Calopogon multiflorus
| Calopogon multiflorus | |
|---|---|
_001.jpg) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Genus: | Calopogon |
| Species: | C. multiflorus |
| Binomial name | |
| Calopogon multiflorus Lindl. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The Many-flowered Grass-pink, Calopogon multiflorus, is a species of orchid. It is a perennial forb that requires recurring ground fires to maintain its habitat. It falls under the genus Calopogon, meaning "beautiful beard" in Greek, referring to the stamen-like bristles or beard on the lip.[1]
Distribution
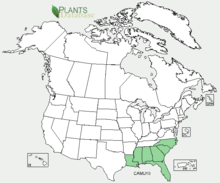
Calopogon multiflorus is distributed throughout southeastern United States. It can be found mainly in Florida and also Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, Louisiana, North Carolina, and South Carolina. This species has become endangered in Florida and North Carolina.[2]
Habitat and ecology
Calopogon multiflorus can be found in dry to moist flatwoods with wiregrass, longleaf pine, and saw palmetto. Its habitat also includes mesic pine savannahs on flat or gently-sloping terrain. These longleaf pine savannas were once widespread in southeastern North America,[3] and they burned naturally at least once a decade (see map in fire ecology). Large areas of suitable habitat have since been lost from logging and fire suppression.
The soil it grows in is usually sandy to loamy and acidic. Other species that are found growing nearby in the same habitat are longleaf pine (Pinus palustris), blackjack oak (Quercus marilandica), little gallberry/ink berry (Ilex glabra), slender bluestem (Schizachyrium tenerum), little bluestem (S. scoparium), and savannah meadow beauty (Rhexia alifanus).[4] Over a wide range, this species typically does not occur on wet savannahs and bogs with pitcher plants, although one location in Louisiana does have some plants coexisting with pitcher plants.[4]
C. multiflorus requires prescribed annual winter fires for its appearance. In this way it is typical of many of the understory plants in pine savannas.[5] It is known to bloom six to eight weeks after a burn, likely benefitting from the lack of competition with other plants, and the nutrients released during a fire.[4]
Morphology
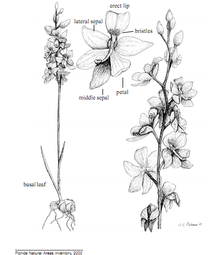
Characteristics of C. multiflorus are a dark purple rachis, a forked corm; pandurate lateral petals; elongated, acuminate floral bracts measuring (0.3–0.8)×(0.3–0.5) cm; and a pungent floral fragrance at peak anthesis.[6]
Pollination
This species falsely lures naïve, recently emerged bees with the offer of pollen, but it is not fulfilled.The beard of the flower is deceptive in that once the insect lands on it, the lip of the beard swings down, hingelike, placing the insect’s head and back on the column thereby picking up the pollinum, or placing the pollinum on the stigma if the insect already carries a load on its back.[1]
Flowering season
The flowering season for C. multiflorus ranges from March to May. The average flowering season in Louisiana is mid-April.[4]
How they grow
After sprouting in early spring, a single leaf, or sometimes two, appear clasping the bloom stem. The number of flowers can range from fifteen to just one flower on a stem. When the flower buds mature, they open in quick succession. Sometimes, it takes only two days for all of the flowers to open. They remain open for a couple days before withering and dropping to the ground.[1]
This species requires full sun to light shade to grow ideally.
Conservation status
Although this orchid is known historically in Florida and other managed areas, it is now rare due to fire suppression and conversion of habitat to pine plantations.[7]
Protection and management
One way to protect this species is to burn flatwoods every 2–3 years during the growing season. These flatwoods can also be protected from bedding, draining, clearcutting, roller-chopping and other soil and hydrology disturbances.[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 James Alexander Fowler; Paul Martin Brown (28 February 2005). Wild orchids of South Carolina: a popular natural history. Univ of South Carolina Press. pp. 15–. ISBN 978-1-57003-566-1. Retrieved 25 May 2011.
- ↑ Calopogon multiflorus Lindl, US Department of Agriculture
- ↑ Peet, R. K. and Allard, D. J. (1993). Longleaf pine vegetation of the southern Atlantic and eastern Gulf Coast regions: a preliminary classification. In The Longleaf Pine Ecosystem: Ecology, Restoration and Management, ed. S. M. Hermann, pp. 45–81. Tallahassee, FL: Tall Timbers Research Station.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Calopogon multiflorus – many-flowered grass-pink, Rare Plants of Louisiana, Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries
- ↑ Peet, R. K. and Allard, D. J. (1993). Longleaf pine vegetation of the southern Atlantic and eastern Gulf Coast regions: a preliminary classification. In The Longleaf Pine Ecosystem: Ecology, Restoration and Management, ed. S. M. Hermann, pp. 45–81. Tallahassee, FL: Tall Timbers Research Station.
- ↑ Goldman, D. H.; Orzell, S. L. (2000). "Morphological, geographical, and ecological re-evaluation of Calopogon multiflorus (Orchidaceae)". Lindleyana 15 (4): 237–251.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 MANY-FLOWERED GRASSPINK. Calopogon multiflorus Lindl. Synonym: Calopogon barbatus, Florida Natural Areas Inventory, Field Guide to Rare Plants.
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.