Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 894–896
| Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 894–896 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Byzantine–Bulgarian wars | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
Bulgarian Empire Pechenegs |
Byzantine Empire Magyars | ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Simeon I the Great |
Leo VI the Wise Prokopios Krenites Leo Katakalon Liüntika | ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| Unknown | Unknown | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Unknown | Heavy | ||||||||
| ||||||
The Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 894–896 (Bulgarian: Българо–византийска война от 894–896), also called the Trade war (Bulgarian: Търговската война), was fought between the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire as a result of the decision of the Byzantine emperor Leo VI to move the Bulgarian market from Constantinople to Thessaloniki which would greatly increase the expenses of the Bulgarian merchants.
Following the defeat of the Byzantine army in the initial stages of the war in 894 Leo VI sought aid from the Magyars who at the time inhabited the steppes to the north-east of Bulgaria. Aided by the Byzantine navy, in 895 the Magyars invaded Dobrudzha and defeated the Bulgarian troops. Simeon I called for truce and deliberately protracted the negotiations with the Byzantines until securing the assistance of the Pechenegs. Cornered between the Bulgarians and the Pechanegs, the Magyars suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of the Bulgarian army and had to migrate westwards, settling in Pannonia.
With the Magyar threat eliminated, Simeon led his hosts south and routed the Byzantine army in the battle of Boulgarophygon in the summer of 896, which forced Byzantium to agree to the Bulgarian terms. The war ended with a peace treaty which restored the Bulgarian market in Constantinople and confirmed Bulgarian domination in the Balkans. The Byzantine Empire was obliged to pay Bulgaria an annual tribute in exchange for the return of captured Byzantine soldiers and civilians. Under the treaty, the Byzantines also ceded an area between the Black Sea and the Strandzha mountains to Bulgaria. Despite several violations, the treaty formally lasted until Leo VI's death in 912.
Background
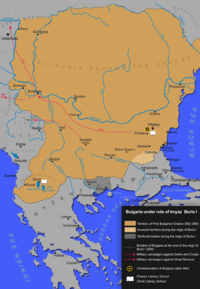
During the reign of Boris I (r. 852–889) Bulgaria underwent major changes — the Christianization of the country and the admission of the disciples of Saints Cyril and Methodius, which marked the beginning of the creation and consolidation of the medieval Bulgarian literature and alphabet. Following intense negotiations with the Papacy in Rome and the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Bulgaria converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity, which caused discontent among part of the nobility who directly associated the new religion with the Byzantine Empire and feared that the country would fall under Byzantine influence.[1]
During the Council of Preslav in 893, assembled after the unsuccessful attempt of Boris I's eldest son Vladimir-Rasate (r. 889–893) to restore the traditional Bulgar religion, Tengriism, it was decided that Old Bulgarian would replace Greek as the language of the church and the Byzantine clergy would be banished and replaced with Bulgarians.[2][3] The Council sealed Boris I's ambitions to secure the cultural and religious independence from the Byzantine Empire[4] and calmed down the concerns among the nobility. It was also decided that his third son Simeon, born after the Christianization and called the "child of peace",[5] would become the next Prince of Bulgaria.[6][7] These events brought an end to the Byzantine hopes to exert influence over the newly Christianized country.[6][8]
Prelude

In 894 Stylianos Zaoutzes, basileopator and leading minister of Leo VI the Wise (r. 886–912), convinced the emperor to move the Bulgarian market from Constantinople to Thessaloniki.[9] That move affected not only private interests but also the international commercial importance of Bulgaria and the principle of Byzantine–Bulgarian trade, regulated with the Treaty of 716 and later agreements on the most favoured nation basis.[10][11][12] The Bulgarian merchants were allowed to live in Constantinople, resided in their own colony and paid favourable taxes.[10] The city was a major destination of trade routes from all over Europe and Asia and the transfer of the Bulgarian market to Thessaloniki cut short the direct access to goods from the east, which under the new circumstances the Bulgarians would have to buy through middlemen, who were close associates of Stylianos Zaoutzes. In Thessaloniki the Bulgarians were also forced to pay higher tariffs to sell their goods, enriching Zaoutzes' cronies.[10]
The Byzantine chronicler Theophanes Continuatus described the reasons for the conflict as follows:
| “ | The cause of the war was the following — the basileopator Stylianos Zaoutzes had an eunuch slave named Mousikos. He befriended Staurakios and Cosmas, who originated from Hellas, merchants greedy for profit and covetous. In their desire to enrich themselves and through the mediation of Mousikos, they moved the market of the Bulgarians from the capital [Constantinople] to Thessaloniki and taxed the Bulgarians with heavier duties. When the Bulgarians acquainted Simeon with the issue, he informed emperor Leo. Infatuated in his predilection to Zaoutzes, he considered all this a trifle. Simeon was infuriated and raised arms against the Romans. | ” |
