols marked with an asterisk (*) are not defined in the IPA. |
| | | Chart image |
- Pulmonics
- Non-pulmonics
- Affricates
- Co-articulated
|
|---|
|
| | |
|
