Clifton Antiquarian Club
 | |
| Formation | 23 January 1884 |
|---|---|
| Type | Non-Governmental Organization |
| Purpose | Investigation of Antiquities |
| Headquarters | 1 Kingfisher Close, Fishpool Hill, Bristol, BS10 6UA, England |
Chairman | Peter Fenn |
Vice-Chairman | Laurie Waite |
Treasurer | John Swann |
Webmaster | Donovan Hawley |
| Website | Clifton Antiquarian Club |
The Clifton Antiquarian Club was founded in 1884 in Bristol to investigate antiquities in the surrounding area of western England and southern Wales. The twenty-eight years of research performed by the membership and associates of the original society fill the first seven volumes of the Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club. The association was dissolved in 1912, but was resurrected in 2006. Two additional volumes of Proceedings have been published by the current incarnation of the society.
Founding
The Clifton Antiquarian Club was established on 23 January 1884 in Bristol, England. The impetus for the formation of the society was a letter that had circulated among archaeologists and others in the Clifton area of Bristol suggesting that an antiquarian club be formed.[1] The first meeting was held at the Bristol Museum and Library, now the Bristol City Museum and Art Gallery, and was attended by twenty-three men from the community. Bishop William Clifford was elected president and Alfred Edmund Hudd was elected secretary. Two vice-presidents and a treasurer were also chosen.[1] The mission of the Clifton Antiquarian Club was the investigation of antiquities in the surrounding area, which included not only western England, but also southern Wales. The society decided to limit membership to forty men at any given time, although there could also be up to ten honorary members. Many of the club's members resided in the Clifton area of Bristol. While women could interact on a limited basis with the society, they were not formal members of the club.[1] The first meeting of the Clifton Antiquarian Club also included a presentation by John Taylor, Bristol City Librarian. He read his research paper "Anglo-Norman Church Doorways" to the assembled men.[1]
Presidents of the Clifton Antiquarian Club

The first president of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, William Joseph Hugh Clifford (1823–1893), was ordained as a priest in August 1850 by Archbishop Errington in Clifton. He was appointed Bishop of Clifton, and in February 1857 he was consecrated as bishop by Pope Pius IX in Rome. The Honorable and Right Reverend William Clifford, Bishop of Clifton, served as president of the Clifton Antiquarian Club from its founding in 1884 until his death on 14 August 1893. He also served as a vice-president in the Bristol and Gloucestershire Archaeological Society and the Somersetshire Archaeological Society, now the Somerset Archaeological and Natural History Society, publishing papers in both of their journals.[2][3]
After the bishop's death in 1893, a new leader of the society was not chosen until the following year. Bishop Clifford was succeeded as president of the Clifton Antiquarian Club by one of its founding members, James Roger Bramble (1841–1908). A solicitor, he was the force behind the creation of St. Vincent Lodge No. 1404 of Bristol.[4] Former Lieutenant Colonel of the Second Gloucester Royal Engineer Volunteers, Bramble was elected as president of the Clifton Antiquarian Club on 10 January 1894 at the tenth annual meeting.[5] He served in his capacity as president until 1899. One of the founders of the club, he had also served as treasurer from 1884 to 1887, and as a vice-president from 1887 to 1893. James Bramble had contributed several papers to the Proceedings. He died on 3 February 1908 at Weston-super-Mare, Somerset.[6]
George Forrest Browne (1833–1930), Bishop of Stepney, became Bishop of Bristol in 1897.[7][8] The bishop had been an explorer of ice caves in France and Switzerland as a young man. He was also the author of a number of books.[9] Bishop Browne was the Disney Professor of Archaeology at the University of Cambridge.[10] In addition, he was the vice-president of the Society of Antiquaries of London. The Bishop of Bristol was elected as a member of the Clifton Antiquarian Club on 24 November 1897.[11] Despite his relatively short tenure as a member of the club, Bishop Browne was elected as president at the fifteenth annual meeting on 19 January 1899. He served until January 1903.[12][13]