The ousting of the merchants from Constantinople was a heavy blow for Bulgarian economic interests.[14] The merchants complained to Simeon I, who in turn raised the issue to Leo VI, but the appeal was left unanswered.[6] Simeon, who according to the Byzantine chroniclers was seeking a pretext to declare war and to implement his plans to seize the Byzantine throne,[15] attacked,[16] provoking what has sometimes been called (inappropriately) the first commercial war in Europe.[8][9] However, many historians including Vasil Zlatarski and John Fine consider those claims unlikely, arguing that in the beginning of his reign Simeon needed to consolidate his power and imperial ambitions had not yet been crystallised, therefore his military intervention was a defensive act to protect the Bulgarian commercial interests.[10][15]
Initial campaigns and Magyar intervention


In the autumn of 894 Simeon I launched an invasion of Byzantine Thrace, taking advantage of Byzantium's engagements with the Arabs to the east, which had left the Balkan provinces vulnerable. Leo VI hastily assembled an army under the generals Prokopios Krenites and Kourtikios and many archons, which included the Imperial Guard that consisted of Khazar mercenaries.[9] In the ensuing battle in the Theme of Macedonia (modern Eastern Thrace), probably around Adrianople,[17] the Byzantines were defeated and their commanders perished. Most of the Khazars were captured and Simeon had their noses cut and "sent them in the capital [Constantinople] for shame of the Romans [i.e. the Byzantines]".[18][19] The Bulgarians looted the region and retired to the north taking many captives.[20]
This failure urged the Byzantines to seek aid from the Magyars, who at the time inhabited the steppes between the Dnieper and the Danube. Leo VI sent his envoy Nicetas Scleros to the Magyar leaders Árpád and Kurszán in 894 or 895 "to give presents" and incite them against the Bulgarians.[21][22] At the same time, in the autumn of 894, Leo VI sent one Anastasios in Regensburg to Arnulf of Carinthia, king of East Francia. While no records have survived of that mission's purpose, it was most likely a pre-emptive move to discourage a German–Bulgarian alliance which existed between Arnulf and Simeon I's predecessor, Vladimir-Rasate.[23]
In the beginning of 895 the talented general Nikephoros Phokas the Elder was summoned to Constantinople and sent against the Bulgarians at the head of a large army.[24] While Simeon concentrated his forces along the southern border to confront Phokas, the Byzantine navy under admiral Eustathios Argyros sailed to the Danube Delta to assist the Magyars.[25] Believing that Simeon I would back off Leo VI sent an envoy, Constantinacios, to propose peace. Simeon I, who had studied in the University of Constantinople and was familiar with the Byzantine diplomacy, was suspicious of the Byzantine rapprochement, charged Constantinacios with espionage and put him into custody.[18][26] The Danube was barred with an iron chain to impede the movement of the Byzantine navy and the bulk of the army was dislocated northwards. The Byzantines, however, managed to break the chain and transported the Magyar hordes south of the river.[18] The Magyars, lead by Árpád's son Liüntika,[22] ravaged Dobrudzha and dealt a heavy defeat on the Bulgarian army, led personally by Simeon I.[21][27] Simeon sought refuge in the strong fortress of Drastar while the Magyars pillaged and looted unopposed, reaching the outskirts of the capital Preslav.[26] Before retreating north, the Magyars sold thousands of captives to the Byzantines.[26][28]
Truce negotiations

Facing a difficult situation with war on two fronts, Simeon sent a peace proposal through admiral Eustathios to buy time to deal with the Magyar menace, promising to return the Byzantine captives. Leo VI gladly complied, ordered Eustathios and Nikephoros Phokas to retreat and sent the diplomat Leo Choirosphaktes to Bulgaria to negotiate the terms.[18][26] That was exactly what Simeon I had aimed. Leo Choirosphaktes was detained in one fortress and was repeatedly refused an audience. Instead, Simeon I exchanged letters with him, protracting the negotiations, showing suspicions over the wording of the Byzantine proposals, constantly seeking clarifications and adding new demands.[21] The main issue was the exchange of the captives — the Byzantine priority was to free the prisoners captured during the Bulgarian campaign of 894.[29] In one of his letters to Choirosphaktes Simeon I demonstrated his diplomatic skills deriding the emperor:
| “ | The eclipse of the sun, and its date, not only to the month, week or day, but to the hour and second, your emperor prophesied to us the year before last in the most marvellous fashion. And he also explained how long the eclipse of the moon will last. And they say he knows many other things about the movements of the heavenly bodies. If this is true, he must also know about the prisoners; and if he knows, he will have told you whether I am going to release them or keep them. So prophesy one thing or the other, and if you know my intentions, you shall get the prisoners as reward for your prophecy and your embassy, by God! Greetings!.
