Cities of the ancient Near East
The largest cities in the Bronze Age ancient Near East housed several tens of thousands. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age with some 30,000 inhabitants was the largest city of the time by far. Ur in the Middle Bronze Age is estimated to have had some 65,000 inhabitants; Babylon in the Late Bronze Age similarly had a population of some 50–60,000, while Niniveh had some 20–30,000, reaching 100,000 only in the Iron Age (ca. 700 BC).
The KI 𒆠 determinative was the Sumerian term for a city or city state.[1] In Akkadian and Hittite orthography, URU𒌷 became a determinative sign denoting a city, or combined with KUR𒆳 "land" the kingdom or territory controlled by a city, e.g. 𒄡𒆳𒌷𒄩𒀜𒌅𒊭 LUGAL KUR URUHa-at-ti "the king of the country of (the city of) Hatti".
Mesopotamia
Lower Mesopotamia

(ordered from north to south)
- Eshnunna (Tell)
- Diniktum
- Tutub (Khafajah)
- Der (Tell Aqar, Durum?)
- Sippar (Tell Abu Habbah)
- Sippar-Amnanum (Tell ed-Der)
- Kutha (Tell Ibrahim)
- Jemdet Nasr (NI.RU)
- Kish (Tell Uheimir & Ingharra)
- Babilim (Babylon)
- Borsippa (Birs Nimrud)
- Mashkan-shapir (Tell Abu Duwari)
- Dilbat (Tell ed-Duleim)
- Nippur (Afak)
- Marad (Tell Wannat es-Sadum)
- Adab (Tell Bismaya)
- Isin (Ishan al-Bahriyat)
- Kisurra (Tell Abu Hatab)
- Shuruppak (Tell Fara)
- Bad-tibira (Tell al-Madineh?)
- Zabalam (Tell Ibzeikh)
- Umma (Tell Jokha)
- Girsu (Tello or Telloh)
- Lagash (Tell al-Hiba)
- Urum (Tell Uqair)
- Uruk (Warka)
- Larsa (Tell as-Senkereh)
- Ur (Tell al-Muqayyar)
- Kuara (Tell al-Lahm)
- Eridu (Tell Abu Shahrain)
- Tell al-'Ubaid
- Akshak
- Akkad
Upper Mesopotamia
(ordered from north to south)
- Urfa
- Shanidar cave
- Urkesh (Tell Mozan)
- Tell Leilan (Shekhna, Shubat-Enlil)
- Tell Arbid
- Harran
- Chagar Bazar
- Itabalhum
- Kahat (Tell Barri)
- Tell el Fakhariya (Washukanni?)
- Hadatu
- Carchemish (Djerabis)
- Til Barsip
- Tell Chuera
- Mumbaqat (Tall Munbāqa, also Ekalte (Mumbaqat))
- Al-Rawda
- Nabada l Beydar)
- Nagar (Tell Brak)
- Telul eth-Thalathat
- Tepe Gawra
- Tell Arpachiyah (Tepe Reshwa)
- Shibaniba (Tell Billa)
- Tarbisu (Sherif Khan)
- Nineveh (Ninua)
- Qatara or Karana (Tell al-Rimah)
- Tell Hamoukar
- Dur Sharrukin (Khorsabad)
- Tell Shemshara
- Arbil (Urbilim, Arba-Ilu)
- Tell Taya
- Tell Hassuna
- Balawat (Imgur-Enlil)
- Tell es-Sweyhat
- Nimrud (Kalhu)
- Emar (Tell Meskene)
- Qal'at Jarmo
- Arrapha
- Kar-Tukulti-Ninurta
- Assur
- Shubat-Enlil
- Ekallatum
- Nuzi (Yorghan Tepe, Gasur)
- Tell al-Fakhar (Kuruhanni?)
