Brahui people
|
A photograph from 1910 with the caption reading "Brahui of Quetta". | |
| Languages | |
|---|---|
|
Brahui Balochi, Urdu and Persian spoken as second languages | |
| Religion | |
| Sunni Islam (Hanafi) | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Dravidian people of South India, Nearby Balochis and Sindhis |
| Part of a series on |
| Dravidian culture and history |
|---|
 |
|
History
|
|
Culture
|
|
Language
|
|
Religion
|
|
Regions
|
|
People
|
| Portal:Dravidian civilizations |
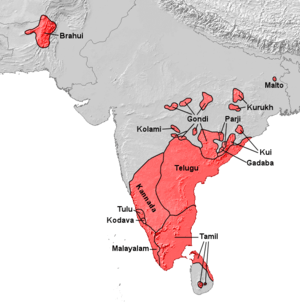
The Brahui (Brahui: براہوئی, Sindhi: بروہي) are an ethnic group of about 2.2 million people with the vast majority found in Sindh and Baluchistan, Pakistan but they are also found in smaller numbers in neighboring Afghanistan and Iran.[1] The Brahuis are almost entirely Sunni Muslims.[2]
Origins
The ethnonym "Brahui" is a very old term and a purely Dravidian one.[3] The fact that other Dravidian languages only exist further south in India has led to several speculations about the origins of the Brahui. There are three hypotheses regarding the Brahui that have been proposed by academics. One theory is that the Brahui are a relict population of Dravidians, surrounded by speakers of Indo-Iranian languages, remaining from a time when Dravidian was more widespread. Another theory is that they migrated to Baluchistan from inner India during the early Muslim period of the 13th or 14th centuries.[4] A third theory says the Brahui migrated to Balochistan from Central India after 1000 AD. The absence of any older Iranian (Avestan) influence in Brahui supports this last hypothesis. The main Iranian contributor to Brahui vocabulary is a northwestern Iranian language, Baluchi, Sindhi and southeastern Iranian language, Pashto.[5]
The History of the Brahui emerges from total darkness with the displacement of a shadowy Hindu dynasty in Kalat called Sewa by the Mirwari Brahuis. There is a Mughal interlude and then Brahui ascendancy again.[6]
It is said that a Hindu dynasty, the Sewa by name, ruled over this part of the country prior to the seventh century, Kalat is still known as Kalat-i-Sewa.[7]
Over the centuries, due to their location, the Brahui have mixed with Iranian peoples as well as the Sindhis, among other Indo-Aryan peoples. They culturally resemble their Baloch and Sindhi neighbors, although they still continue to speak their Brahui language.
Brahui tribes include Mohammad Hassani صدام بروهي لاركانه , Yagizehi, Mengal, Natwani, Zagar Mengal, Mirwani, Bangulzai, Banulzai, Kheazai, Sarparah, Muhammad Shahi, Kurd, Meskanzai (Sarparah), Sumulani, Zarakzai (Zehri), Sasoli, Sataksai, Qambarani, Rodeni, Pandrani, Jattak.[8] ←
Language

The Brahui language is a language within the Dravidian subgroup of languages.[3] While it does contain many words similar to their equivalents in the Iranian Baloch language, it also has many loan words from Indo-Aryan languages as well as the Dravidian words of its own. It is mainly spoken in the Kalat areas of Balochistan, Pakistan, although there are a considerable number of speakers in Southern Afghanistan and Iranian Balochistan. It has three dialects: Sarawani (spoken in the north), Jhalawani (spoken in the southeast), and Chaghi (spoken in the northwest and west) The 2013 edition of Ethnologue reports that there are some 4.2 million speakers; 4 million live in Pakistan, mainly in the province of Balochistan.[1] Due to its isolation, Brahui's vocabulary is only 15% Dravidian, while the remainder is dominated by Persian, Balochi, and other Indo-Aryan languages (for example, of the number names from "one" to "ten," "four" through "ten" are borrowed from Persian [9]), while the grammar and overall morphology still resemble other Dravidian tongues. Brahui is generally written in the Perso-Arabic script and there is even a Latin alphabet that has been developed for use with Brahui.
Dialects
Kalat, Jhalawan, and Sarawan, with Kalat as the standard dialect. At present Brahui is spoken in Sistan va Baluchestan, Pakistani Balochistan, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Sindh and the Persian Gulf Arab states.
Physical characteristics
Physically the Brahui resemble their Baloch and Pashtun neighbours, for the confederacy has been highly absorptive.[10]
Genetics
Brahuis display a variety of Y-DNA haplogroups, the two most important being haplogroup R1a - with its mass diffusion among populations of Central/South Asia and associated with the early eastern migrations of Indo-Iranian nomads - and haplogroup J, which, though found among other subcontinental peoples, is nevertheless more typical of Near-Eastern populations.[11][12] Other, relatively minor, low-frequency haplogroups among the Brahui are those of L, E1b1a, G, and N.[11][12]
References
- ↑ "Ethnic Groups of South Asia and the Pacific: An Encyclopedia: An Encyclopedia". Retrieved 22 December 2014.
- ↑ Dictionary of Languages: The Definitive Reference to More Than 400 Languages. Columbia University Press. 2004-03-01. ISBN 9780231115698. Retrieved 2010-09-09.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Brahui, a Dravidian language: a descriptive and comparative study. Foreign Language Study. Retrieved 2010-09-09.
- ↑ [Sergent, Genèse de l'Inde]
- ↑ J. H. Elfenbein, A periplous of the ‘Brahui problem’, Studia Iranica vol. 16 (1987), pp. 215-233.
- ↑ Language and linguistic area: essays By Murray Barnson Emeneau, Selected and introduced by Anwar S. Dil, Stanford University Press. Page 334
- ↑ Population Census Organisation, Statistics Division, Govt. of Pakistan, 1999, 1998 district census report of Kalat Page 7.
- ↑ Shahwani Infrastructure Project Development Facility: Balochistan
- ↑ http://zompist.com/euro.htm#dravidian
- ↑ "Brahui". Retrieved 22 December 2014.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Qamar Raheel et al. "Y-Chromosomal DNA Variation in Pakistan". American Journal of Human Genetics 70 (1107–1124): 2002.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Sengupta, S; Zhivotovsky, LA; King, R; Mehdi, SQ; Edmonds, CA; Chow, CE; Lin, AA; Mitra, M et al. (2006).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Brahui. |
- South Asia Language Resource Center
- Brahui people, Britannica.com
- Qamar, Raheel; Ayub, Qasim; Mohyuddin, Aisha; Helgason, Agnar; Kehkashan, Mazhar; Atika, Mansoor; Zerjal, Tatjana; Tyler-Smith, Chris; Mehdi, S. Qasim (2002-03-15). "Y-Chromosomal DNA Variation in Pakistan". American Journal of Human Genetics 70 (5): 1107–1124. doi:10.1086/339929. Retrieved 5 April 2015.
