CCHCR1
| Coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Symbols | CCHCR1 ; C6orf18; HCR; SBP | ||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 605310 MGI: 2385321 HomoloGene: 10396 GeneCards: CCHCR1 Gene | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| RNA expression pattern | |||||||||||||
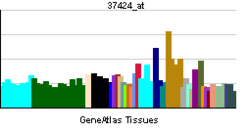 | |||||||||||||
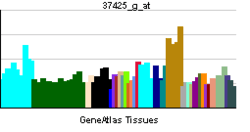 | |||||||||||||
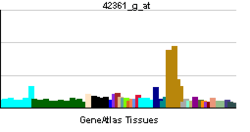 | |||||||||||||
| More reference expression data | |||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||
| Entrez | 54535 | 240084 | |||||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000204536 | ENSMUSG00000040312 | |||||||||||
| UniProt | Q8TD31 | Q8K2I2 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001105563 | NM_146248 | |||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001099033 | NP_666360 | |||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 6: 31.11 – 31.13 Mb | Chr 17: 35.52 – 35.53 Mb | |||||||||||
| PubMed search | |||||||||||||
Coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1, also known as CCHCR1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CCHCR1 gene.[1][2][3]
Clinical significance
In genetically engineered mice, certain CCHCR1 polymorphisms cause upregulation of the expression of cytokeratins 6 (KRT6A), 16 (KRT16) and 17 (KRT17) and change in expression in other genes associated with terminal differentiation and formation of the cornified cell envelope. These CCHCR1 polymorphisms may therefore be associated with a susceptibility to psoriasis.[4] Defective functioning of CCHCR1 may lead to abnormal keratinocyte proliferation which is a key feature of psoriasis.[5]
Interactions
CCHCR1 has been shown to interact with POLR2C.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: CCHCR1 coiled-coil alpha-helical rod protein 1".
- ↑ Asumalahti K, Laitinen T, Itkonen-Vatjus R, Lokki ML, Suomela S, Snellman E et al. (June 2000). "A candidate gene for psoriasis near HLA-C, HCR (Pg8), is highly polymorphic with a disease-associated susceptibility allele". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (10): 1533–42. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.10.1533. PMID 10888604.
- ↑ Oka A, Tamiya G, Tomizawa M, Ota M, Katsuyama Y, Makino S et al. (November 1999). "Association analysis using refined microsatellite markers localizes a susceptibility locus for psoriasis vulgaris within a 111 kb segment telomeric to the HLA-C gene". Hum. Mol. Genet. 8 (12): 2165–70. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.12.2165. PMID 10545595.
- ↑ Elomaa O, Majuri I, Suomela S, Asumalahti K, Jiao H, Mirzaei Z et al. (August 2004). "Transgenic mouse models support HCR as an effector gene in the PSORS1 locus". Hum. Mol. Genet. 13 (15): 1551–61. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh178. PMID 15190014.
- ↑ Tiala I, Wakkinen J, Suomela S, Puolakkainen P, Tammi R, Forsberg S et al. (April 2008). "The PSORS1 locus gene CCHCR1 affects keratinocyte proliferation in transgenic mice". Hum. Mol. Genet. 17 (7): 1043–51. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm377. PMID 18174193.
- ↑ Corbi N, Bruno T, De Angelis R, Di Padova M, Libri V, Di Certo MG et al. (September 2005). "RNA polymerase II subunit 3 is retained in the cytoplasm by its interaction with HCR, the psoriasis vulgaris candidate gene product". J. Cell. Sci. 118 (Pt 18): 4253–60. doi:10.1242/jcs.02545. PMID 16141233.
Further reading
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, Fuldner RA, Bult CJ, Lee NH et al. (1995). "Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence" (PDF). Nature 377 (6547 Suppl): 3–174. PMID 7566098.
- Oka A, Tamiya G, Tomizawa M, Ota M, Katsuyama Y, Makino S et al. (1999). "Association analysis using refined microsatellite markers localizes a susceptibility locus for psoriasis vulgaris within a 111 kb segment telomeric to the HLA-C gene". Hum. Mol. Genet. 8 (12): 2165–70. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.12.2165. PMID 10545595.
- Asumalahti K, Laitinen T, Itkonen-Vatjus R, Lokki ML, Suomela S, Snellman E et al. (2000). "A candidate gene for psoriasis near HLA-C, HCR (Pg8), is highly polymorphic with a disease-associated susceptibility allele". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (10): 1533–42. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.10.1533. PMID 10888604.
- O'Brien KP, Holm SJ, Nilsson S, Carlén L, Rosenmüller T, Enerbäck C et al. (2001). "The HCR gene on 6p21 is unlikely to be a psoriasis susceptibility gene". J. Invest. Dermatol. 116 (5): 750–4. doi:10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01323.x. PMID 11348465.