At the nineteenth annual meeting of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, held on 21 January 1903, Conwy Lloyd Morgan (1852–1936) was elected as president to succeed the Bishop of Bristol.[13][14] Morgan had been elected principal of University College, Bristol in 1887.[15] He served from 1903 to 1906 as president of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, and resigned on 31 January 1906, proposing that his predecessor, the Bishop of Bristol, be elected as president.[16] In 1910, the university charter of the college was granted and he agreed to accept a vice-chancellorship on a temporary basis, with the understanding that he would resume the chair of his department. Initially appointed the chairman of the geology and zoology department in 1884, he became the chair of the psychology and ethics department after his 1910 vice-chancellorship. He retired in 1919, living in Clifton until 1925 or 1926. The Professor Emeritus of Zoology and Geology at the University of Bristol moved to Hastings, where he died in 1936.[15]
On 31 January 1906, at the twenty-second annual meeting of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, the Bishop of Bristol, George Forrest Browne, was elected as president.[16] He was re-elected in 1907 and 1908, and served at the time of dissolution of the club in 1912.[17] He died on 1 June 1930.[18]
Alfred Hudd, Secretary
The secretary of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, Alfred Edmund Hudd of Pembroke Road in Clifton, Bristol, retained that position during all twenty-eight years of the original society. He had the distinction of being the only member of the Clifton Antiquarian Club to remain with the organisation from its inception in 1884 until its end in 1912. Hudd served as editor of the society's seven volumes of Proceedings.[17] He also contributed 21 papers to the Proceedings.[19] His service to the organisation was acknowledged on 5 January 1898 when the club presented him with a silver bowl and a set of four silver candlesticks.[20] In 1911, the membership of the Clifton Antiquarian Club again presented him with a tribute, an inscribed, inlaid grandfather clock.[17]
Alfred Hudd was also a member of the Bristol and Gloucestershire Archaeological Society.[21] In addition, he was a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London and was closely involved with the Caerwent Exploration Fund. At a meeting of the Society of Antiquaries of London in February 1899, Alfred Trice Martin, a founding member of the Clifton Antiquarian Club and a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London, had proposed a systematic excavation of Caerwent, a Roman town in south Wales.[22] The Caerwent Exploration Fund was established by the Clifton Antiquarian Club shortly thereafter, in 1899. In September of that year, at Caerwent, Godfrey Morgan, Lord Tredegar, was elected President of the Fund and Alfred Hudd was elected Treasurer.[22][23] Alfred Hudd and Thomas Ashby, Junior, both members of the Executive Committee of the Fund, supervised the excavations.[24] During the period between 1899 and 1913, two-thirds of the Roman town was revealed.[25] The archive of Caerwent, excavated by the Caerwent Exploration Fund, is in the archaeology collection of Newport Museum.[24] The reports on the Caerwent excavation were published in Archaeologia, the journal of the Society of Antiquaries of London.[22]
Lectures

It was decided at the first meeting of the Clifton Antiquarian Club that at least two meetings would be held every year. One of those general meetings would be scheduled for January of each year. At that annual meeting, election of officers and new members would take place.[1] Members and, occasionally, associates of the club, male and female, made presentations to the society at its meetings. Their papers were read to the membership and eventually compiled in the leather-bound volumes of the Clifton Antiquarian Club Proceedings. At a total of 21 papers, Alfred E. Hudd was one of the most prolific contributors to the Proceedings.[19]
Although her husband Reverend William Oakeley was a member of the society, British heiress and antiquarian Mary Ellen Bagnall Oakeley (pictured) was never invited to be a member.[17] However, as a friend of the club, Bagnall Oakeley made presentations to the membership, and did so even before her husband became a member in 1891. The five papers that she submitted to the Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club cover the period from 1887 (Volume 1 of the Proceedings) to 1896 (Volume 3 of the Proceedings). In chronological order, they include:[19]
