City Observatory
| City Observatory, Edinburgh | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Front of the Playfair Building | |||||
| Code | 961 | ||||
| Location | Calton Hill, Edinburgh, Scotland | ||||
| Coordinates | 55°57′17″N 3°11′0″W / 55.95472°N 3.18333°WCoordinates: 55°57′17″N 3°11′0″W / 55.95472°N 3.18333°W | ||||
| Altitude | 107 m | ||||
| Established | 1776 | ||||
| Closed | 2009 | ||||
| Telescopes | |||||
| |||||

The City Observatory is an astronomical observatory on Calton Hill in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is also known as the Calton Hill Observatory.
The site is enclosed by a boundary wall with a monument to John Playfair, president of the Edinburgh Astronomical Institution, in the southeast corner. The oldest part is the Gothic Tower in the southwest corner, facing Princes Street and Edinburgh Castle. It is also known as Observatory House, the Old Observatory, or after its designer James Craig House. The central building with the appearance of a Greek temple is the Playfair Building, named after the building's designer William Henry Playfair. This houses the 6-inch (15 cm) refractor in its dome and the 6.4-inch (16 cm) transit telescope in its eastern wing. The largest dome of the site is the City Dome in the northeast corner. During the early 20th century this contained a 22-inch (56 cm) refractor.
History
Thomas Short's observatory
In 1776 Thomas Short returned to Edinburgh, bringing with him a 12-foot (3.7 m, focal length) reflecting telescope made by his late brother James Short. He intended to open a public observatory on Calton Hill as a commercial enterprise. However, in 1736 Colin Maclaurin, professor of mathematics at the University of Edinburgh, had collected funds for a university observatory. Due to the Porteous Riots and the Jacobite Rebellion of 1745 the funds were left unused. These were made available to build Short's observatory; and the City of Edinburgh provided a plot of land on Calton Hill. The observatory was to be open to university students.
James Craig designed the observatory, which, under Robert Adam's influence, was to look like a fortification with a wall and Gothic towers at its corners. The city controlled the building project, but the money ran out after only the first of the towers was built. Short moved into this as residence and ran the observatory until his death in 1788. An actual observatory, smaller than originally planned, was also built where the Playfair Building is now. After Short's death the observatory was kept going by his family for a while, then leased to opticians and finally abandoned around 1807. The site reverted to the city.
Short's daughter Maria Theresa Short was to return to Edinburgh in 1827. She ran a second – a popular and commercial rather than scientific – observatory elsewhere on Calton Hill. In 1850 this was removed[1] and she moved to Castle Hill, where her enterprise eventually became today's Camera Obscura on the Royal Mile.
The Royal Observatory


In 1812 the observatory was handed over to the Edinburgh Astronomical Institution, which opened its popular observatory in the Gothic Tower. In 1818 work began on the Playfair Building. Designed by William Henry Playfair this was to become the scientific observatory of the Institution. Following a loyal address to George IV in 1822 this became the Royal Observatory. Again the funds proved insufficient, so that the purchase of instruments and the employment of an observer depended on funding from the Government. After much delay the instrumentation was completed in 1831 with delivery of the transit telescope. Fraunhofer had made the lens, but after his death it fell to Repsold - and after his death to Repsold's son - to complete and install the instrument.
In 1834 Thomas Henderson took up the position of observer. This was now the post of Astronomer Royal for Scotland and Regius Professor of Astronomy in the University of Edinburgh. Until his death in 1844 he worked on Calton Hill. In 1839 he published his results regarding the distance of alpha Centauri based on observations he had made 1832/33 at the Royal Observatory, Cape of Good Hope. In 1846 Charles Piazzi Smyth became second Astronomer Royal for Scotland and set about reducing and publishing the backlog of Henderson's observations. In 1847 the Astronomical Institution - having run out of money - handed the Royal Observatory over to the Government.
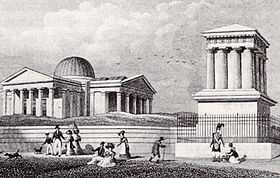
According to the English journalist William Jerdan, naturalist and oceanographer Edward Forbes, F.R.S. and his "The Red Lions", a dining club for younger members of the British Association, (named after the tavern where the first meeting was held), had occasion to run up to the observatory of Calton Hill for astronomical studies.[2]
The main purpose of the observatory was a time service. The transits of stars through the meridian were observed and used to keep the observatory clock accurate. Accurate time was important for navigation, and mariners would bring ships' chronometers from the port of Leith up to Calton Hill for adjustment. In 1854 the time ball was installed on Nelson's Monument next to the observatory and visible from the port. This was controlled by electrical pulses from the observatory clock. A few years later the One O'Clock Gun on Edinburgh Castle was added. This was also controlled through an electrical wire, spanning the city from Calton Hill to the Castle. Today the time ball and One O' Clock Gun are tourist attractions. They are no longer controlled from a state of the art clock, but are triggered "by hand".
By 1888, when Smyth resigned, through underfunding the observatory's equipment had become largely obsolete. Also, the site had originally not been chosen through scientific investigation and its proximity to the city was causing problems. In 1896 the Royal Observatory moved to a new site on Blackford Hill. The Calton Hill Observatory, once again, reverted to the City of Edinburgh.
The City Observatory

