Bohai Economic Rim
| Bohai Economic Rim [1]
环渤海经济圈 | |
|---|---|
 Tianjin | |
 The 3 Main Economic Rims of China | |
| Country |
|
| Major Cities |
Beijing Tianjin Dalian Tangshan Shenyang Jinan Qingdao Weihai |
| Population | |
| • Metro | 66,400,000 |
| Bohai Economic Rim | |||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 环渤海经济圈 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese | 環渤海經濟圈 | ||||||
| Hanyu Pinyin | Huán Bóhǎi Jīngjìquān | ||||||
| |||||||
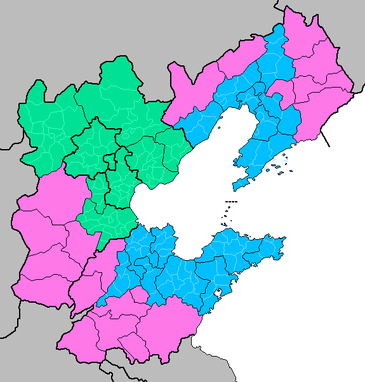
The Bohai Economic Rim (BER) or Bohai Bay Economic Rim is the economic hinterland surrounding Beijing and Tianjin. It also includes areas in Hebei, Liaoning and Shandong which surrounds the Bohai Sea. This region has gone through major changes in economic and infrastructures. This emerging region is rising as a Northern economic power house and rivals the Pearl River Delta in the south and the Yangtze River Delta in the east .
Economy
The Bohai Economic Rim has traditionally been involved in heavy industries and manufacturing. Tianjin's strengths have always been in aviation, logistics and shipping. Beijing complements this with strong petrochemical, education and R&D industries. The area is becoming a significant growth cluster for the automobile, electronics, petrochemical sectors, especially with Shenyang's automotive industry, software and aircraft, Dalian attracting foreign investments in manufacturing and Qingdao for its health services.[2][3]
The Chinese central government has made it a priority to integrate all the cities in the Bohai Bay rim and foster economic development. This includes building an advanced communications network, better highways, increased education and scientific resources as well as tapping natural resources off the Bohai rim.[4]
In recent decades, petroleum and natural gas deposits have been discovered in Bo Hai.
Transport
Air
Major airports:
- Beijing Capital International Airport
- Tianjin Binhai International Airport
- Shenyang Taoxian International Airport
- Dalian Zhoushuizi International Airport
- Jinan Yaoqiang International Airport
- Qingdao Liuting International Airport
Regional airports:
- Beijing Nanyuan Airport
- Tangshan Sannühe Airport
- Handan Airport
- Qinhuangdao Shanhaiguan Airport
- Qinhuangdao Beidaihe Airport
- Zhangjiakou Ningyuan Airport
- Xingtai Dalian Airport
- Chengde Airport
- Weihai Airport
- Yantai Laishan International Airport
Land
There are many major highways servicing the routes within the Bohai rim area. This includes the following expressways:
- Jingjintang Expressway, from Beijing, through Tianjin's urban area, to Tanggu District / TEDA
- Jinghu Expressway, from Jinjing Gonglu Bridge to Shanghai (together with Jingjintang Expressway, this is the expressway from Beijing to Shanghai)
- Jingshen Expressway, through Baodi District on its way from Beijing to Shenyang
- Tangjin Expressway, from Tanggu District, Tianjin, to Tangshan, Hebei -- known in Tianjin as the Jintang Expressway
- Baojin Expressway, from Beichen District, Tianjin, to Baoding, Hebei -- known in Tianjin as the Jinbao Expressway
- Jinbin Expressway, from Zhangguizhuang Bridge to Hujiayuan Bridge, both within Tianjin
- Jinji Expressway, from central Tianjin to Jixian County
The following six China National Highways pass through Tianjin:
- China National Highway 102, through Ji County, Tianjin on its way from Beijing to Harbin
- China National Highway 103, from Beijing, through Tianjin's urban area, to Tanggu District
- China National Highway 104, from Beijing, through Tianjin Municipality, to Fuzhou
- China National Highway 105, from Beijing, through Tianjin Municipality, to Macau
- China National Highway 112, circular highway around Beijing, passes through Tianjin Municipality
- China National Highway 205, from Shanhaiguan, Hebei, through Tianjin Municipality, to Guangzhou
Rail
Since 2000, there have been rapid infrastructure developments within the Bohai Economic Rim. Rail projects of varied natures have been built, including high-speed inter-city rail, metros and suburban rail.
High-speed rail
In 2006, the Chinese government had plans to construct 710 kilometres (440 mi) of high-speed railway in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region by 2020.[5]
In August 2008, the Beijing–Tianjin Intercity Railway opened providing a direct route between Beijing and Tianjin. The initial trains run on average 300 km/h and have cut journey times between the two municipalities to half an hour.[6] Also under construction is the Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway, which will connect the Bohai Economic Rim to the Yangtze River Delta.
Light rail
Metros
- Binhai Mass Transit
- Beijing Metro
- Shenyang Metro
- Tianjin Metro
- Dalian Metro
- Qingdao Metro (under construction)
Suburban railway
Geography
The gulf is formed by the Liaodong Peninsula to the northeast and the Shandong Peninsula to the south. Bo Hai consists of three bays: Laizhou Bay to the south, Liaodong Bay to the north, and Bohai Wan to the west. The rivers Huang He, Liao He, Hai He and Luan River empty into Bo Hai.