- Terqa (Tell Ashara)
- Doura Europos
- Mari (Tell Hariri)
- Haradum (Khirbet ed-Diniyeh)
- Tell es Sawwan
- Nerebtum or Kiti (Tell Ishchali)
- Tell Agrab
- Dur-Kurigalzu (Aqar Quf)
- Shaduppum (Tell Harmal)
- Seleucia
- Ctesiphon (Taq Kisra)
- Zenobia (Halabiye)
- Zalabiye
- Hatra
Zagros and Elam
(ordered from north to south)
- Hasanlu
- Takht-i-Suleiman
- Behistun
- Godin Tepe
- Awan
- Chogha Mish
- Tepe Sialk
- Susa
- Kabnak (Haft Tepe)
- Dur Untash (Chogha Zanbil)
- Shahr-i-Sokhte
- Pasargadai
- Naqsh-e Rustam
- Estakhr (Istakhr)
- Parsa (Persepolis)
- Tall-i Bakun
- Anshan (Tall-i Malyan or Tepe Malyan)
- Konar Sandal
- Shimashki (Kerman)
- Tepe Yahya
- Marhasi (Waraḫše, Marhaši, Marhashi, Parhasi, Barhasi)
Anatolia
(ordered from north to south)
- Miletus
- Sfard (Sardis)
- Nicaea
- Sapinuwa
- Yazilikaya
- Alaca Höyük
- Maşat Höyük
- Alishar Hüyük
- Hattusa
- Ilios (Wilusa, Ilion, Troas, Troy)
- Kanesh (Nesa, Kültepe)
- Arslantepe (Malatya)
- Çayönü (Amed, Diyarbakir)
- Sam'al (Zincirli Höyük)
- Çatalhöyük
- Beycesultan
- Karatepe
- Tushhan (Ziyaret Tepe)
- Adana
- Tarsus
- Zephyrion (Mersin)
- Gözlükule
- Sultantepe
- Attalia (Antalya)
The Levant
(all ordered alphabetically)
- Acco (Acre)
- Admah
- Adoraim (Adora, Dura)
- Alalah (Alalakh)
- Aleppo
- Al-Sinnabra (Khirbat al-Karak, Bet Yerah)
- Aphek (Antipatris, Tell Afik)
- Arad Rabbah (Tel Arad)
- Arqa (Arkat)
- Arwad (Tartus, Aradus, Arvad, Arphad, Ruad Island)
- Ashdod
- Ashkelon
- Baalbek (Heliopolis)
- Batroun (Botrys)
- Beersheba
- Beth Shean (Beth Shan)
- Bet Shemesh (house of Shamash)
- Bethany (beyond the Jordan)
- Bet-el
- Bezer
- Byblos (Gubla, Kepen)
- Capernaum
- Dan
- Damascus (Dimasqu, Dimashq)
- Deir Alla (Pethor?)
- Dhiban (Dibon)
- Dor (D-jr, Dora)
- Ebla (Tell Mardikh)
- En Gedi (Tell Goren)
- Enfeh (Ampi)
- Ekron (Tel Miqne)
- Et-Tell (Ai?)
- Gerasa / Jarash
- Gath
- Gaza
- Gezer
- Gibeah (Tell el-Ful?)
- Gilgal Refaim (Rujm el-Hiri)
- Gomorrah
- Hamath (Hama, Epiphania)
- Hazor
- Hebron
- Herodion (Herodium)
- Jawa
- Jericho (Tell es Sultan)

- Jerusalem (Jebus)
- Jezreel
- Kabri (Rehov?)
- Kadesh Barnea
- Kedesh (Qadesh)
- Khirbet el-Qom
- Khirbet Qeiyafa (Elah Fortress)
- Kir of Moab (Kerak)
- Kumidi (Kamid al lawz)
- Lachish (Tell ed-Duweir)
- Megiddo
- Qatna (Tell Mishrifeh)
- Qumran
- Rabat Amon (Philadelphia)
- Samaria
- Sarepta
- Sharuhen (Tell el-Ajjul)
- Shiloh
- Sidon
- Sodom
- Tadmor (Palmyra)
- Tall Zira'a
- Tell Balata (Shechem)
- Tell el-Hesi (Eglon?)
- Tell Kazel
- Tell Qarqur (Karkar?)
- Tell Tweini (Gibala?)