In the wake of the Royal Observatory moving to Blackford Hill, a new City Observatory was created on Calton Hill toward the end of the 19th century. The 6-inch (15 cm) Cooke refractor was donated by William McEwan and installed in the dome on the Playfair Building. Additional domes were built for a 13-inch (33 cm) reflector donated by Robert Cox and for a 13-inch (33 cm) refractor transferred from the Dunecht observatory. Only remnants of these two domes remain today. The City Dome was built to house a 22-inch (56 cm) refractor. This did not perform very well and was dismantled in 1926. The dome remained and was used as a lecture theatre.
The observatory opened in 1898 with William Peck as City Astronomer. After his death in 1925 his assistant John McDougal Field continued to run the City Observatory.
In 1924 the Astronomical Society of Edinburgh was formed with Field as first president. William Peck and Ralph Sampson, the then Astronomer Royal for Scotland, were honorary presidents. Field died in 1937; and in 1938 the observatory was leased to the Society, which ran the City Observatory until vandalism and theft of roofing material rendered the site unusable in 2009.[3]
In 2009 the Astronomical Society of Edinburgh moved out of the City Observatory and the buildings reverted to the City of Edinburgh Council.[4] The Council renovated the Observatory House building structure and the interior was restored by the Vivat Trust (a charity which aims to preserve old buildings) who let it as holiday accommodation.[5][6] After being unoccupied for several years, in 2012 the Council started a £1,000,000 program[4] to renovate the remaining buildings in partnership with the Collective Gallery.[7] In 2014 the Collective Gallery relocated from Cockburn Street, Edinburgh, opened an exhibition in the City Dome[8] and received an award of £900,000 from Creative Scotland to further develop the site.[9][8]
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to City Observatory, Edinburgh. |
Other public observatories
- Airdrie Public Observatory
- Coats Observatory, Paisley
- Mills Observatory, Dundee. The only full-time public observatory in the United Kingdom.
References
- Gavine, D. (1981). Astronomy in Scotland 1745-1900. PhD thesis. Open University.
- Brück, H.A. (1983). The story of astronomy in Edinburgh from its beginnings until 1975. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 0-85224-480-0.
- Gavine, D. (1981-1985). "The Calton Hill observatories". ASE Journal, 4-11. Astronomical Society of Edinburgh. ISSN 1756-5103
- ↑ Gavine, D. (1981). Astronomy in Scotland 1745-1900. Milton Keynes: Open University.
- ↑ Jerdan, W. (1866). Men I Have Known. London: George Routledge and Sons.
- ↑ Astronomical Society of Edinburgh (2009). "Closure of the City Observatory". Astronomical Society of Edinburgh. Retrieved 2009-01-25.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Little, Frank; Williams, David; Gray, Kate (February 2014) "Calton Hill Newsletter" issued by the City of Edinburgh Council and Collective, Edition 3
- ↑ Old Observatory House Only In Edinburgh.com, Retrieved 28 February 2014
- ↑ Old Observatory House "An iconic eighteenth century Gothic style building at the top of Calton Hill offering spacious city centre holiday accommodation for eight.", Vivat Trust web page, Retrieved 28 February 2014
- ↑ (2014) Collective Programme Collective Gallery website, Retrieved 28 February 2014
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 (29 January 2014) Calton Hill observatory set for new galleries The Edinburgh Evening News, Retrieved 28 February 2014
- ↑ (28 January 2014) Capital Funding for 12 Scottish Arts & Culture Organisations - Edinburgh Creative Scotland, Retrieved 28 February 2014
Further reading
- Shepherd, J., Rule, G. (1984, 1995). A guide to Edinburgh's popular observatory. http://www.astronomyedinburgh.org/publications/booklet/.
- Gavine, D. (1998). "Thomas Henderson 1798-1844 - Scotland's First Astronomer Royal". ASE Journal, 38. http://www.astronomyedinburgh.org/publications/journals/38/hend.html. ISSN 1756-5111
