Carbonic anhydrase
| Carbonate dehydratase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
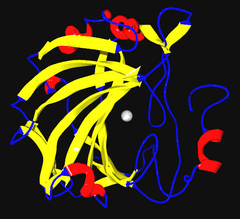
Ribbon diagram of human carbonic anhydrase II, with zinc ion visible in the center | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.2.1.1 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9001-03-0 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Eukaryotic-type carbonic anhydrase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Carb_anhydrase | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00194 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001148 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00146 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1can | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1can | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) form a family of enzymes that catalyze the rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to bicarbonate and protons (or vice versa), a reversible reaction that occurs relatively slowly in the absence of a catalyst.[1] The active site of most carbonic anhydrases contains a zinc ion; they are therefore classified as metalloenzymes.
One of the functions of the enzyme in animals is to interconvert carbon dioxide and bicarbonate to maintain acid-base balance in blood and other tissues, and to help transport carbon dioxide out of tissues.
Reaction
The reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase is:
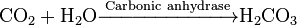 (in tissues - high CO2 concentration)[2]
(in tissues - high CO2 concentration)[2]
The reaction rate of carbonic anhydrase is one of the fastest of all enzymes, and its rate is typically limited by the diffusion rate of its substrates. Typical catalytic rates of the different forms of this enzyme ranging between 104 and 106 reactions per second.[3]
The reverse reaction is relatively slow (kinetics in the 15-second range) in the absence of a catalyst. This is why a carbonated drink does not instantly degas when opening the container; however it will rapidly degas in the mouth when it comes in contact with carbonic anhydrase that is contained in saliva.[4]
An anhydrase is defined as an enzyme that catalyzes the removal of a water molecule from a compound, and so it is this "reverse" reaction that gives carbonic anhydrase its name, because it removes a water molecule from carbonic acid.
Mechanism
A zinc prosthetic group in the enzyme is coordinated in three positions by histidine side-chains. The fourth coordination position is occupied by water. This causes polarisation of the hydrogen-oxygen bond, making the oxygen slightly more negative, thereby weakening the bond.
A fourth histidine is placed close to the substrate of water and accepts a proton, in an example of general acid - general base catalysis (see the article "Acid catalysis"). This leaves a hydroxide attached to the zinc.
The active site also contains specificity pocket for carbon dioxide, bringing it close to the hydroxide group. This allows the electron-rich hydroxide to attack the carbon dioxide, forming bicarbonate.
Families

There are at least five distinct CA families (α, β, γ, δ and ε). These families have no significant amino acid sequence similarity and in most cases are thought to be an example of convergent evolution. The α-CAs are found in humans.
α-CA
The CA enzymes found in mammals are divided into four broad subgroups,[5] which, in turn consist of several isoforms:
- the cytosolic CAs (CA-I, CA-II, CA-III, CA-VII and CA XIII) (CA1, CA2, CA3, CA7, CA13)
- mitochondrial CAs (CA-VA and CA-VB) (CA5A, CA5B)
- secreted CAs (CA-VI) (CA6)
- membrane-associated CAs (CA-IV, CA-IX, CA-XII, CA-XIV and CA-XV) (CA4, CA9, CA12, CA14)
There are three additional "acatalytic" CA isoforms (CA-VIII, CA-X, and CA-XI) (CA8, CA10, CA11) whose functions remain unclear.[6]
| Isoform | Gene | Molecular mass[7] | Location (cell) | Location (tissue)[7] | Specific activity of human enzymes (except for mouse CA XV) (s−1)[8] | Sensitivity to sulfonamides (acetazolamide in this table) KI (nM)[8] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA-I | CA1 | 29 kDa | cytosol | red blood cell and GI tract | 2.0 × 105 | 250 |