- Tirzah (Tell el-Farah North)
- Tyros (Tylos, Tyre)
- Ugarit (Ras Shamra)
- Umm el-Marra
- Zeboim
- Zemar (Sumura, Sumur)
- Zoara (Zoar, Bela)
Arabian Peninsula
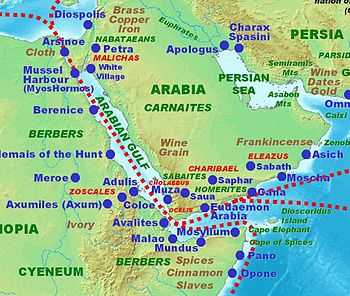
- Bakkah (Mecca)
- Barbar Temple
- Dedan (Al-`Ula)
- Dibba Al-Hisn
- Dumat Al-Jandal (Dumah)
- Ḥaram
- Kaminahu (Kamna)
- Lihyan
- Qal'at al-Bahrain
- Qarnāwu (Kárna)
- Mada'in Saleh (Al-Hijr, el Hijr, and Hegra)
- Ma'rib
- Ṣirwāḥ
- Tayma (Tema)
- Tell Abraq
- Ubar (Aram, Iram, Irum, Irem, Erum)
- Yathrib (Medina)
Kerma (Doukki Gel)
- Jebel Barkal
- Napata
- Meroë
- Aksum (Axum)
Horn of Africa
Egypt
This is a list of ancient Egyptian sites, throughout all of Egypt and Nubia. Sites are listed by their classical name whenever possible, if not by their modern name, and lastly with their ancient name if no other is available.
Nomes


A nome is a subnational administrative division of Ancient Egypt.
Lower Egypt
Upper Egypt
- Nome 1: Land of the arch or To Khentit: the frontier (Ta-Seti)
- Nome 2: Throne of Horus
- Nome 3: The rural (Shrine)
- Nome 4: The sceptre
- Nome 5: The two falcons
- Nome 6: The crocodile
- Nome 7: Sistrum
- Nome 8: Great lands
- Nome 9: Minu (Min)
- Nome 10: Cobra
- Nome 11: The Set animal (Seth)
- Nome 12: Viper mountain
- Nome 13: Upper pomegranate tree (Upper Sycamore and Viper)
- Nome 14: Lower pomegranate tree (Lower Sycamore and Viper)
- Nome 15: Hare
- Nome 16: Oryx
- Nome 17: The black dog (Jackal)
- Nome 18: Falcon with spread wings (Nemty)
- Nome 19: The pure sceptre (Two Sceptres)
- Nome 20: Upper laurel (Southern Sycamore)
- Nome 21: Lower laurel (Northern Sycamore)
- Nome 22: Knife
Lower Egypt (The Nile Delta)
- Alexandria
- Athribis (Modern: "Tell Atrib", Ancient: "Hut-Heryib" or "Hut-Tahery-Ibt")
- Avaris (Modern: "Tell el-Dab'a", Ancient: "Pi-Ri'amsese")
- Behbeit el-Hagar
- Bilbeis
- Bubastis (Modern: "Tell Basta", Ancient: "Bast")
- Busiris (Modern: "Abu Sir Bana")
- Buto (Modern: "Tell el-Fara'in", Ancient: "Pe")
- Cairo (or near Cairo)
- Abu Rawash
- Giza Necropolis (Giza Plateau)
- Khufu's Pyramid (Great Pyramid)
- Khafre's Pyramid
- Menkaure's Pyramid
- Great Sphinx of Giza
- Heliopolis (Modern: "Tell-Hisn", Ancient: "Iunu")
- Letopolis (Modern: "Ausim", Ancient: "Khem")
- Hermopolis Parva (Modern: "El-Baqliya" Ancient: "Ba'h")
- Iseum (Modern: "Behbeit el-Hagar", Ancient: "Hebyt")
- Kom el-Hisn (Ancient: "Imu" or "Yamu")
- Leontopolis (Yahudiya) (Modern: "Tell el-Yahudiya", Ancient: "Nay-Ta-Hut")
- Leontopolis (Modern: "Tell el-Muqdam")
- Naukratis (Modern: "el-Gi'eif", "el-Niqrash","el-Nibeira")
- Memphite Necropolis (Memphis)
- Abu Ghurab
- Abusir (Busiris)
- Pyramid of Neferefre
- Pyramid of Neferirkare
- Pyramid of Nyuserre
- Pyramid of Sahure
- Sun temple of Nyuserre