- "Notes on the Stitches Employed in the Embroidery of the Copes." (Appendix to 20 December 1887, appeared in Volume 1)[26]
- "Notes on Round Towers." (Read on 12 October 1891, appeared in Volume 2)[27]
- "Early Christian Settlements in Ireland." (Read on 20 November 1893, appeared in Volume 3)[28]
- "A Week in the Aran Islands." (Read on 22 November 1894, appeared in Volume 3)[29]
- "On a Great Hoard of Roman Coins." (Read on 28 January 1896, appeared in Volume 3)[30]
Other women who contributed papers to the Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club included E. Hodges (Read on 19 June 1894, appeared in Volume 3)[31] and Ida M. Roper (Read on 8 November 1905, appeared in Volume 6; second presentation in Volume 7 ).[19][32]
Excursions

It was also decided at the first meeting of the club that two excursions would be held every year. Women were allowed to attend as the guests of members.[1] The Clifton Antiquarian Club's first excursion took place on 29 May 1884. Thirty members and friends of the club visited the Ashton Court mansion (pictured) and estate at the outskirts of Bristol.[33][34] The Ashton Court mansion and stables are now on the National Heritage List for England.[35] The group then inspected Long Ashton Church and the Ashton Cross. Later, the club ventured to churches and houses in villages of the Somerset area, including Barrow Gurney, Stanton Drew, Chew Magna, and Dundry.[33] In Somerset, the group also toured the earthworks at Maes Knoll (pictured below), the remains of a univallate hillfort from the Iron Age, now a scheduled ancient monument.[33][36]
However, women not only accompanied men on the day trips; sometimes they actively participated in the investigations. On 20 July 1889, the club undertook an excursion to Tintern Abbey and Monmouth. Bagnall Oakeley and her husband served as guides for the Monmouth portion of the excursion. The group visited St Thomas Church, the gatehouse on the Monnow Bridge, the ruins of Monmouth Castle, the Church of St Mary, and "Geoffrey's" Window.[37]
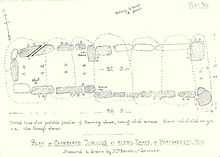
Another example of this was the project sponsored jointly by the Clifton Antiquarian Club and the Monmouthshire and Caerleon Antiquarian Association on 22 August 1888. The excursion is described in editor Alfred Edmund Hudd's postscript to the 1888 paper authored by the Reverend William Oakeley, "The Chambered Tumulus at Heston Brake, Monmouthshire," found in Volume 2 of the Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club.[38] On that day, the tumulus at the site Heston Brake in Portskewett was opened and examined under the direction of the members of the two associations. There was evidence that the tumulus had been previously disturbed. The few relics which remained, fragments of pottery and human bones and teeth, are now in the Caerleon Museum, the National Roman Legion Museum. At the time of that 1888 excavation, Bagnall Oakeley made measurements of all the components of the tumulus. Her illustration (pictured), which accompanies her husband's paper, is entitled, "Plan of Chambered Tumulus at Heston Brake, nr Portskewett, Mon."[38]
Original proceedings

The 28 years of research presented by the members and associates of the Clifton Antiquarian Club were compiled in seven volumes of Proceedings. At the time of dissolution of the society, an attempt was made to find a buyer for the hundreds of volumes of the Proceedings that they had in stock. The club was offered £9:10s by a bookseller, but that offer was declined. Today, a single seven volume set of the original leather-bound Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club sells for more than £500.[17]
The seven volumes of the original Proceedings are as follows:
| No. | Years Covered | Year Published | Editor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume 1 | 1884–1888 | 1888 | Alfred E. Hudd |
| Volume 2 | 1888–1893 | 1893 | Alfred E. Hudd |
| Volume 3 | 1893–1896 | 1897 | Alfred E. Hudd |
| Volume 4 | 1897–1899 | 1900 | Alfred E. Hudd |
| Volume 5 | 1900–1903 | 1904 | Alfred E. Hudd |
| Volume 6 | 1904–1908 | 1908 | Alfred E. Hudd |
| Volume 7 | 1908–1912 | 1912 | Alfred E. Hudd |
Dissolution
The membership of the Clifton Antiquarian Club dwindled through attrition due to retirement or death in its last years. The society was formally dissolved on 15 January 1912. The occasion was the 28th annual general meeting of the association. At the invitation of Bishop George Forrest Browne, Bishop of Bristol, then president of the original club, the final meeting was held at the Bishop's Palace in Redland Green. On 2 December 1940, the Bishop's Palace was destroyed during the course of a bombing raid.[17]