- Asumalahti K, Veal C, Laitinen T, Suomela S, Allen M, Elomaa O et al. (2002). "Coding haplotype analysis supports HCR as the putative susceptibility gene for psoriasis at the MHC PSORS1 locus". Hum. Mol. Genet. 11 (5): 589–97. doi:10.1093/hmg/11.5.589. PMID 11875053.
- Xu YC, Wu RF, Gu Y, Yang YS, Yang MC, Nwariaku FE et al. (2002). "Involvement of TRAF4 in oxidative activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (31): 28051–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202665200. PMID 12023963.
- Sugawara T, Shimizu H, Hoshi N, Nakajima A, Fujimoto S (2003). "Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein-binding protein cloned by a yeast two-hybrid system". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (43): 42487–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.M302291200. PMID 12909641.
- Suomela S, Elomaa O, Asumalahti K, Kariniemi AL, Karvonen SL, Peltonen J et al. (2003). "HCR, a candidate gene for psoriasis, is expressed differently in psoriasis and other hyperproliferative skin disorders and is downregulated by interferon-gamma in keratinocytes". J. Invest. Dermatol. 121 (6): 1360–4. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12642.x. PMID 14675183.
- Brandenberger R, Wei H, Zhang S, Lei S, Murage J, Fisk GJ et al. (2004). "Transcriptome characterization elucidates signaling networks that control human ES cell growth and differentiation". Nat. Biotechnol. 22 (6): 707–16. doi:10.1038/nbt971. PMID 15146197.
- Lim J, Hao T, Shaw C, Patel AJ, Szabó G, Rual JF et al. (2006). "A protein-protein interaction network for human inherited ataxias and disorders of Purkinje cell degeneration". Cell 125 (4): 801–14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.032. PMID 16713569.
- Chang J, Nicolas E, Marks D, Sander C, Lerro A, Buendia MA et al. (2004). "miR-122, a mammalian liver-specific microRNA, is processed from hcr mRNA and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1". RNA Biol 1 (2): 106–13. doi:10.4161/rna.1.2.1066. PMID 17179747.
- Tiala I, Suomela S, Huuhtanen J, Wakkinen J, Hölttä-Vuori M, Kainu K et al. (2007). "The CCHCR1 (HCR) gene is relevant for skin steroidogenesis and downregulated in cultured psoriatic keratinocytes". J. Mol. Med. 85 (6): 589–601. doi:10.1007/s00109-006-0155-0. PMID 17221218.
- Suomela S, Kainu K, Onkamo P, Tiala I, Himberg J, Koskinen L et al. (2007). "Clinical associations of the risk alleles of HLA-Cw6 and CCHCR1*WWCC in psoriasis". Acta Derm. Venereol. 87 (2): 127–34. doi:10.2340/00015555-0184. PMID 17340018.
- "Ulmus americana L. American Elm". United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2014-04-14. Retrieved 2014-04-14.
- Corbi N, Bruno T, De Angelis R, Di Padova M, Libri V, Di Certo MG et al. (Sep 2005). "RNA polymerase II subunit 3 is retained in the cytoplasm by its interaction with HCR, the psoriasis vulgaris candidate gene product". Journal of Cell Science 118 (Pt 18): 4253–60. doi:10.1242/jcs.02545. PMID 16141233.
- Edward F. Gilman, Dennis G. Watson (2011-06-03). "Ulmus parvifolia: Chinese Elm". University of Florida IFAS Extention. Retrieved 2014-04-14.
- "Ulmus L. Elm". United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2014-04-14. Retrieved 2014-04-14.
- ZymoprepTM Yeast Plasmid Miniprep II, Zymo Research
- Tiala I, Wakkinen J, Suomela S, Puolakkainen P, Tammi R, Forsberg S et al. (Apr 2008). "The PSORS1 locus gene CCHCR1 affects keratinocyte proliferation in transgenic mice". Human Molecular Genetics 17 (7): 1043–51. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddm377. PMID 18174193.
- "Ulmus L. Elm". United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2014-04-14. Retrieved 2014-04-14.
- Elomaa O, Majuri I, Suomela S, Asumalahti K, Jiao H, Mirzaei Z et al. (Aug 2004). "Transgenic mouse models support HCR as an effector gene in the PSORS1 locus". Human Molecular Genetics 13 (15): 1551–61. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh178. PMID 15190014.
- Caldwell, Guy A; Williams, Shelli N; Caldwell, Kim A (2006-09-11). Integrated Genomics: A Discovery-Based Laboratory Course (1 ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ISBN 0470095024.