Biuret
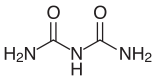 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Imidodicarbonic diamide | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(Carbamoylamino)methanamide | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3DMet | B00969 |
| 1703510 | |
| 108-19-0 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:18138 |
| ChemSpider | 7625 |
| EC number | 203-559-0 |
| 49702 | |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image Image |
| KEGG | C06555 |
| MeSH | Biuret |
| PubChem | 7913 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C2H5N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 103.08 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Specific heat capacity (C) |
131.3 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Std molar entropy (S |
146.1 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH |
−565.8–−561.6 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH |
−940.1–−935.9 kJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+351+338 | |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S26, S36 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
urea, triuret, cyanuric acid |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
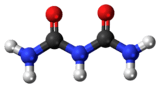
Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula H2NC(O)NHC(O)NH2. It is the result of condensation of two molecules of urea and is a problematic impurity in urea-based fertilizers. This white solid is soluble in hot water. Biuret was first prepared and studied by Gustav Heinrich Wiedemann (1826 - 1899) for his doctoral dissertation, which was submitted in 1847. His findings were reported in several articles.[2][3][4][5]
The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the functional group -(HN-CO-)2N-. Thus dimethyl biuret is CH3HN-CO-NR'-CO-NHCH3. A variety of organic derivatives are possible.
Preparation
The parent compound can be prepared by heating urea above the melting point at which temperature ammonia is expelled:[6]
- 2 CO(NH2)2 → H2N-CO-NH-CO-NH2 + NH3
Under related conditions, pyrolysis of urea affords triuret ((H2N-CO-NH)2CO).[6] In general, organic biurets (those with alkyl or aryl groups in place of one or more H atoms) are prepared by trimerization of isocyanates. For example the trimer of 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate is also known as HDI-biuret.
Applications
Biuret is also used as a non-protein nitrogen source in ruminant feed,[7] where it is converted into protein by gut microorganisms.[8] It is less favored than urea, due to its higher cost and lower digestibility[9] but this characteristic also slows down its digestion and so decreases the risk of ammonia toxicity.[9][10]
Biuret test
The biuret test is a chemical test for proteins and polypeptides. It is based on the biuret reagent, a blue solution that turns violet upon contact with proteins, or any substance with peptide bonds. The test and reagent do not actually contain biuret; they are so named because both biuret and proteins have the same response to the test.
Related compounds
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Scifinder, version 2007.1; Chemical Abstracts Service: Columbus, OH; RN 108-19-0 (accessed June 15, 2012)
- ↑ Wiedemann, G. (1848). "Ueber ein neues Zersetzungsproduct des Harnstoffs" [On a new decomposition product of urea]. Annalen der Physik 150 (5): 67–84. doi:10.1002/andp.18491500508.
- ↑ Wiedemann, G. (1847). "Neues Zersetzungsproduct des Harnstoffs" [New decomposition product of urea]. Journal für praktische Chemie 42 (3–4): 255–256. This notice reports that biuret reacts with alkaline copper sulfate to produce a red solution -- the so-called "Biuret test"
- ↑ Wiedemann, G. (1848). "Ueber eine neue, aus dem Harnstoff entstehende Verbindung" [On a new compound arising from urea]. Journal für praktische Chemie 43 (5): 271–280.
- ↑ Wiedemann, G. (1848). "Biuret. Zersetzungsprodukt des Harnstoffs" [Biuret: decomposition product of urea]. Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie 68 (3): 323–326. doi:10.1002/jlac.18480680318.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Meessen, J. H.; Petersen, H. (2005), "Urea", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_333
- ↑ Beef cattle feed, Encyclopædia Britannica Online
- ↑ Kunkle, B.; Fletcher, J.; Mayo, D. (2013). "Florida Cow-Calf Management, 2nd Edition - Feeding the Cow Herd". IFAS Extension, University of Florida. Publication #AN117.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Oltjen, R. R.; Williams, E. E.; Slyter, L. L.; Richardson, G. V. (1969). "Urea versus biuret in a roughage diet for steers". Journal of Animal Science 29 (5): 816–822. PMID 5391979.
- ↑ Fonnesbeck, P. V.; Kearl, L. C.; Harris, L. E. (1975). "Feed Grade Biuret as a Protein Replacement for Ruminants. A Review". Journal of Animal Science 40 (6): 1150–1184.