Bowyer–Watson algorithm
In computational geometry, the Bowyer–Watson algorithm is a method for computing the Delaunay triangulation of a finite set of points in any number of dimensions. The algorithm can be used to obtain a Voronoi diagram of the points, which is the dual graph of the Delaunay triangulation.
The Bowyer–Watson algorithm is an incremental algorithm. It works by adding points, one at a time, to a valid Delaunay triangulation of a subset of the desired points. After every insertion, any triangles whose circumcircles contain the new point are deleted, leaving a star-shaped polygonal hole which is then re-triangulated using the new point. By using the connectivity of the triangulation to efficiently locate triangles to remove, the algorithm can take O(N log N) operations to triangulate N points, although special degenerate cases exist where this goes up to O(N2).[1]
The algorithm is sometimes known just as the Bowyer Algorithm or the Watson Algorithm. Adrian Bowyer and David Watson devised it independently of each other at the same time, and each published a paper on it in the same issue of The Computer Journal (see below).
-
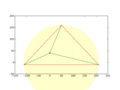
First step: insert a node in an enclosing "super"-triangle
-
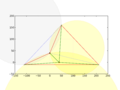
Insert second node
-

Insert third node
-
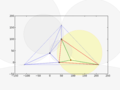
Insert fourth node
-
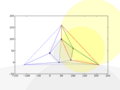
Insert fifth (and last) node
-
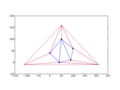
Remove super-triangle edges
Pseudocode
The following pseudocode describes a basic implementation of the Bowyer-Watson algorithm. Efficiency can be improved in a number of ways. For example, the triangle connectivity can be used to locate the triangles which contain the new point in their circumcircle, without having to check all of the triangles. Pre-computing the circumcircles can save time at the expense of additional memory usage. And if the points are uniformly distributed, sorting them along a space filling Hilbert curve prior to insertion can also speed point location.[2]
function BowyerWatson (pointList) // pointList is a set of coordinates defining the points to be triangulated triangulation := empty triangle mesh data structure add super-triangle to triangulation // must be large enough to completely contain all the points in pointList for each point in pointList do // add all the points one at a time to the triangulation badTriangles := empty set for each triangle in triangulation do // first find all the triangles that are no longer valid due to the insertion if point is inside circumcircle of triangle add triangle to badTriangles polygon := empty set for each triangle in badTriangles do // find the boundary of the polygonal hole for each edge in triangle do if edge is not shared by any other triangles in badTriangles add edge to polygon for each triangle in badTriangles do // remove them from the data structure remove triangle from triangulation for each edge in polygon do // re-triangulate the polygonal hole newTri := form a triangle from edge to point add newTri to triangulation for each triangle in triangulation // done inserting points, now clean up if triangle contains a vertex from original super-triangle remove triangle from triangulation return triangulation
See also
References
- ↑ Rebay, S. Efficient Unstructured Mesh Generation by Means of Delaunay Triangulation and Bowyer-Watson Algorithm. Journal of Computational Physics Volume 106 Issue 1, May 1993, p. 127.
- ↑ Liu, Yuanxin, and Jack Snoeyink. "A comparison of five implementations of 3D Delaunay tessellation." Combinatorial and Computational Geometry 52 (2005): 439-458.
- Bowyer, Adrian (1981). "Computing Dirichlet tessellations". Comput. J. 24 (2): 162–166. doi:10.1093/comjnl/24.2.162.
- Watson, David F. (1981). "Computing the n-dimensional Delaunay tessellation with application to Voronoi polytopes". Comput. J. 24 (2): 167–172. doi:10.1093/comjnl/24.2.167.
- Efficient Triangulation Algorithm Suitable for Terrain Modelling generic explanations with source code examples in several languages.