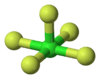
Chlorine pentafluoride
| |||
 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 13637-63-3 | |||
| |||
| Jmol-3D images | Image | ||
| PubChem | 61654 | ||
| RTECS number | FO2975000 | ||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| ClF5 | |||
| Molar mass | 130.445 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colorless gas | ||
| Density | 4.5 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −103 °C (−153 °F; 170 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −13.1 °C (8.4 °F; 260.0 K) | ||
| hydrolyzes | |||
| Structure | |||
| Molecular shape | Square pyramidal | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std molar entropy (S |
310.73 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−238.49 kJ mol−1 | ||
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Chlorine pentafluoride is an interhalogen compound with formula ClF5. This colourless gas is an strong oxidant that was once a candidate oxidizer for rockets. The molecule adopts a square pyramidal structure with C4v symmetry,[1] as confirmed by its high resolution 19F NMR spectrum.[2]
Preparation
Some of the earliest research on the preparation was classified.[3][4] It was first prepared by fluorination of chlorine trifluoride at high temperatures and high pressures:
- ClF3 + F2 → ClF5
NiF2 catalyzes this reaction.[5]
Certain metal fluorides, MClF4 (i.e. KClF4, RbClF4, CsClF4) react with F2 to produce ClF5 and the corresponding alkali metal fluoride.[4]
Reactions
In a highly exothermic reaction, water hydrolyses ClF5 to produce chloryl fluoride and hydrogen fluoride:[6]
- ClF
5 + 2 H
2O → FClO
2 + 4 HF
It is also a strong fluorinating agent. At room temperature it reacts readily with all elements except noble gases, nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 833. ISBN 0080379419.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Pilipovich, D., Maya, W., Lawton, E.A., Bauer, H.F., Sheehan, D. F., Ogimachi, N. N., Wilson, R. D., Gunderloy, F. C., Bedwell, V. E. (1967). "Chlorine pentafluoride. Preparation and Properties". Inorganic Chemistry 6 (10): 1918. doi:10.1021/ic50056a036.
- ↑ Clark, John (1972). Ignition! An Informal History of Liquid Rocket Propellants. Rutgers University Press. pp. 87–88. ISBN 0-8135-0725-1.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Smith D. F. (1963). "Chlorine Pentafluoride". Science 141 (3585): 1039–1040. doi:10.1126/science.141.3585.1039. PMID 17739492.
- ↑ Šmalc, A., Žemva, B., Slivnik, J., and Lutar K. (1981). "On the Synthesis of Chlorine Pentafluoride". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry 17 (4): 381–383. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81783-2.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 834. ISBN 0080379419.
External links
| ||||||
| ||||||||||