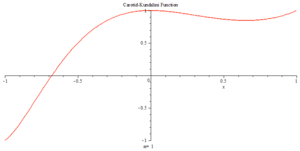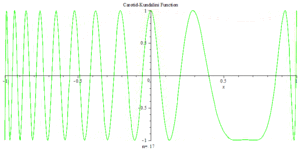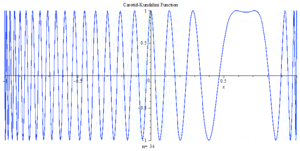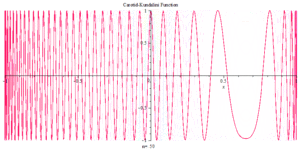
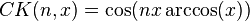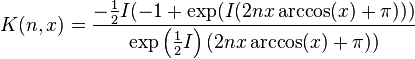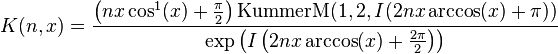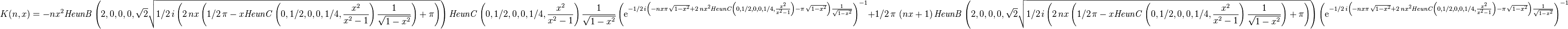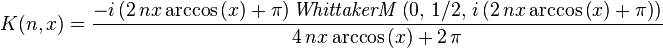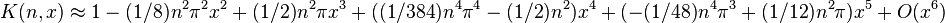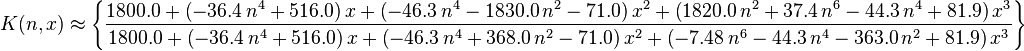Carotid–Kundalini function
Carotid–Kundalini function 2D animation with Maple

Carotid–Kundalini fractal land -1<x<0<br>Gaussian mountain -0.5<x<0.5<br>Oscillation land 0.5 <x

Carotid Kundalini function density plot with Maple
Carotid-Kundalini function derivative density plot
Carotid-Kundalini imaginary density plot

Carotid–Kundalini function phase diagram animation (Maple)

Carotid-Kundalini function derivative lace
The Carotid–Kundalini functionis closely associated with Carotid-Kundalini fractals coined by popular science columnist Clifford A. Pickover[1] and it is defined as follows[2]
Relations With Other Special Functions
Series Expansion
Pate Approximation
External links
- Carotid–Kundalini function
- Carotid-Kundalini fractal
- Carotid-Kundalini Fractal Explorer
- Carotid-Kundalini Fractals
References
- ↑
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W. "Carotid–Kundalini Function." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Carotid-KundaliniFunction.html