Climate of Egypt

Egypt essentially has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh). The climate is generally extremely dry all over the country except on the northern Mediterranean coast which receives more rainfall in winter. In addition to rarity of rain, extreme heat during summer months is also a general climate feature of Egypt although daytime temperature are obviously more moderated along the northern coast.
The prevailing winds from the Mediterranean Sea continuously blow over the northern coast without the interposition of an eventual mountain range and thus, greatly moderate temperatures throughout the year. Because of this effect, averages low temperature vary from 9.5 °C (49.1 °F) during wintertime to 23 °C (73.4 °F) to summertime and averages high temperatures vary from 17 °C (62.6 °F) during wintertime to 32 °C (89.6 °F) in summertime. Though temperatures are moderated along the coasts, the situation changes very much farther in the interior of the country where the prevailing northerly winds aren't felt anymore. Thus, in the central and the southern parts, daytime temperatures are hotter especially in summers where averages high temperatures easily soar over 40 °C (104 °F) in cities and places such as Aswan, Luxor, Asyut or Sohag which are located in the deserts of Egypt. Some mountainous locations in Sinai, such as Saint Catherine, have cooler night temperatures more than any other location, because of their high elevation.
Every year, sometime from March to May, an extremely hot, dry and dusty wind blows from the south or the southwest. This wind is called khamasīn. When the flow of dry air continuously blows over vast desert regions, it picks up fine sand and dust particles and finally results in a dusty wind which is generally felt in the periphery of the desert. When this wind blows over Egypt, it causes high temperatures to soar temporarily at dangerous levels, usually over 45 °C (113 °F), the relative humidity levels to drop under 5%. The khamasīn causes sudden, early heat waves and the absolute highest temperature records in Egypt.
Egypt receives between 200 mm (7.87 in) and 20 mm (0.79 in) of annual average precipitation along the narrow Mediterranean coast, but south to Cairo, the average drastically drops to reach nearly 0 mm (0.00 in) in the central and the southern part of the country. The cloudiest rainiest places are in and around Alexandria and Rafah. The sunshine duration is also extremely high all over Egypt, ranging from a "low" of 3,300 hours along the northernmost part in places such as Alexandria to reach a high of over 4,000 hours farther in the interior, in most of the country.
| Climate data for Cairo | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 31 (88) |
34.2 (93.6) |
37.9 (100.2) |
43.2 (109.8) |
47.8 (118) |
46.4 (115.5) |
42.6 (108.7) |
43.4 (110.1) |
43.7 (110.7) |
41 (106) |
37.4 (99.3) |
30.2 (86.4) |
47.8 (118) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 18.9 (66) |
20.4 (68.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
28.3 (82.9) |
32 (90) |
33.9 (93) |
34.7 (94.5) |
34.2 (93.6) |
32.6 (90.7) |
29.2 (84.6) |
24.8 (76.6) |
20.3 (68.5) |
27.7 (81.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.6 (56.5) |
14.9 (58.8) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.2 (70.2) |
24.5 (76.1) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.6 (81.7) |
27.4 (81.3) |
26 (79) |
23.3 (73.9) |
18.9 (66) |
15 (59) |
21.38 (70.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 9 (48) |
9.7 (49.5) |
11.6 (52.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
17.7 (63.9) |
20.1 (68.2) |
22 (72) |
22.1 (71.8) |
20.5 (68.9) |
17.4 (63.3) |
14.1 (57.4) |
10.4 (50.7) |
15.8 (60.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
5 (41) |
7.6 (45.7) |
12.3 (54.1) |
16 (61) |
18.2 (64.8) |
19 (66) |
14.5 (58.1) |
12.3 (54.1) |
5.2 (41.4) |
3 (37) |
1.2 (34.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 5 (0.2) |
3.8 (0.15) |
3.8 (0.15) |
1.1 (0.043) |
0.5 (0.02) |
0.1 (0.004) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.7 (0.028) |
3.8 (0.15) |
5.9 (0.232) |
24.7 (0.972) |
| Avg. precipitation days (≥ 0.01 mm) | 3.5 | 2.7 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.8 | 14.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 59 | 54 | 53 | 47 | 46 | 49 | 58 | 61 | 60 | 60 | 61 | 61 | 56 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 213 | 234 | 269 | 291 | 324 | 357 | 363 | 351 | 311 | 292 | 248 | 198 | 3,451 |
| Source #1: World Meteorological Organization (UN) (1971–2000),[1] NOAA for mean, record high and low and humidity[2] | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: Danish Meteorological Institute for sunshine (1931–1960)[3] | |||||||||||||
General information
| Alexandria | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luxor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saint Catherine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
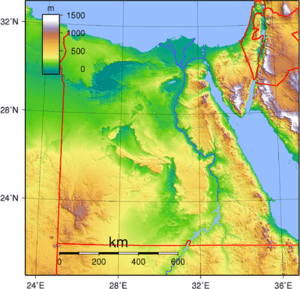
- Notable climatic features
- [7]
- Rafah and Alexandria are the wettest places
- Asyut is the driest city
- Aswan and Luxor are the cities with the hottest summer days
- Saint Catherine has the coldest nights and coldest winters
- Cities or resorts with coolest summer days
- Places with least temperature fluctuation
- Wettest places
- Cities or resorts with warmest winter nights
- Cities with most temperature fluctuation between days and nights
See also
References
- ↑ "Weather Information for Cairo". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved April 14, 2014.
- ↑ "Cairo (A) Climate Normals 1961–1990". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved April 14, 2014.
- ↑ Cappelen, John; Jensen, Jens. "Egypten - Cairo" (PDF). Climate Data for Selected Stations (1931-1960) (in Danish). Danish Meteorological Institute. p. 82. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 27, 2013. Retrieved April 14, 2014.
- ↑ "World Weather Information Service - Alexandria". World Meteorological Organization. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- ↑ "Luxor, Egypt: Climate, Global Warming, and Daylight Charts and Data". Climate Charts. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- ↑ "St. Katrine, Egypt: Climate, Global Warming, and Daylight Charts and Data". Climate Charts. Retrieved 10 July 2013.
- ↑ "Egypt Climate Index". Climate Charts. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||