Resurrection

In June 2006, an excursion to the Heston Brake chambered tumulus site in Portskewett led to mention of the original Clifton Antiquarian Club. Heston Brake, the site of the August 1888 excursion, proved to be the inspiration for the resurrection of the Clifton Antiquarian Club as it exists today. A complete set of the seven volumes of the original Proceedings was obtained and examined. The decision was made to adhere to the primary objectives of the original society. A major departure from the old version of the club, however, was inclusion of women in the membership, such that women now comprise 50% of the members. Other changes include a new junior section of the society, CAC Kids, with child-friendly activities.[39] In addition, there is an increasingly comprehensive website on which some of the publications from the original Proceedings are available.[17] The new version of the Clifton Antiquarian Club was incorporated on 12 October 2006. It is located at 1 Kingfisher Close, Fishpool Hill, Bristol, BS10 6UA, England.[40]
Recent lectures
Lectures are held twice annually, summer and winter, most often at the University of Bristol Wills Memorial Building. Both members and non-members are welcome at the lectures. The subject of the talks generally alternates between the prehistory and medieval eras.[17] The lectures that have been given by the current version of the Clifton Antiquarian Club include:[41]
| No. | Date | Lecturer | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | January 2007 | Dr. Christopher Chippindale | Philip Crocker – Learning and illustration: A 19th century view of prehistoric south west Britain |
| 2 | June 2007 | Dr Volker Heyd | The Emergence of Complex Societies in the south east of Europe |
| 3 | January 2008 | Dr Angelo Fossati | The Rock Art Tradition of Valcamonica, North Italy: A World Heritage view |
| 4 | June 2008 | Dr Tim Malim | Dykes, Death and Disease: the frontiers of Anglo-Saxon migration |
| 5 | January 2009 | Professor Mark Horton | The Cannibals of Thornbury – an intriguing account of violence and butchery in the Iron Age |
| 6 | June 2009 | Dr Michael Costen | Common-fields and the Agricultural Revolution in Somerset 900–1100 AD |
| 7 | January 2010 | Dr Jean Clottes | The Cave Paintings of Chauvet |
| 8 | June 2010 | Professor David Austin | Castles on the Edge: The Experience of Medieval Borderlands |
| 9 | January 2011 | Professor Richard Bradley | Stages and Screens: Rethinking the Henge Monuments of Northern Britain |
| 10 | June 2011 | Professor Howard Williams | Shipping Hel: The topography and necrogeography of a Viking boat-grave cemetery |
| 11 | January 2012 | Dr Philip de Jersey | Different Iron Ages: the archaeology of the Channel Islands in the late first millennium BC |
| 12 | September 2012 | Simon West | The Romanisation of St Albans & district |
| 13 | May 2013 | Dr Keith Wilkinson | The Hrazdan Valley Palaeolithic Project 2008-12 |
| 14 | November 2013 | Dr Clive Bond | The Sweet Track: a Neolithic water cult? |
| 15 | April 2014 | Dr Jacqueline Cahill Wilson | What did the Romans ever do for us? |
| 16 | November 2014 | Neil Holbrook | The Cemeteries of Roman Cirencester |
Recent excursions
In addition, at least two excursions are scheduled by the Clifton Antiquarian Club each year; some are day trips, others are longer tours.[17] During the September 2010 excursion to the Gower Peninsula, Dr. George Nash of the University of Bristol and other members of the Clifton Antiquarian Club discovered a carving of a reindeer in one of the caves. This represents the second discovery of Upper Palaeolithic rock art in the British Isles, and the first in Wales. Carbon dating has placed the carving at approximately 12,600 years, although Dr. Nash believes it to be older.[42] The carving may represent the oldest specimen of rock art in the British Isles.[43][44]
The excursions which have been undertaken the last several years include:[45]
| No. | Date | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | July 2009 | Oxford, Oxfordshire | Research Laboratory for Archaeology & the History of Art |
| 2 | September 2009 | Erme Valley, Dartmoor, Devon | The longest stone row |
| 3 | October/November 2009 | Dorset | Pimperne long barrow, Colliton Park, Maiden Castle, Portland Castle, Nine Stones, megalithic monuments, Lulworth Cove, Badbury Rings |
| 4 | December 2009 | Cotswolds | Bulwarks, Rodmartin long barrow, Stroudwater canal, Sapperton Canal Tunnel, Church of the Holy Rood, St Michael's Church, Duntisbourne Rouse, Crickley Hill |
