Centroacinar cell
"Acinar cell" redirects here. For other types, see
Acinus.
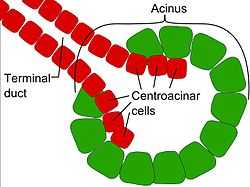
Centroacinar cells are spindle-shaped cells in the exocrine pancreas. Centroacinar cells are an extension of the intercalated duct cells into each pancreatic acinus.[1] The intercalated ducts take the bicarbonate to intralobular ducts which become lobular ducts. These lobular ducts finally converge to form the main pancreatic duct.[1]
These cells are commonly known as duct cells, and secrete an aqueous bicarbonate solution under stimulation by the hormone secretin. They also secrete mucin.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wendy Lackey M.A. (February 2011). "lectures ession 12". Oral Cavity and Upper GI tract (coursepack from Michigan State University College of Human Medicine). p. 327.
External links
|
|---|
| | Liver | |
|---|
| | Biliary tract | |
|---|
| | Pancreas | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Development
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Congenital
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Gluten sensitivity
- Other
- Symptoms and signs
- Blood tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- anabolic steroids
- antacids
- diarrhoea and infection
- bile and liver
- functional gastrointestinal disorders
- laxatives
- peptic ulcer and reflux
- nausea and vomiting
- other
- Surgery
|
|---|
|
|