Centralite
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
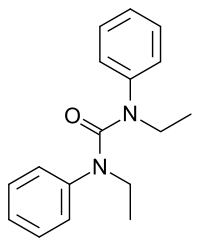
| IUPAC name
1,3-Diethyl-1,3-diphenylurea | |
| Other names
Ethyl centralite N,N′-Diethylcarbanilide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 85-98-3 | |
| ChemSpider | 6567 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 6828 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C17H20N2O |
| Molar mass | 268.35 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to light grey crystalline powder |
| Density | 0.8 g/cm3 |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility in Acetone, ethanol and benzene | Soluble |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Centralite (empirical formula: C17H20N2O) is a gunshot residue also known as ethyl centralite. Its IUPAC name is 1,3-diethyl-1,3-diphenylurea. Ethyl centralite is insoluble in water, but is soluble in acetone, ethanol and benzene. It is mainly used as a burning rate moderator and stabilizer for smokeless powder, and also a plasticizer for celluloid.
Naming
Synonyms
N,N'-diethyl-N,N'-diphenyl-; Carbanilide, N,N'-diethyl-; Centralite 1; 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-diphenylurea; Carbamite; Centralite; Centralite I; Ethyl centralite; N,N'-Diethyl-N,N'-diphenylurea; N,N'-Diethylcarbanilide; sym-Diethyldiphenylurea; 1,3-diethyldiphenylurea; Urea, N,N'-diethyl N,N'-diphenyl-; N,N'-diethyl-N,N'-diphenyl-urea; ethylcentralite; s-Diethyldiphenylurea; Bis(N-ethyl-N-phenyl)urea; Centralite-1; Centralite1; N,N-Diethylcarbanilide; Urea, 1,3-diethyl-1,3-diphenyl-; Usaf ek-1047; N,N'-Diethyl-N'-diphenyl-L-harnstoff; Diethyldiphenylharnstoff; 1,3-diethyl-1,3-diphenyl-urea; Centralit; Ethylcentralit; 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-diphenylharnstoff; ZENTRALIT; N,N'-Diphenyl-N,N'-diethylharnstoff; N,N'-Diphenyl-N,N'-diethylurea; N,N'-Diphenyl-N,N'-dimethylharnstoff; N,N'-Diphenyl-N,N'-dimethylurea; Diethyldiphenylurea.
The term "Centralite" was originally applied to dimethyldiphenylurea developed about 1906 at the German Central War Laboratory Zentralstelle fuer Wissenschaftlichtechnische Untersuchungen in Neubabelsberg as a deterrent coating for smokeless powder in military rifle cartridges. Thereafter, all hydrocarbon-substituted symmetrical diphenyl urea compounds used as smokeless powder deterrents (or moderants) were called centralites after the laboratory. The preferred ethyl centralite became known as Centralite No. 1 and the original methyl centralite was identified as Centralite No. 2. Butyl centralite was also used as a celluloid plasticizer.[2][3]
Notes
Its reaction history is considerably more complicated than that of diphenylurea. Ending up with nitrated anilines, the methyl analog centralite-2 or sym-dimethyldiphenylurea is also known and is used somewhat abroad. The centralite are considered to be somewhat less effective as stabilizers than 2-nitrodiphenylamine, but they are also quite good plasticizers. When found in propellants they are frequently used at higher fractions than the diphenylamines to take advantage of their plasticizing properties.
References
- Davis, Tenney L. (1943). The Chemistry of Powder & Explosives (Angriff Press [1992] ed.). John Wiley & Sons Inc. ISBN 0-913022-00-4.
- Davis, William C., Jr. (1981). Handloading. National Rifle Association of America. ISBN 0-935998-34-9.