| CA-II | CA2 | 29 kDa | cytosol | almost ubiquitous | 1.4 × 106 | 12 |
| CA-III | CA3 | 29 kDa | cytosol | 8% of soluble protein in Type I muscle | 1.3 × 104 | 240000 |
| CA-IV | CA4 | 35 kDa | extracellular GPI-linked | GI tract, kidney, endothelium | 1.1 × 106 | 74 |
| CA-VA | CA5A | 34.7 kDa (predicted) | mitochondria | liver | 2.9 × 105 | 63 |
| CA-VB | CA5B | 36.4 kDa (predicted) | mitochondria | widely distributed | 9.5 × 105 | 54 |
| CA-VI | CA6 | 39-42 kDa | secretory | saliva and milk | 3.4 × 105 | 11 |
| CA-VII | CA7 | 29 kDa | cytosol | widely distributed | 9.5 × 105 | 2.5 |
| CA-IX | CA9 | 54, 58 kDa | cell membrane-associated | normal GI tract, several cancers | 1.1 × 106 | 16 |
| CA-XII | CA12 | 44 kDa | extracellularily located active site | kidney, certain cancers | 4.2 × 105 | 5.7 |
| CA-XIII[9] | CA13 | 29 kDa | cytosol | widely distributed | 1.5 × 105 | 16 |
| CA-XIV | CA14 | 54 kDa | extracellularily located active site | kidney, heart, skeletal muscle, brain | 3.1 × 105 | 41 |
| CA-XV[10] | CA15 | 34-36 kDa | extracellular GPI-linked | kidney, not expressed in human tissues | 4.7 × 105 | 72 |
β-CA
Most prokaryotic and plant chloroplast CAs belong to the beta family. Two signature patterns for this family have been identified:
- C-[SA]-D-S-R-[LIVM]-x-[AP]
- [EQ]-[YF]-A-[LIVM]-x(2)-[LIVM]-x(4)-[LIVMF](3)-x-G-H-x(2)-C-G
γ-CA
The gamma class of CAs come from methanogens, methane-producing bacteria that grow in hot springs.
δ-CA
The delta class of CAs has been described in diatoms. The distinction of this class of CA has recently[11] come into question, however.
ζ-CA
The Zeta class of CAs occurs exclusively in bacteria in a few chemolithotrophs and marine cyanobacteria that contain cso-carboxysomes.[12] Recent 3-dimensional analyses[11] suggest that ζ-CA bears some structural resemblance to β-CA, particularly near the metal ion site. Thus, the two forms may be distantly related, even though the underlying amino acid sequence has since diverged considerably.
Structure and function
Several forms of carbonic anhydrase occur in nature. In the best-studied α-carbonic anhydrase form present in animals, the zinc ion is coordinated by the imidazole rings of 3 histidine residues, His94, His96, and His119.
The primary function of the enzyme in animals is to interconvert carbon dioxide and bicarbonate to maintain acid-base balance in blood and other tissues, and to help transport carbon dioxide out of tissues.
There are at least 14 different isoforms in mammals. Plants contain a different form called β-carbonic anhydrase, which, from an evolutionary standpoint, is a distinct enzyme, but participates in the same reaction and also uses a zinc ion in its active site. In plants, carbonic anhydrase helps raise the concentration of CO2 within the chloroplast in order to increase the carboxylation rate of the enzyme RuBisCO. This is the reaction that integrates CO2 into organic carbon sugars during photosynthesis, and can use only the CO2 form of carbon, not carbonic acid or bicarbonate.
A cadmium-containing carbonic anhydrase was found to be expressed in marine diatoms during zinc limitation.[13] In the open ocean, zinc is often in such low concentrations that it can limit the growth of phytoplankton like diatoms; thus, a carbonic anhydrase using a different metal ion would be beneficial in these environments. Cadmium has in general been thought of as a very toxic heavy metal without biological function. This peculiar carbonic anhydrase form hosts the only known beneficial cadmium-dependent biological reaction.[13]
Industrial applications
Modified carbonic anhydrase enzymes have been used to replace methyl diethanolamine ("MDEA") in carbon dioxide capture.
See also
References
- ↑ Badger MR, Price GD (1994). "The role of carbonic anhydrase in photosynthesis". Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Bio. 45: 369–392. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.45.060194.002101.
