Breitspurbahn
| By transport mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tram · Rapid transit Miniature · Scale model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By size (list) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change of gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Break-of-gauge · Dual gauge · Conversion (list) · Bogie exchange · Variable gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| By location | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America · South America · Europe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Breitspurbahn (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁaɪtʃpuːɐ̯baːn], translation: broad-gauge railway) was a planned 3 m (9 ft 10 1⁄8 in) broad-gauge railway, proposed by Adolf Hitler during the Nazi regime in Germany, supposed to run on 3-metre gauge track with double-deck coaches between major cities of Grossdeutschland, Hitler's expanded Germany.[1]
History
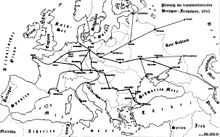
Since reparations due after World War I had to be paid, the Germany railway company Deutsche Reichsbahn lacked money for appropriate expansion and sufficient maintenance of their track network and rolling stock.[2]
After the seizure of power of Hitler and the NSDAP, commercial and civilian traffic had increased due to economic stimulation. Deutsche Reichsbahn was now faced with a serious capacity problem. As a result, in part driven by their military objectives, the government began to prepare plans to modernize the railway network and increase transport capacity. Hitler believed that the standard Stephenson gauge was obsolete and was too narrow for the full development of railways.[1] Also, as Hitler envisioned the future German empire as being essentially a land-based Empire (as represented by the Heartland Theory of Halford Mackinder), the new German railways were imagined as a land-based equivalent of the cruise ships and freighters connecting the maritime British Empire.[1]
Hitler embraced a suggestion from Fritz Todt to build a new high-capacity Reichsspurbahn (Imperial Gauge Railway) with notably increased gauge. Objections from railway experts — who foresaw difficulties in introducing a new, incompatible gauge (and proposed 4-track standard gauge lines instead), and who could not imagine any use for the vast transport capacity of such a railway — were ignored, and Hitler ordered the Breitspurbahn to be built with initial lines between Hamburg, Berlin, Nuremberg, Munich, and Linz.
The project engaged commercial partners Krauss-Maffei, Henschel, Borsig, BBC, and Krupp, but did not develop beyond line planning and initial survey. Throughout World War II, 100 officials and 80 engineers continued to work on the project.[3]
Tracks
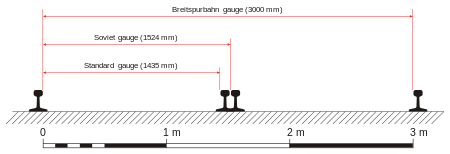
Originally proposed to run on a 4-metre (13 ft 1.5 in) track, the Breitspurbahn was ultimately developed with a track gauge of 3 m (9 ft 10 1⁄8 in), over double the width of the common standard gauge track, and three times the width of the common semi-narrow metre gauge track. Planning called for a ballastless track (much as was developed 30 years later for San Francisco BART and 40 years later for German high-speed lines) which consisted of two parallel pre-stressed concrete "walls" sunk into the ground, joined at the top by a flat transverse slab. The rails were fixed on top of the "walls", with an elastic material between rail and concrete. Because it did not have conventional railway sleepers, this track would also have formed an ideal road for maintenance and military purposes.
Vehicles

Locomotives
41 different locomotive designs were suggested by the industry partners. These ranged from classical steam locomotives through steam turbine, gas turbine-electric and diesel-hydraulic to electric locomotives. The designs ranged from 12 axles (UIC: 3'Fo3', Whyte: 6-12-6) to 52 axles (UIC: 2'Fo'Fo'2' + 5T5 + 5T5 + 2'Fo'Fo'2', Whyte: 4-12-12-4 + 10-10 + 10-10 + 4-12-12-4). Several designs were short listed with passenger locomotives to be mainly electric and diesel-hydraulic, and freight locomotives to be mainly conventional steam. Power ranged from 11,400 to 18,400 kW (15,300 to 24,700 hp). All locomotives would have automatic couplers, ranged from Janney couplers to SA3 couplers.
Multiple units
Diesel and electric multiple units of between 5 and 8 vehicles were proposed for shorter distance journeys. Despite being of somewhat lower standard, proposed designs included promenades, bars, lounges and large dining rooms.
