Bisindolylmaleimide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
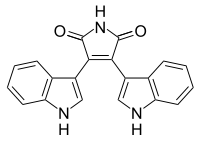
| IUPAC name
3,4-Di(1H-indol-2-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | 8862983 |
| |
| Jmol-3D images | Image |
| PubChem | 10687637 |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula |
C20H13N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 327.34 g·mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data is given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Bisindolylmaleimide is an organic compound that forms the core chemical structure of a variety of biologically active compounds.[1]
Examples of bisindolylmaleimide derivatives include:
- Bisindolylmaleimide I
- Enzastaurin
- Ruboxistaurin
- Tivantinib
References
- ↑ Faul, Margaret M.; Winneroski, Leonard L.; Krumrich, Christine A. (1998). "A New, Efficient Method for the Synthesis of Bisindolylmaleimides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 63 (17): 6053. doi:10.1021/jo980513c. PMID 11672217.
External links
![]() Media related to Bisindolylmaleimides at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bisindolylmaleimides at Wikimedia Commons