Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling
The Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling in organic chemistry is a coupling reaction between a terminal alkyne and a haloalkyne catalyzed by a copper(I) salt such as copper(I) bromide and an amine base.[1][2] The reaction product is a di-acetylene or di-alkyne.
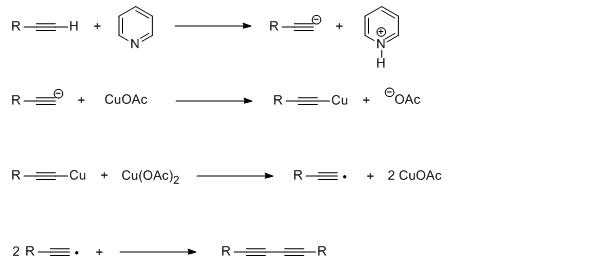
The reaction mechanism involves deprotonation by base of the acetylenic proton followed by formation of a copper(I) acetylide. A cycle of oxidative addition and reductive elimination on the copper center then creates a new carbon-carbon bond.
Related couplings are the Glaser coupling and the Eglinton coupling.
Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling
In one study[3] the Cadiot–Chodkiewicz coupling has been applied in the synthesis of acetylene macrocycles starting from cis-1,4-diethynyl-1,4-dimethoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene. This compound is also the starting material for the dibromide through NBS and silver nitrate:

The coupling reaction itself takes place in methanol with piperidine, the hydrochloric acid salt of hydroxylamine and copper(I) bromide.
Eglinton reaction
In the related Eglinton reaction[4] two terminal alkynes are coupled directly by a copper(II) salt such as cupric acetate.

The Eglinton Reaction[5] has been used to synthesize a number of fungal antibiotics and is important for carbon-carbon bond formation via the oxidative coupling of alkynes.[6]
This procedure was used in the synthesis of cyclooctadecanonaene.[7] Another example is the synthesis of diphenyldiacetylene from phenylacetylene.[8]
Hay coupling
The Hay coupling (1962) is another version of the Glaser coupling with the TMEDA complex of copper(I) chloride.[9] An example is the coupling of trimethylsilylacetylene.[10]
See Also
- Glaser coupling - Another alkyne coupling reaction catalysed by copper (I).
- Sonogashira coupling - Pd/Cu catalysed coupling of an alkyne with an aryl or vinyl halide
- Castro–Stephens coupling - A cross-coupling reaction between a copper(I) acetylide and an aryl halide
References
- ↑ Chodkiewicz, W. Ann. Chim. Paris 1957, 2, 819–69.
- ↑ Cadiot, P.; Chodkiewicz, W. In Chemistry of Acetylenes; Viehe, H. G., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, 1969; pp 597–647.
- ↑ Bandyopadhyay, Arkasish; Varghese, Babu; Sankararaman, Sethuraman. "Synthesis of 1,4-Cyclohexadiene-Based Acetylenic Macrocycles with Cadiot−Chodkiewicz Coupling. Structure of a Tub-Shaped Tetrameric Container". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 71 (12): 4544–4548. doi:10.1021/jo0605290.
- ↑ G. Eglinton and A. R. Galbraith, J. Chem. Soc., 889 (1959).
- ↑ Eglinton, G.; Galbraith, A. R.; Chem. Ind. 1956, 737.
- ↑ Eglinton, G.; McRae, W. Adv. Org. Chem. 1963, 4, 225.
- ↑ K. Stöckel and F. Sondheimer (1988). "[18]Annulene". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 6, p. 68
- ↑ I. D. Campbell and G. Eglinton (1973). "Diphenyldiacetylene". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 5, p. 517
- ↑ Hay, Allan S. "Oxidative Coupling of Acetylenes. II". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 27 (9): 3320–3321. doi:10.1021/jo01056a511.
- ↑ Graham E. Jones, David A. Kendrick, and Andrew B. Holmes (1993). "1,4-Bis(trimethylsilyl)buta-1,3-diyne". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 8, p. 63