Carriages
The proposal was that high-performance-locomotives should pull 8-axle double-floor carriages with a length of 42 metres (138 ft), width of 6 metres (19 ft 8 in) and height of 7 metres (23 ft 0 in).[1] The carriages would have Dutch doors (with retractable staircase). The trains would be fitted with a restaurant, cinema, swimming pool, barbershop and sauna. The whole train would have a length of about 500 metres (1,640 ft), allowing a capacity of between 2,000 and 4,000 passengers, travelling at speeds of 200 kilometres per hour (120 mph). Designs included:
- 1st/2nd class day car: 48 first class seats in 12 compartments, 144 second class seats in 24 compartments, bar, lounge, reading room, luggage compartments, 12 toilets.
- 3rd class day car: 460 seats in 56 compartments, lounge, 12 toilets.
- 1st/2nd class dining car: 130 seats at 24 tables, kitchen, pantry.
- 3rd class day car with dining room: 244 seats in 28 compartments, 176 seat dining room, kitchen, pantry.
- 1st/2nd class sleeping car: 16 first class beds in 16 cabins, 41 second class beds in 19 cabins, breakfast room, kitchen, washrooms, 10 toilets.
- 2nd class sleeping car: 104 beds in 104 cabins, washrooms, 12 toilets.
- 3rd class sleeping car: 264 beds in 44 cabins, breakfast room, kitchen, shower rooms, 10 toilets.
- Day/night car for Ost-Arbeiter: 480 seats in 52 cabins, kitchen, washrooms, staff room.
- Cinema car: 196 seat cinema.
- Observation car: 16 first class seats in 4 compartments, 32 second class seats in 8 compartments, 160 third class seats in 20 compartments, galley, cold buffet, bar, observation deck.
- Mail car: mail storage and sorting, parcel space, crew room, space for 6 automobiles, dog kennels.
- Baggage car: baggage rooms, space for 2 automobiles, dog kennels, canteen, crew room, multiple 20 mm anti-aircraft guns, ammunition storage and gun crews.
Proposed routes
Early plans for routes considered India and Vladivostok as the ultimate goals of the railways, but by 1943 the planning was focused exclusively on European cities.[1] Ukraine and the Volga Basin were seen as especially important targets, as these areas were viewed as the future granaries of the Nazi empire,[1] potentially through the "settlement strings". or Siedlungsperlen of the proposed Wehrbauer settlements within the conquered Lebensraum territories, which would also be linked by the planned easternmost reaches of the Reichsautobahn freeway network.[4]
- East-West: Rostov - Donetsk - Poltava - Kyiv - Lviv - Kraków - Katowice - Wrocław - Cottbus - Welthauptstadt Germania (Berlin) - Hanover - Bielefeld - Ruhrgebiet - Aachen - Liège - St. Quentin - Paris
- North-Southeast: Hamburg - Wittenberge - Welthauptstadt Germania (Berlin) - Leipzig - Gotha - Bamberg - Nuremberg - Munich - Simbach am Inn - Linz - Vienna - Bratislava - Budapest - Belgrade - Bucharest - Varna/Burgas - Istanbul
- North-South-Parallel: Welthauptstadt Germania (Berlin) - Dresden - Aussig - Prague - Jihlava - Znojmo - Vienna - Trieste - Rome
- East-West 2: Munich - Augsburg - Stuttgart - Karlsruhe - Metz - Reims - Paris - Marseille - Spain
For further routes, see German version and Dutch version.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Puffert, Douglas J. (2009). Tracks across continents, paths through history: the economic dynamics of standardization in railway gauge. Chicago : University of Chicago Press. ISBN 9780226685090. p 182
- ↑ "Google Translate". Translate.google.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-12-10.
- ↑ Housden, K. (2000). Hitler : Biography of a Revolutionary. Routledge. p. 156 ISBN 0-415-16358-7
- ↑ Norman Rich, Hitler's War Aims Volume 2 The Establishment of the New Order, New York: Norton, 1974, ISBN 9780393055092, p. 356.
- Die Breitspurbahn, Anton Joachimsthaler. Herbig, 1996. ISBN 3-7766-1352-1
- Broader than Broad: Hitler's Great Dream: Three Meter Gauge Rails Across Europe, Barnes, Robin. Locomotives International. 1998. ISBN 1-900340-07-0
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Breitspurbahn. |
- breitspurbahn.de Pictures of the "Breitspurbahn"
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
