Bugula
| Bugula | |
|---|---|
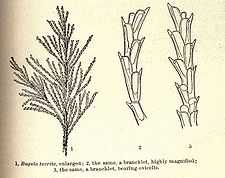 | |
| Buggula turrita (enlarged); branchlet (highly magnified); branchlet bearing ovicells | |
 | |
| Bugula flabellata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Bryozoa |
| Class: | Gymnolaemata |
| Order: | Cheilostomata |
| Family: | Bugulidae |
| Genus: | Bugula (Oken, 1815) |
Bugula is a genus of common colonial arborescent bryozoa, often mistaken for seaweed. It commonly grows upright in bushy colonies of up to 15 cm in height.[1]
Distribution
The species Spiral tufted bryozoa or Bugula turrita is found from Maine to North Carolina, in the United States.[2] The native distribution of Bugula neritina is presumed to be tropical and subtropical waters; however it has become widespread globally due to attachment to the hulls of vessels.[1] It is considered an invasive species in some countries.
Bugula neritina
Bugula neritina attracted interest as a source of cytotoxic chemicals, bryostatins, under clinical investigation as anti-cancer agents. In 2001 pharmaceutical company GPC Biotech licensed Bryostatin 1 from Arizona State University for commercial development as a treatment for cancer. GPC Biotech canceled development in 2003, saying that Bryostatin 1 showed little effectiveness and some toxic side-effects.[3]
Other uses
Dried Bugula are commonly used as decorations:
"Air fern", the so-called everlasting plant that supposedly absorbs from air all the moisture it needs to live, is commonly dried colonies of the bryozoan Bugula that have been artificially coloured.[4]
However, it should be noted that Sertularia argentea are also sold as "air ferns."[5]
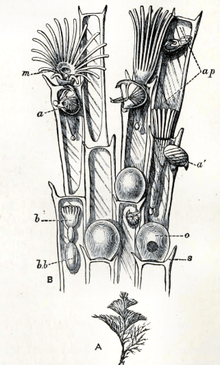
Species
- Bugula alba
- Bugula angustiloba
- Bugula aperta
- Bugula apsteini
- Bugula aquilirostris
- Bugula aspinosa
- Bugula avicularia
- Bugula bengalensis
- Bugula biota
- Bugula borealis
- Bugula bowiei
- Bugula calathus
- Bugula californica
- Bugula capensis
- Bugula carvalhoi
- Bugula ceylonensis
- Bugula crosslandi
- Bugula cucullata
- Bugula cuspidata
- Bugula decipiens
- Bugula dentata
- Bugula dispar
- Bugula ditrupae
- Bugula eburnea
- Bugula expansa
- Bugula fastigiata
- Bugula flabellata
- Bugula foliolata
- Bugula fulva
- Bugula gautieri
- Bugula gnoma
- Bugula gracilis
- Bugula grayi
- Bugula guara
- Bugula harmsworthi
- Bugula hessei
- Bugula hummelincki
- Bugula hyadesi
- Bugula ingens
- Bugula intermedia
- Bugula longirostrata
- Bugula longissima
- Bugula lophodendron
- Bugula marcusi
- Bugula microoecia
- Bugula migottoi
- Bugula miniatella
- Bugula minima
- Bugula mollis
- Bugula multiserialis
- Bugula neritina
- Bugula neritinoides
- Bugula orientalis
- Bugula pacifica
- Bugula paternostrae
- Bugula pedata
- Bugula philippsae
- Bugula plumosa
- Bugula prenanti
- Bugula prismatica
- Bugula protensa
- Bugula providensis
- Bugula pugeti
- Bugula purpurotincta
- Bugula robusta
- Bugula robustoides
- Bugula rochae
- Bugula rylandi
- Bugula scaphoides
- Bugula scaphula
- Bugula serrata
- Bugula simplex
- Bugula simpliciformis
- Bugula solorensis
- Bugula spicata
- Bugula stolonifera
- Bugula subglobosa
- Bugula tricuspis
- Bugula tschukotkensis
- Bugula turbinata
- Bugula turrita
- Bugula umbelliformis
- Bugula vectifera
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Bugula neritina". exoticsguide.org. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ↑ Andrew J. Martinez (2003). Marine Life of the North Atlantic: Canada to New England. Aqua Quest Publications. Retrieved 2007-02-17.
- ↑ "Bryostatin 1". 19 June 2006. Retrieved 2009-08-20.
- ↑ Frank K. McKinney. "The Bryozoa". International Bryozoology Association. Archived from the original on 2006-12-13. Retrieved 2007-02-17.
- ↑ "Encyclopedia of Marine Life of Britain and Ireland - Cnidaria". habitas.org.uk. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
External Links
- Smithsonian Marine Station at Fort Pierce
- Introduced Marine Species of Hawai'i
- Exotics Guide - Bugula neritina
| Wikispecies has information related to: Bugula |