| 5 | March 2010 | Avebury, Wiltshire | Stone tools Recognition Day at Avebury Study Centre, |
| 6 | April 2010 | Garreg Las, Wales | Rock art |
| 7 | May 2010 | Cranborne Chase | Down Farm |
| 8 | September 2010 | Gower Peninsula, Wales | Rotherslade Bay, Hunts Bay, Cotswold-Severn long barrow, Parc le Breos Cwm, Cat Hole cave, Minchin Hole |
| 9 | October 2010 | Valcamonica, Italy | Seradina, San Siro, Bedolina, Paspardo, Roman Archaeological National Museum, amphitheatre, Naquane National Park |
| 10 | December 2010 | Bristol | Defensive walls, Floating Harbour |
| 11 | September 2011 | Wiltshire | Stonehenge |
| 12 | October 2011 | Sardinia, Italy | Tamuli, Sant' Andrea Priu, Anghelu Ruju |
| 13 | November 2011 | Bristol | Bristol Museum |
| 14 | December 2011 | St Fagans, Wales | Welsh National History Museum, Neolithic long barrows of Tinkinswood and St Lythans |
| 15 | February 2012 | Cotswolds | Neolithic long barrows |
| 16 | March/April 2012 | St Albans and Verulamium | St Albans clock tower, Roman theatre, Verulamium Museum, Nunnery, St Albans Cathedral |
| 17 | September 2012 | Marlborough Downs | Devil's Den burial chamber, medieval settlement of Raddun, experimental earthwork on Overton Down |
| 18 | October 2012 | Gibraltar | Gibraltar Museum, Mediterranean Steps, Great Siege Tunnels, St. Michael's Cave |
| 19 | December 2012 | Somerset & Dorset | South Cadbury hill fort, Ham Hill, Sherborne |
| 20 | March 2013 | Bristol | Clifton, Burwalls and Stokeleigh camps |
| 21 | April 2013 | Forest of Dean | Lydney Park, Hopewell Colliery |
| 22 | July 2013 | Somerset | Mendips walk, Rowberrow Cavern, Doleberry Warren hill fort |
| 23 | October 2013 | Brittany, France | Finistere, allée couverte burial chambers, dolmens, medieval churches |
| 24 | December 2013 | Salisbury | Old Sarum, Salisbury Cathedral |
| 25 | March 2014 | Devon | The long barrows of Dartmoor |
| 26 | October 2014 | Friesland & Drenthe, The Netherlands | Passage graves, medieval churches, farmhouses & fort |
Recent proceedings
The current Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club are published every two to three years. Members have the opportunity to have their personal research published in the Proceedings. However, there is now an editorial board which ensures that the content of the Proceedings is of the highest standards. Volume 8, Landscape Enquiries, was published in December 2007. The thirteen chapter book includes contributions from members of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, as well as non-member scholars from Britain, Australia, Italy, Norway, and the United States.[46] Volume 9 of the Proceedings, Early Medieval Enquiries, was published in March 2010. The subject of the latter book is early medieval Britain and it features eighteen papers that relate to British history in the period AD 410 to 1066. The tenth volume of the Proceedings was published in December 2014 and exclusively contained members current archaeological work together with details of all the club's recent activities.[17]
Research projects

In January 2007, the Clifton Antiquarian Club initiated a survey of the eastern aspect of Rhossili Down. The site of the highest point on the Gower Peninsula, Rhossili Down is also the location of the Sweyne's Howe monuments.[47] The society published a preliminary report in the eighth volume of the Proceedings. In addition, the club completed a comprehensive survey of a circular enclosure several hundred metres southeast of the monuments in December 2009[17]
Another recent project was conducted at Delancey Park on Guernsey, one of the Channel Islands.[48] Delancey Park was the site of their preliminary excavation of a Neolithic chambered monument in 2010.[49][50] That preliminary excavation assisted the club in determining what areas might contain undisturbed archaeology, and also allowed evaluation of the effect of previous investigations. The initial excavation revealed that the north side was fairly intact. Subsequent investigation of this area through large scale excavations was undertaken in 2011.[51] Analysis of the finds is pending.[17] Other projects include the Cae-Dyni chambered monument in North Wales[52] and Arthur's Stone, the Neolithic chambered monument, in Herefordshire.[53]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1888). "First Meeting". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1884–1888, Vol. I. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 1–11. