Calliophis intestinalis
| Calliophis intestinalis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Vertebrata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Elapidae |
| Genus: | Calliophis |
| Species: | C. intestinalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Calliophis intestinalis (Laurenti, 1768) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Calliophis intestinalis, commonly known as the banded Malaysian coral snake, is a species of venomous elapid snake endemic to Southeast Asia.[1]
Geographic range
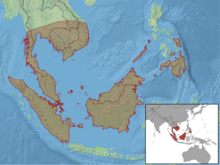
C. intestinalis is found in Borneo, Indonesia, Java, Malaysia, the Mentawai Archipelago, the Philippines, Singapore, Sumatra, Thailand, and Vietnam.[3]
Venom
This small species possesses a potent venom, and human fatalities from its bite have been recorded.[4]
Subspecies
Seven subspecies are recognized, including the nominotypical subspecies.[3][5]
- Calliophis intestinalis bilineata (W. Peters, 1881)
- Calliophis intestinalis everetti (Boulenger, 1896)
- Calliophis intestinalis intestinalis (Laurenti, 1768)
- Calliophis intestinalis lineata (Gray, 1835)
- Calliophis intestinalis philippina (Günther, 1864)
- Calliophis intestinalis suluensis (Steindachner, 1891)
- Calliophis intestinalis thepassi (Bleeker, 1859)
Nota bene: A trinomial authority in parentheses indicates that the subspecies was originally described in a genus other than Calliophis.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.iucnredlist.org/apps/redlist/details/177500/0
- ↑ Boulenger GA. 1896. Catalogue of the Snakes in the British Museum (Natural History). Volume III., Containing the Colubridæ (Opisthoglyphae and Proteroglyphæ), ... London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis, printers). xiv + 727 pp. + Plates I-XXV. (Doliophis intestinalis, pp. 401-404).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org.
- ↑ Das I. 2006. A Photographic Guide to Snakes and Other Reptiles of Borneo. Sanibel Island, Florida: Ralph Curtis Books. 144 pp. ISBN 0-88359-061-1. (Calliophis intestinalis, p. 62).
- ↑ ITIS (Integrated Taxonomic Information System). www.itis.gov.
Further reading
- Boulenger GA. 1890. The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma. Reptilia and Batrachia. London: Secretary of State for India in Council. (Taylor and Francis, printers). xviii + 541 pp. (Adeniophis intestinalis, pp. 386-387).
- Cantor TE. 1847. Catalogue of Reptiles Inhabiting the Malayan Peninsula and Islands. J. Asiatic Soc. Bengal, Calcutta 16 (2): 607-656, 897-952, 1026-1078. (Elaps intestinalis, p. 1028).
- Laurenti JN. 1768. Specimen medicum, exhibens synopsin reptilium emendatum cum experimentis circa venena et antidota reptilium austriacorum. Vienna: "Joan. Thom. Nob. de Trattnern". 214 pp. + Plates I-V. (Aspis intestinalis, p. 106).
- Slowinski JB, Boundy J, Lawson R. 2001. The phylogenetic relationships of Asian coral snakes (Elapidae: Calliophis and Maticora) based on morphological and molecular characters. Herpetologica 57 (2): 233-245.