—letter of Simeon I to Leo Choirosphaktes[30] |
” |
Choirosphaktes replied with an ambiguous answer, which was used by Simeon to claim that Leo could not prophesy the future and to refuse the return of the captives, further prolonging the negotiations.[31]
Defeat of the Magyars and battle of Boulgarophygon
While exchanging correspondence with Leo Choirosphaktes, Simeon sent envoys to forge an alliance with the Pechenegs, the eastern neighbours of the Magyars, and in the beginning of 896 the Bulgarians and Pechenegs attacked the Magyar homeland on two fronts.[32] In the decisive battle the Bulgarian army dealt a crushing defeat on the Magyars in the steppes along the Southern Bug river. The struggle was so bloody that it is said that the victorious Bulgarians lost 20,000 riders.[33] At the same time, the Pechenegs advanced westwards and prevented the Magyars from returning to their homeland.[34] The blow on the Magyars was so heavy that they were forced to migrate further west in search of new pastures, eventually settling in the Pannonian Basin, where they established the powerful Kingdom of Hungary.[28][34]

With the Magyar threat eliminated, Simeon returned to Preslav "proud of the victory"[32] and demanded the return of all Bulgarian captives as a precondition for further peace negotiations. Leo VI, who was in a difficult situation, facing the Arabs in the east and deprived of the services of the capable general Nikephoros Phokas, who was either disgraced as a result of the intrigues of Stylianos Zaoutzes or died in early 896, had to comply.[33][35] Leo Choirosphaktes and a Bulgarian envoy called Theodore, a trusted man of Simeon's, were sent to Constantinople to arrange the transfer which was successfully implemented.[36] Interpreting that as a sign of weakness, Simeon claimed that not all Bulgarians had been released and in the summer of 896 invaded Thrace.[34] The Byzantines secured an uneasy truce with the Arabs and transferred to Europe "all themes and tagmata",[32] i. e. all forces of the empire. The troops were commanded by the Domestic of the Schools Leo Katakalon, who lacked the ability of Phokas.[33] The two armies clashed in the battle of Boulgarophygon and the Byzantines were thoroughly routed — most of the soldiers perished, including the second-in-command, the protovestiarios Theodosius. Katakalon managed to escape with a few survivors.[9][32][34][37] The defeat was so grave that one Byzantine soldier retired from society and became an ascetic under the name of Luke the Stylite.[33]
The Byzantine sources have not recorded the aftermath of the battle but, according to the accounts of the contemporary Arab historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, the Bulgarians marched towards Constantinople. Leo VI was in such a panic that he considered arming Arab prisoners of war and sending them against the Bulgarians in return for their freedom, but eventually abandoned the idea.[34][38] Further negotiations followed until the Byzantines agreed to the Bulgarian demands.[34]
Aftermath

The war ended with a peace treaty which confirmed the Bulgarian domination on the Balkans,[39] restored the status of Bulgaria as a most favoured nation, abolished the commercial restrictions and obliged the Byzantine Empire to pay annual tribute. Under the treaty, the Byzantines also ceded an area between the Black Sea and Strandzhaa[›] to Bulgaria. In exchange, the Bulgarians released the captured Byzantine soldiers and civilians, who were allegedly 120,000.[40][41] The peace treaty remained in force until Leo VI's death in 912 although Simeon I did violate it following the Sack of Thessaloniki in 904, extracting further territorial concessions in Macedonia.[42]
The Bulgarian monarch was satisfied with the results and considered that he had superiority over the Byzantine Empire to achieve his political ambitions — to assume the throne in Constantinople.[32] Despite the success, however, Simeon I realized that there was still a lot to do in order to prevail over the Empire for good. He needed his own political and ideological base and launched an ambitious construction programme in Preslav so that it could rival Constantinople.[43] In addition, Simeon I took precautions to reduce the Byzantine influence over the Western Balkans by imposing his authority over the Principality of Serbia in return for recognizing Petar Gojniković as its ruler.[44]
The devastation in Dobrudzha at the hands of the Magyars indicated how vulnerable Bulgaria was to attacks from the north under the influence of the Byzantine diplomacy.[39] That experience paid off well in 917, when Simeon managed to counter the Byzantine efforts to ally with the Serbs or the Pechenegs, and forced them to fight alone in the battle of Achelous, where the Byzantines were soundly defeated in one of the biggest disasters in Byzantine history.[45]
See also
|
Footnotes
Notes
^ a: The borders established after the treaty are unknown but according to contemporary chronicles in 907 the town of Medea lied on the Byzantine–Bulgarian border.[46]
Citations
- ↑ Andreev & Lalkov 1996, pp. 73, 75
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 261–262
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 272–273
- ↑ Andreev & Lalkov 1996, p. 87