- ↑ Carbonic acid has a pKa of around 6.36 (the exact value depends on the medium) so at pH 7 a small percentage of the bicarbonate is protonated. See carbonic acid for details concerning the equilibria HCO3− + H+
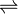 H2CO3 and H2CO3
H2CO3 and H2CO3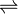 CO2 + H2O
CO2 + H2O - ↑ Lindskog S (1997). "Structure and mechanism of carbonic anhydrase". Pharmacol. Ther. 74 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1016/S0163-7258(96)00198-2. PMID 9336012.
- ↑ Thatcher BJ, Doherty AE, Orvisky E, Martin BM, Henkin RI (September 1998). "Gustin from human parotid saliva is carbonic anhydrase VI". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 250 (3): 635–41. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9356. PMID 9784398.
- ↑ Breton S (2001). "The cellular physiology of carbonic anhydrases". JOP 2 (4 Suppl): 159–64. PMID 11875253.
- ↑ Lovejoy DA, Hewett-Emmett D, Porter CA, Cepoi D, Sheffield A, Vale WW et al. (1998). "Evolutionarily conserved, "acatalytic" carbonic anhydrase-related protein XI contains a sequence motif present in the neuropeptide sauvagine: the human CA-RP XI gene (CA11) is embedded between the secretor gene cluster and the DBP gene at 19q13.3". Genomics 54 (3): 484–93. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5585. PMID 9878252.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Unless else specified: Walter F., PhD. Boron (2005). Medical Physiology: A Cellular And Molecular Approaoch. Elsevier/Saunders. ISBN 1-4160-2328-3. Page 638
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Hilvo M, Baranauskiene L, Salzano AM, Scaloni A, Matulis D, Innocenti A et al. (2008). "Biochemical characterization of CA IX, one of the most active carbonic anhydrase isozymes". J. Biol. Chem. 283 (41): 27799–809. doi:10.1074/jbc.M800938200. PMID 18703501.
- ↑ Lehtonen J, Shen B, Vihinen M, Casini A, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT et al. (2004). "Characterization of CA XIII, a novel member of the carbonic anhydrase isozyme family". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (4): 2719–27. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308984200. PMID 14600151.
- ↑ Hilvo M, Tolvanen M, Clark A, Shen B, Shah GN, Waheed A et al. (2005). "Characterization of CA XV, a new GPI-anchored form of carbonic anhydrase". Biochem. J. 392 (Pt 1): 83–92. doi:10.1042/BJ20051102. PMC 1317667. PMID 16083424.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Sawaya MR, Cannon GC, Heinhorst S, Tanaka S, Williams EB, Yeates TO et al. (2006). "The structure of beta-carbonic anhydrase from the carboxysomal shell reveals a distinct subclass with one active site for the price of two". J. Biol. Chem. 281 (11): 7546–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.M510464200. PMID 16407248.
- ↑ So AK, Espie GS, Williams EB, Shively JM, Heinhorst S, Cannon GC (2004). "A novel evolutionary lineage of carbonic anhydrase (zeta class) is a component of the carboxysome shell". J. Bacteriol. 186 (3): 623–30. doi:10.1128/JB.186.3.623-630.2004. PMC 321498. PMID 14729686.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Lane TW, Saito MA, George GN, Pickering IJ, Prince RC, Morel FM (May 2005). "Biochemistry: a cadmium enzyme from a marine diatom". Nature 435 (7038): 42. doi:10.1038/435042a. PMID 15875011. Lay summary – SSRL Science Highlight.
Further reading
- Lyall V, Alam RI, Phan DQ, Ereso GL, Phan TH, Malik SA et al. (September 2001). "Decrease in rat taste receptor cell intracellular pH is the proximate stimulus in sour taste transduction". Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. 281 (3): C1005–13. PMID 11502578.
- Goodsell D (2004-01-01). "Carbonic Anhydrase". PDB Molecule of the Month. Protein Data Bank. Retrieved 2011-05-28.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
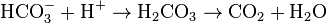 (in
(in 