- Sun temple of Userkaf
- Dahshur
- Bent Pyramid
- Black Pyramid
- Red Pyramid
- White Pyramid
- Helwan
- Mit Rahina
- Saqqara
- Zawyet el'Aryan
- Mendes (Modern: "Tell el-Rub'a", Ancient: "'Anpet")
- Tell Tebilla
- Qantir / El-Khata'na
- Sais (Modern: "Sa el-Hagar", Ancient: "Zau")
- Saft el-Hinna (Ancient: "Per-Sopdu")
- Sebennytos (Modern: "Samannud", Ancient: "Tjebnutjer")
- Shagamba
- Suwa
- Taposiris Magna (Modern: "Abusir")
- Tanis (Modern: "San el-Hagar", Ancient: "Djan'net")
- Tell el-Maskhuta (Ancient: "Tjeku")
- Tell el-Rataba
- Tell el-Sahaba
- Tell Nabasha
- Tell Qua'
- Terenuthis (Modern: "Kom Abu Billo")
- Thmuis (Modern: "Tell el-Timai")
- Tura
- Xois (Modern: "Sakha")
Middle Egypt
The area from about Al Fayyum to Asyut is usually referred to as Middle Egypt.
- Akoris (Modern: "Tihna el-Gebel")
- Ankyronpolis (Modern: "el-Hiba", Ancient: "Teudjoi")
- Antinoopolis (Modern: "el-Sheikh 'Ibada")
- Deir el-Bersha
- Deir el-Gabrawi
- Dishasha
- Dja (Modern: "Medinet Madi" Ancient: "Narmouthis")
- el-'Amarna (Ancient: "Akhetaten")
- el-Sheikh Sa'id
- Faiyum
- Hermopolis Magna (Modern: "El Ashmunein", Ancient: "Khmun")
- Hebenu (Modern: "Kom el-Ahmar")
- Beni Hasan
- Speos Artemidos (Modern: "Istabl 'Antar")
- Zawyet el-Maiyitin
- Hur (Ancient: "Herwer")
- Lykopolis (Modern: "Asyut", Ancient: "Zawty")
- Meir
- Oxyrhynchus (Modern: "el-Bahnasa", Ancient: "Per-Medjed")
- Sharuna
- Tuna el-Gebel
Upper Egypt
Northern Upper Egypt
- Abydos (Ancient: "Abedju")
- el-'Araba el Madfuna
- Kom el-Sultan
- Umm el-Qa'ab
- Shunet ez Zebib
- Osireion
- Apollinopolis Parva (Modern: "Qus", Ancient: "Gesa" or "Gesy")
- Qus Necropolis
- Antaeopolis (Modern: "Qaw el-Kebir", Ancient: "Tjebu" or "Djew-Qa")
- Athribis (Modern: "Wannina", Ancient: "Hut-Repyt")
- Beit Khallaf
- Tentyris (Modern: "Dendera", Ancient: "Iunet" or "Tantere")
- Temple of Hathor
- Diospolis Parva (Modern: "Hiw", Ancient: "Hut-Sekhem")
- el-Hawawish
- el-Salamuni
- Khemmis or Panopolis (Modern: "Akhmin", Ancient: "Ipu" or "Khent-Min")
- Khenoboskion (Modern: "el-Qasr", "el-Saiyad")
- Koptos (Modern: "Qift", Ancient: "Gebtu")
- Naga ed-Der
- Nag' el-Madamud (Ancient: "Mabu")
- Ombos (Naqada) (Modern: "Naqada", Ancient: "Nubt")
- Shanhûr
Southern Upper Egypt
- Aphroditopolis (Modern: "Gebelein", Ancient: "Per-Hathor")
- Apollinopolis Magna (Modern: "Edfu", Ancient: "Djeba, Mesen")
- Aswan
- Agilkia Island
- Elephantine Island
- New Kalabsha
- Northern Granite Quarries
- Philae Island
- Qubbet el-Hawa
- Sehel Island
- Southern Granite Quarries
- el-Mo'alla (Ancient: "Hefat")
- Eileithyiaspolis (Modern: "el-Kab", Ancient: "Nekheb")
- Gebel el-Silsila (Ancient: "Kheny")
- Hermonthis (Modern: "Armant", Ancient: "Iuny")
- Hierakonpolis (Modern: "Kom el-Ahmar", Ancient: "Nekhen")
