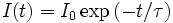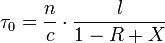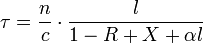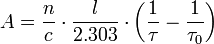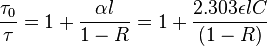Cavity ring-down spectroscopy
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) is a highly sensitive optical spectroscopic technique that enables measurement of absolute optical extinction by samples that scatter and absorb light. It has been widely used to study gaseous samples which absorb light at specific wavelengths, and in turn to determine mole fractions down to the parts per trillion level. The technique is also known as cavity ring-down laser absorption spectroscopy (CRLAS).
A typical CRDS setup consists of a laser that is used to illuminate a high-finesse optical cavity, which in its simplest form consists of two highly reflective mirrors. When the laser is in resonance with a cavity mode, intensity builds up in the cavity due to constructive interference. The laser is then turned off in order to allow the measurement of the exponentially decaying light intensity leaking from the cavity. During this decay, light is reflected back and forth thousands of times between the mirrors giving an effective path length for the extinction on the order of a few kilometers.
If something that absorbs light is placed in the cavity, the amount of light decreases faster—it makes fewer bounces before it is all gone. A CRDS setup measures how long it takes for the light to decay to 1/e of its initial intensity, and this "ringdown time" can be used to calculate the concentration of the absorbing substance in the gas mixture in the cavity.
Detailed description
Cavity ring down spectroscopy is a form of laser absorption spectroscopy. In CRDS, a laser pulse is trapped in a highly reflective (typically R > 99.9%) detection cavity. The intensity of the trapped pulse will decrease by a fixed percentage during each round trip within the cell due to both absorption and scattering by the medium within the cell and reflectivity losses. The intensity of light within the cavity is then determined as an exponential function of time.
The principle of operation is based on the measurement of a decay rate rather than an absolute absorbance. This is one reason for the increased sensitivity over traditional absorption spectroscopy, as the technique is then immune to shot-to-shot laser fluctuations. The decay constant, τ, which is the time taken for the intensity of light to fall to 1/e of the initial intensity, is called the ring-down time and is dependent on the loss mechanism(s) within the cavity. For an empty cavity, the decay constant is dependent on mirror loss and various optical phenomena like scattering and refraction:
where n is the index of refraction within the cavity, c is the speed of light in vacuum, l is the cavity length, R is the mirror reflectivity, and X takes into account other miscellaneous optical losses. This equation uses the approximation ln(1+x) ≈ x for x close to zero, which is the case under cavity ring-down conditions. Often, the miscellaneous losses are factored into an effective mirror loss for simplicity. An absorbing species in the cavity will increase losses according to the Beer-Lambert law. Assuming the sample fills the entire cavity,
where α is the absorption coefficient for a specific analyte concentration. The decadic absorbance, A, due to the analyte can be determined from both ring-down times.
Alternatively, the molar absorptivity, ε, and analyte concentration, C, can be determined from the ratio of both ring-down times. If X can be neglected, one obtains
Advantages of CRDS
There are two main advantages to CRDS over other absorption methods:
First, it is not affected by fluctuations in the laser intensity. In most absorption measurements, the light source must be assumed to remain steady between blank (no analyte), standard (known amount of analyte), and sample (unknown amount of analyte). Any drift (change in the light source) between measurements will introduce errors. In CRDS, the ringdown time does not depend on the intensity of the laser, so fluctuations of this type are not a problem.
Second, it is very sensitive due to its long pathlength. In absorption measurements, the smallest amount that can be detected is proportional to the length that the light travels through a sample. Since the light reflects many times between the mirrors, it ends up traveling long distances. For example, a laser pulse making 500 round trips through a 1 meter cavity will effectively have traveled through 1 kilometer of sample.
Thus the advantages include:
- High sensitivity due to the multipass nature (i.e. long pathlength) of the detection cell.
- Immunity to shot variations in laser intensity due to the measurement of a rate constant.
- Wide range of use for a given set of mirrors; typically ±5% of the center wavelength.
- High throughput, individual ring down events occur on the millisecond time scale.
- No need for a fluorophore, which makes it more attractive than LIF or REMPI for some (e.g. rapidly predissociating) systems.
Disadvantages of CRDS
- Spectra cannot be acquired quickly due to the monochromatic laser source which is used. Having said this, some groups are now beginning to develop the use of broadband LED or supercontinuum sources[1][2][3] for CRDS, the light of which can then be dispersed by a grating onto a CCD, or Fourier transformed spectrometer (mainly in broadband analogues of CRDS). Perhaps more importantly, the development of ICOS based techniques have now been demonstrated over the range from the near UV to the mid-infrared.
- Analytes are limited both by the availability of tunable laser light at the appropriate wavelength and also the availability of high reflectance mirrors at those wavelengths.
- Expense: the requirement for laser systems and high reflectivity mirrors often makes CRDS orders of magnitude more expensive than some alternative spectroscopic techniques.
See also
- Absorption spectroscopy
- Laser absorption spectrometry
- Noise-Immune Cavity-Enhanced Optical-Heterodyne Molecular Spectroscopy (NICE-OHMS)
- Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (TDLAS)
References
- ↑ K. Stelmaszczyk et al. (2009). "Towards supercontinuum cavity ring-down spectroscopy". Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O. 94 (3): 369. Bibcode:2009ApPhB..94..369S. doi:10.1007/s00340-008-3320-z.
- ↑ K. Stelmaszczyk et al. (2009). "Cavity ring-down absorption spectrography based on filament-generated supercontinuum light". Opt. Express 17 (5): 3673. Bibcode:2009OExpr..17.3673S. doi:10.1364/OE.17.003673.
- ↑ W. Nakaema et al. (2011). "PCF-Based Cavity Enhanced Spectroscopic Sensors for Simultaneous Multicomponent Trace Gas Analysis". Sensors 11 (2): 1620. doi:10.3390/s110201620.
- Anthony O'Keefe; David A.G. Deacon (1988). "Cavity ring-down Optical Spectrometer for absorption measurements using pulsed laser sources". Review of Scientific Instruments 59: 2544. Bibcode:1988RScI...59.2544O. doi:10.1063/1.1139895.
- Piotr Zalicki; Richard N. Zare (15 February 1995). "Cavity ring-down spectroscopy for quantitative absorption measurements". The Journal of Chemical Physics 102 (7): 2708–2717. Bibcode:1995JChPh.102.2708Z. doi:10.1063/1.468647.
- Giel Berden; Rudy Peeters; Gerard Meijer (2000). "Cavity ring-down spectroscopy: Experimental schemes and applications". International Reviews in Physical Chemistry 19 (4): 565–607. Bibcode:2000IRPC...19..565B. doi:10.1080/014423500750040627.