The Bohai economic rim includes Beijing, Tianjin, part of Hebei province, part of Liaoning province, and part of Shandong province. List of major cities or ports in these municipalities and provinces are listed below:
Inner Rim
- Municipalities: Beijing and Tianjin (Binhai)
- Hebei Province: Tangshan, Qinhuangdao, Cangzhou, Langfang, Chengde and Zhangjiakou
| City | Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population | Image | Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 北京 | Beijing | 17,430,000 |  |
Beijing is a metropolis in northern China and the capital of the People's Republic of China. Governed as a municipality under direct administration of the central government. Beijing is China's second largest city after Shanghai, with more than 17 million people in Beijing's area of jurisdiction |
| Tianjin | 天津 | Tianjin | 11,760,000 |  |
The third largest city of the People's Republic of China in terms of urban population. Administratively it is one of the four municipalities that have provincial-level status, reporting directly to the central government. Also, its urban land area is the third largest in China, ranked only after Beijing and Shanghai. |
| Tangshan | 唐山 | Tangshan | 7,474,000 |  |
Tangshan, a coastal city along the Bohai Bay and neighboring Beijing and Tianjin, is a prefecture-level city in Hebei Province, People's Republic of China. Its GDP has surpassed 612.12 billion Yuan in 2013,[7] ranked the 1st of Hebei Province and 19th of Mainland China. It is also known for the 1976 Tangshan earthquake, 7.5 on the Richter scale which flattened the city. |
South Rim (Shandong)
| City | Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population | Image | Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jinan | 济南 | Jinan | 5,900,000 |  |
Jinan is a sub-provincial city and the capital of Shandong Province in the People's Republic of China. |
| Qingdao | 青岛 | Qingdao | 7,579,900 |  |
Qingdao is a major city in eastern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It borders Yantai to the northeast, Weifang to the west and Rizhao to the southwest. Lying across the Shandong Peninsula while looking out to the Yellow Sea, Qingdao today is a major seaport, naval base, and industrial center |
| Weihai | 威海 | Weihai | 2,596,753 |  |
Weihai is a prefecture-level city in eastern Shandong province, People's Republic of China. The easternmost prefecture-level city in the province and a major seaport, Weihai borders Yantai to the west and looks out to the Yellow Sea to the east. |
North Rim (Liaoning)
| City | Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population | Image | Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shenyang | 沈阳 | Shenyang | 8,240,000 | |
Shenyang is a sub-provincial city and capital of Liaoning province in Northeast China. Along with its nearby cities, Shenyang is an important industrial center in China, and the transportation and commercial centre of China's northeastern region. |
| Dalian | 大连 | Dalian | 6,200,000 | |
Dalian is the second largest city of Liaoning Province, after Shenyang, the provincial capital. Dalian is a financial, shipping and logistics center for Northeast Asia. |
| Dandong | 丹东 | Dandong | 2,409,697 |  |
Dandong is the largest border city in China. Dandong border with Sinuiju in North Korea. |
Pollution
A Xinhua News Agency report in February, 2007, states: “Effluent has turned the sea a dark red and given it an acrid stench at Guanxi’s Silver Beach, a national tourist attraction. Local staff say it is not the first time this has happened – sometimes it occurs every few days. They blame the run-off from nearby shellfish processing plants.” [8]
Jiaozhou Bay-Laizhou Bay Canal
In April 2004, an official of the Shandong province raised the possibility of constructing a canal between Jiaozhou Bay and Laizhou Bay as a means of easing the pollution problem in the Bo Hai.[9] The proposed canal will also be open to ships traveling between Bo Hai and the Yellow Sea. A meeting held in Qingdao in October, 2006, was attended by more than a hundred members of academia.
See also
References
- ↑ "Foreign investment shows trend of "moving northward"". china-embassy.org. 2004-05-14. Retrieved 2010-01-09.
- ↑ Regional Definition: Bohai Sea Unep.Org Retrieved 2010-01-09
- ↑ Tianjin at a Glance uschina.org Retrieved 2010-01-09
- ↑ Gain a strategic advantage in the Bohai Bay region sdic.com.cn 2007-06-11 Retrieved 2010-01-16
- ↑ Dingding, Xin (2006-11-27). "High-speed rail to link Beijing, Tianjin before Games". China Daily. Retrieved 2015-04-27 – via HighBeam. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ Express railway brings Beijing and Tianjin closer China Daily 2008-09-27 Retrieved 2010-01-16
- ↑ 2013年唐山完成地區生產總值6121.2億元 http://ts.yzdsb.com.cn/system/2014/03/10/013620031.shtml
- ↑ China’s water resources: environmental security needed chinadialogue.net 2007-03-07 Retrieved 2010-01-09
- ↑ (Chinese) 國家擬投千億 開鑿運河連通渤黃 takungpao.com 2007-11-23 Retrieved 2010-01-09
External links
- Bohai Economic Rim 环渤海湾经济圈
- Bohai Rim's future 环渤海——中国经济的未来
- Rising investment in Bohai Rim 环渤海经济圈正在吸引越来越多房产商的目光
- Cooperation between Bohai Rim and Northeast region
- Info on Bohai surrounding region
- Role of Tangshan in Bohai Rim
Coordinates: 38°42′N 118°6′E / 38.700°N 118.100°E
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||