- ↑ Andreev & Lalkov 1996, p. 91
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Andreev & Lalkov 1996, p. 92
- ↑ Runciman 1930, p. 137
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Bakalov et al 2003, p. 251
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Mladjov, Ian. "Selections on Byzantium. Selections from the Chronicle of Ioannes Skylitzes, translated and adapted from B. Flusin and J.-C. Cheynet (2003)". Retrieved 8 November 2014.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Fine 1991, p. 137
- ↑ Runciman 1930, p. 144
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, p. 286
- ↑ "Chronographia by Theophanes Continuatus" in GIBI, vol. V, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, pp. 121–122
- ↑ Obolensky 1971, p. 105
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Zlatarski 1972, pp. 288–289
- ↑ Andreev & Lalkov 1996, pp. 92–93
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 289–290
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 Andreev & Lalkov 1996, p. 93
- ↑ Whittow 1996, pp. 286–287
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, p. 290
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Fine 1991, p. 138
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Spinei 2003, p. 52
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 294–295
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, p. 295
- ↑ Runciman 1930, pp. 145–146
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 Runciman 1930, p. 146
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 297–299
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Bozhilov & Gyuzelev 1999, p. 248
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 301–305
- ↑ Fine 1991, pp. 138–139
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 306–307
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 32.3 32.4 Andreev & Lalkov 1996, p. 94
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 Runciman 1930, p. 147
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 34.3 34.4 34.5 Fine 1991, p. 139
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, p. 315
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 312–313
- ↑ Kazhdan 1991, p. 317
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, p. 317
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Whittow 1996, p. 287
- ↑ Fine 1991, pp. 139–140
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, pp. 318–321
- ↑ Fine 1991, p. 140
- ↑ Andreev & Lalkov 1996, pp. 94–95
- ↑ Fine 1991, p. 141
- ↑ Andreev & Lalkov 1996, pp. 99–100
- ↑ Zlatarski 1972, p. 320
Sources
- Андреев (Andreev), Йордан (Jordan); Лалков (Lalkov), Милчо (Milcho) (1996). Българските ханове и царе (The Bulgarian Khans and Tsars) (in Bulgarian). Велико Търново (Veliko Tarnovo): Абагар (Abagar). ISBN 954-427-216-X.
- Бакалов (Bakalov), Георги (Georgi); Петър Ангелов (Petar Angelov), Пламен Павлов (Plamen Pavlov), Тотю Коев (Totyu Koev), Емил Александров (Emil Aleksandrov) и колектив (2003). История на българите от древността до края на XVI век (History of the Bulgarians from Antiquity to the end of the XVI century) (in Bulgarian). София (Sofia): Знание (Znanie). ISBN 954-621-186-9.
- Божилов (Bozhilov), Иван (Ivan); Васил Гюзелев (Vasil Gyuzelev) (1999). История на средновековна България VII–XIV век (History of Medieval Bulgaria VII–XIV centuries) (in Bulgarian). София (Sofia): Анубис (Anubis). ISBN 954-426-204-0.
- Колектив (Collective) (1964). "11. Продължителят на Теофан (11. Theophanis Continuati)". Гръцки извори за българската история (ГИБИ), том V (Greek Sources for Bulgarian History (GIBI), volume V) (in Bulgarian and Greek). София (Sofia): Издателство на БАН (Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Press).
- Fine, J. (1991). The Early Medieval Balkans, A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-08149-7.
- Kazhdan, A.; collective (1991). The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. New York, Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-504652-8.
- Obolensky, D. (1971). The Byzantine Commonwealth: Eastern Europe, 500–1453. New York, Washington: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 0-19-504652-8.
- Runciman, Steven (1930). "The Two Eagles". A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. London: George Bell & Sons. OCLC 832687.
- Spinei, Victor (2003). The Great Migrations in the East and South East of Europe from the Ninth to the Thirteenth Century. Romanian Cultural Institute (Center for Transylvanian Studies) and Museum of Brăila Istros Publishing House. ISBN 973-85894-5-2.
- Whittow, Mark (1996). The Making of Byzantium (600–1025). Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-20497-2.
- Златарски (Zlatarski), Васил (Vasil) (1972) [1927]. История на българската държава през средните векове. Том I. История на Първото българско царство. (History of the Bulgarian state in the Middle Ages. Volume I. History of the First Bulgarian Empire.) (in Bulgarian) (2 ed.). София (Sofia): Наука и изкуство (Nauka i izkustvo). OCLC 67080314.
External links
- Mladjov, Ian. "Selections from the Chronicle of Ioannes Skylitzes, translated and adapted from B. Flusin and J.-C. Cheynet (2003)". Hosted on the Department of History, University of Michigan. Retrieved 8 November 2014.