- Kom Ombo
- Ombos (Modern: "Kom Ombo", Ancient: "Nubt")
- Latopolis (Modern: "Esna", Ancient: "Iunyt, Senet, Tasenet")
- Medamud
- Thebes (Modern: "Luxor", Ancient: "Niwt-rst" or "Waset")
- Deir el-Medina
- Temple of Hathor
- Workmen's Village
- Workmen's Tombs
- Shrine to Meretseger & Ptah
- Deir el-Bahri
- Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut
- Mortuary Temple of Mentuhotep II
- Mortuary Temple of Thotmose III
- el-Malqata
- Karnak (Ancient: "Ipet-Isut")
- Temple of Amenhotep IV
- Precinct of Amon-Re
- Precinct of Montu
- Precinct of Mut
- Luxor (Ancient: "Ipet-Resyt")
- Medinet Habu
- Mortuary Temple & Palace of Ramesses III
- Mortuary Temple of Ay & Horemheb
- Mortuary Temple of Amenhotep III
- Mortuary Temple of Merneptah
- Mortuary Temple of Ramesses IV
- Mortuary Temple of Thutmose IV
- Mortuary Temple of Thutmose III
- Qasr el-'Aguz
- Temple of Thoth
- Qurna
- Tombs of the Nobles
- Ramesseum (Mortuary Temple of Ramesses II)
- Valley of the Kings (Modern: "Wadi el-Muluk")
- Valley of the Queens (Modern: "Biban el-Harim")
- Deir el-Medina
- Tuphium (Modern: "Tod", Ancient: "Djerty")
Lower Nubia

- Amada
- Abu Simbel
- Contra Pselchis (Modern: "Quban", Ancient: "Baki")
- Debod
- el-Lessiya
- Mi'am (Modern: "'Aniba")
- Primis (Modern: "Qasr Ibrim")
- Pselchis (Modern: "el-Dakka", Ancient: "Pselqet")
- Talmis (Modern: "Kalabsha")
- Beit el-Wali
- Temple of Derr
- Gerf Hussein
- Qasr Ibrim
- Wadi es-Sebua
- Taphis (Modern: "Tafa")
- Tutzis (Modern: "Dendur")
- Tzitzis (Modern: "Qertassi")
Upper Nubia
The Oases and Mediterranean coast
- Siwa Oasis
- Aghurmi
- el-Zeitun
- Gebel el-Mawta
- Qaret el-Musabberin
- Umm el-'Ebeida
- Bahriya Oasis
- el-Qasr
- el-Bawiti
- el-Hayz
- Farafra Oasis
- 'Ain el-Wadi
- el-Qasr
- el-Dakhla Oasis
- Amheida
- Balat
- Deir el-Hager
- el-Qasr
- Kellis (Modern: "Ismant el-Kharab")
- Mut el-Kharab
- Qaret el-Muzawwaqa
- el-Kharga Oasis
- Baris
- Gebel el-Teir
- Hibis
- Kysis (Modern: "Dush")
- Nadurs
- Qasr el-Ghueida
- Qasr Zaiyan
- Mediterranean Coast
Sinai
- Aqaba
- Arsinoe
- Eilat (Elath)
- Kuntillet Ajrud
- Pelusium (Sin)
- Rud el-'Air
- Serabit el-Khadim
- Tell Kedwa
- Wadi Maghareh
Eastern Desert
Notes and references
Bibliography
- Atlas of Ancient Egypt, John Baines & Jaromir Malek, America University of Cairo Press, 2002
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ancient Near East maps. |
- City-state
- Sumerian King List
- Historical cities
- Short chronology timeline
- List of oldest continuously inhabited cities
References
External links
- Geospatial: Mapping Iraq's Ancient Cities
- Ancient cities grew pretty much like modern ones, say scientists (February 2015), Christian Science Monitor
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

