Brood II
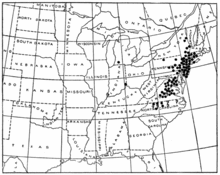
Brood II is one of 15 separate broods of Magicicada (periodical cicadas) that appear regularly throughout the northeastern United States. Every 17 years, Brood II tunnels en masse to the surface of the ground, lays eggs, and then dies off over the span of several weeks.
Although entomologist C. L. Marlatt published an account in 1907 in which he argued for the existence of 30 broods, over the years a number have been consolidated and only 15 are recognized today as being distinct.[1] Brood II is among the 12 different broods with 17-year cycles.
It last appeared in the late spring and summer of 2013, and will emerge again in 2030 and 2047.[2]
The 4-centimeter long (1.5 in) black insects do not sting or bite. Once they emerge, they spend their short, two-week adult lives climbing trees, shedding their crunchy skins and reproducing. They can number up to a million per hectare (2.5 acres).
2013 Emergence

In 2013, to aid in accurately mapping the geographic range of Brood II, National Public Radio's science show Radiolab created the Cicada Tracker project. It encouraged listeners to use a mix of Arduino-based tools to report the underground soil temperature so as to predict when the cicadas would appear.[3] The National Geographic Society sponsored a citizen science project, the Magicicada Mapping Project, to track actual emergence.[4]
References
- ↑ Susan L. Post (2004). "A Trill of a Lifetime". University of Illinois. Archived from the original on May 11, 2012. Retrieved October 12, 2013.
- ↑ "Brood II". Cicada Mania. 2013-02-16. Retrieved 2013-04-08.
- ↑ "Cicada Tracker | Radiolab". Project.wnyc.org. Retrieved 2013-04-08.
- ↑ "Citizen Science: Cicada Watch". 17 April 2013. Retrieved 24 April 2013.
External links
| ||||||