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ "Clifton". newadvent.org. Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1893). "In Memoriam". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1888–1893, Vol. II. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 275–276. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "Saint Vincent Lodge No. 1404 in the Province of Bristol". saint-vincent-lodge.org.uk. Saint Vincent Lodge No. 1404. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1897). "Tenth Annual Meeting – January 10th, 1894". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1893–1896, Vol. III. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 82. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1908). "Obituary". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1904–1908, Vol. VI. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 243. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ "The Rev George Forrest Browne". showcaves.com. Showcaves.com. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ "Bishop of Bristol". The Advertiser (Adelaide). 4 August 1897. p. 5. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "The Bishop of Stepney". stgite.org.uk. St George-in-the-East Church. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ John Moreland (2003). "George Forrest Browne, Early Medieval Sculpture and Nineteenth-Century Reformation Historiography". Journal of the British Archaeological Association (Maney Publishing) 156 (17): 150–166. doi:10.1179/006812803799451449. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1900). "Meeting, November 24th, 1897". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1897–1899, Vol. IV. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 83–84. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1900). "Fifteenth Annual Meeting – January 19th, 1899". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1897–1899, Vol. IV. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 300. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1904). "Nineteenth Annual Meeting – January 21st, 1903". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1900–1903, Vol. V. Clifton Antiquarian Club. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "Conwy Lloyd Morgan". rsbm.royalsocietypublishing.org. Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Gifford Lectures – Authors – Conwy Lloyd Morgan". giffordlectures.org. Kelly Van Andel, University of Glasgow. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1908). "Twenty-second Annual Meeting – January 31st, 1906". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1904–1908, Vol. VI. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 153–154. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 17.5 17.6 17.7 17.8 17.9 17.10 17.11 "History and Mission Statement". cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Clifton Aquarium Club. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ "George Forrest Browne". findagrave.com. Find A Grave. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 "Index to the proceedings, Volumes 1–7, 1884–1912" (PDF). cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Clifton Antiquarian Club. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ "The Antiquary (Volume 34)". ebooksread.com. Elliot Stock. 1898. p. 60. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "Hudd, Alfred E.". biab.ac.uk. British and Irish Archaeological Bibliography. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Ashby Jun., Thomas; Hudd, Alfred E.; Martin, A. T. (1901). "XV.-Excavations at Caerwent, Monmouthshire, on the Site of the Roman City of Venta Silurum, in 1899 and 1900". Archaeologia (Second Series) 57 (2): 295–316. doi:10.1017/s0261340900014156. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "The Antiquary (Volume 35)". ebooksread.com. Elliott Stock. 1899. pp. 279–280. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Museum – Caerwent". newport.gov.uk. Newport City Council. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ "In the second of two features, the Review’s Sarah Daly looks at the Roman legacy still surviving in Caerwent". The Chepstow Review – Tindle Newspapers Ltd. 18 January 2012. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1888). Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1884–1888, Vol. I. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 229, 238. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1893). "Notes on Round Towers". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1888–1893, Vol. II. