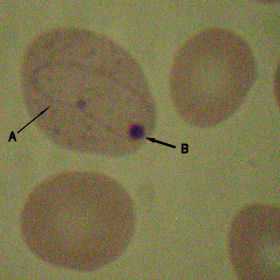
Cabot rings
Cabot rings are thin, red-violet staining, threadlike strands in the shape of a loop or figure-8 that are found on rare occasions in red blood cells (erythrocytes). They are believed to be microtubules that are remnants from a mitotic spindle, and their presence indicates an abnormality in the production of red blood cells.[1]
Histologic appearance
Cabot rings appear under a microscope as ring or loop-shaped structures. Cabot rings stains red or purple with a Wright's stain.
Associated conditions
Cabot rings have been observed in a handful of cases in patients with pernicious anemia, lead poisoning, certain other disorders of red blood cell production (erythropoiesis).[1]
History
They were first described in 1903 by American physician, Richard Clarke Cabot (1868-1939).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McPherson, Richard A; MR Pincus. Henry's clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods (22nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. p. 526. ISBN 978-1437709742.
Further reading
- Kass, L (July 1975). "Origin and composition of Cabot rings in pernicious anemia.". American Journal of Clinical Pathology 64 (1): 53–7. PMID 1155375.
External links
|
|---|
| | Inclusion bodies | |
|---|
| | Tests | |
|---|
| | Other | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Immune system
- Cells
- Physiology
- coagulation
- proteins
- granule contents
- colony-stimulating
- heme and porphyrin
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Red blood cell
- Monocyte and granulocyte
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Histiocytosis
- Symptoms and signs
- Blood tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Transfusion
- Drugs
- thrombosis
- bleeding
- other
|
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| | Red blood cells | |
|---|
| | Lymphocytes | |
|---|
| | Small molecules | |
|---|
| | Proteins | |
|---|
| | Minerals | |
|---|
| | Pathogens/sepsis | |
|---|
| |
|---|
| | Description |
- Immune system
- Cells
- Physiology
- coagulation
- proteins
- granule contents
- colony-stimulating
- heme and porphyrin
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Red blood cell
- Monocyte and granulocyte
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Histiocytosis
- Symptoms and signs
- Blood tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Transfusion
- Drugs
- thrombosis
- bleeding
- other
|
|---|
|
|---|
| | Description |
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Development
- Cells
|
|---|
| | Disease |
- Electrolyte and acid-base
- Congenital
- Neoplasms and cancer
- Other
- Symptoms and signs
- Urine tests
- Blood tests
|
|---|
| | Treatment |
- Procedures
- Drugs
- Intravenous fluids
|
|---|
|
|