Calcium chromate
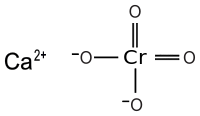 Calcium chromate | |
 Calcium chromate dihydrate | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Calcium dioxido-dioxo-chromium | |
| Other names
Calcium chromate (VI) Calcium monochromate Calcium Chrome Yellow C. I. Pigment Yellow 33 Gelbin Yellow Ultramarine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 13765-19-0 | |
| ChemSpider | 24471 |
| EC number | 237-66-8 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 26264 |
| RTECS number | GB2750000 |
| |
| Properties | |
| CaCrO4 | |
| Molar mass | 156.072 g/mol |
| Appearance | bright yellow powder |
| Density | 3.12 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 2,710 °C (4,910 °F; 2,980 K) |
| anhydrous 4.5 g/100 mL (0 °C) 2.25 g/100 mL (20 °C) dihydrate 16.3 g/100mL (20 °C) 18.2 g/100mL (40 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in acid practically insoluble in alcohol |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | monoclinic |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions |
calcium dichromate |
| Other cations |
Beryllium chromate Magnesium chromate Strontium chromate Barium chromate Radium chromate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Calcium chromate (CaCrO4) is a bright yellow solid. It normally occurs as the dihydrate.
Properties
Calcium chromate loses water at 200 °C. It reacts with organic matter or reducing agents to form chromium(III). The solid will react explosively with hydrazine. If mixed with boron and ignited, calcium chromate will burn violently.[1]
Uses
It is used as a pigment, a corrosion inhibitor, and in electroplating, photochemical processing, and industrial waste treatment.