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 142. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1897). "Early Christian Settlements in Ireland". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club 1893–1896, Vol. III. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 22. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1897). "A Week in the Aran Islands". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1893–1896, Vol. III. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 99. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1897). "On a Great Hoard of Roman Coins". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1893–1896, Vol. III. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 162. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1897). "Horton Court, Gloucestershire, and its Associations". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1893–1896, Vol. III. Clifton Antiquarian Club. p. 54. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1908). "On the Costume of an Effigy at Winterbourne, Gloucestershire". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1904–1908, Vol. VI. Wm. Pollard & Co. Ltd. p. 55. Retrieved 5 May 2012.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1888). "The First Excursion". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1884–1888, Vol. I. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 68–74. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ "Welcome to Ashton Court Mansion". ashtoncourtmansion.co.uk. Ashton Court Mansion. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ "Images of England: Ashton Court Mansion and Stables". imagesofengland.org.uk. English Heritage. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ "Pastscape: Maes Knoll". pastscape.org.uk. English Heritage. Retrieved 2 May 2012.
- ↑ Alfred E. Hudd, ed. (1893). "Excursion to Tintern and Monmouth". Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club for 1888–1893, Vol. II. Clifton Antiquarian Club. pp. 89–90. Retrieved 4 May 2012.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Rev William Bagnall-Oakeley, M.A. "The Chambered Tumulus at Heston Brake, Monmouthshire" (PDF). cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Proceedings of the Clifton Antiquarian Club, Volume 2. Retrieved 3 May 2012.
- ↑ "The Heritage Journal – Archaeology Societies – SouthWest". heritageaction.wordpress.com. Heritage Action. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Clifton Antiquarian Club". cdrex.com. Company Data Rex. Retrieved 21 December 2013.
- ↑ "Club Lecture Roll of Honour". cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Clifton Antiquarian Club. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Tests confirm age of prehistoric carving in Wales". World Archaeology News. 9 August 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Carving in Wales Could Be The Oldest in United Kingdom". Huffington Post. 8 February 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Rock Art on the Gower Peninsula". bradshawfoundation.com. Bradshaw Foundation. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Past Trips and Events". cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Clifton Antiquarian Club. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Landscape Enquiries" (PDF). artdept-online.com. Art Dept Online. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Rhossili Down, Hillend and beach walk". nationaltrust.org.uk. National Trust. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ↑ "New Excavation of Important Neolithic Site on the Channel island of Guernsey". ArchNews. 2 February 2011. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Archaeologists make 'spectacular' discovery at Delancey". news.bbc.co.uk. BBC. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ↑ "Neolithic excavations: feast or famine?". British Archaeology (Council for British Archaeology (CBA)) (115). Nov–Dec 2010. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ Juliet Pouteaux (24 June 2011). "Delancey dig reveals 20th century excavators got there beforehand". Guernsey. Retrieved 8 May 2012.
- ↑ "Cupmarks discovered on the Cae-Dyni chambered monument, Criccieth, Caernarvonshire, North Wales". cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Clifton Antiquarian Club. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ↑ "Evaluation program and results at the Neolithic Chambered Monument of Arthur's Stone, Herefordshire". cliftonantiquarian.co.uk. Clifton Antiquarian Club. Retrieved 7 May 2012.



