Birnbaum–Saunders distribution
The Birnbaum–Saunders distribution, also known as the fatigue life distribution, is a probability distribution used extensively in reliability applications to model failure times. There are several alternative formulations of this distribution in the literature. It is named after Z. W. Birnbaum and S. C. Saunders.
Theory
This distribution was developed to model failures due to cracks. A material is placed under repeated cycles of stress. The jth cycle leads to an increase in the crack by Xj amount. The sum of the Xj is assumed to be normally distributed with mean nμ and variance nσ2. The probability that the crack does not exceed a critical length ω is
where Φ() is the cdf of normal distribution.
If T is the number of cycles to failure then the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of T is
The more usual form of this distribution is:
Here α is the shape parameter and β is the location parameter.
Properties
The Birnbaum–Saunders distribution is unimodal with a median of β.
The mean (μ), variance (σ2), skewness (γ) and kurtosis (κ) are as follows:
Given a data set that is thought to be Birnbaum-Saunders distributed the parameters' values are best estimated by maximum likelihood.
Differential equation
The cdf of the Birnbaum-Saunders distribution is a solution of the following differential equation:
If T is Birnbaum-Saunders distributed with parameters α and β then T−1 is also Birnbaum-Saunders distributed with parameters α and β−1.
Transformation
Let T be a Birnbaum-Saunders distributed variate with parameters α and β. A useful transformation of T is
![X = \frac{ 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \left( \frac{ T }{ \beta } \right)^{ 0.5 } - \left( \frac{ T }{ \beta } \right)^{ -0.5 } \right]](../I/m/155d46850c2e18498029a386aa902aa1.png) .
.
Equivalently
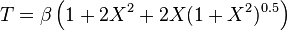 .
.
X is then distributed normally with a mean of zero and a variance of α2 / 4.
Probability density function
The general formula for the probability density function (pdf) is
where γ is the shape parameter, μ is the location parameter, β is the scale parameter, and 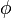 is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution.
is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution.
Standard fatigue life distribution
The case where μ = 0 and β = 1 is called the standard fatigue life distribution. The pdf for the standard fatigue life distribution reduces to
Since the general form of probability functions can be expressed in terms of the standard distribution, all of the subsequent formulas are given for the standard form of the function.
Cumulative distribution function
The formula for the cumulative distribution function is
where Φ is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution.
Quantile function
The formula for the quantile function is
where Φ −1 is the quantile function of the standard normal distribution.
External links
References
- Birnbaum, Z. W.; Saunders, S. C. (1969), "A new family of life distributions", Journal of Applied Probability 6 (2): 319–327, doi:10.2307/3212003, JSTOR 3212003
- Desmond, A.F. (1985), "Stochastic models of failure in random environments", Canadian Journal of Statistics 13 (3): 171–183, doi:10.2307/3315148, JSTOR 3315148
- Johnson, N.; Kotz, S.; Balakrishnan, N. (1995), Continuous Univariate Distributions 2 (2nd ed.), New York: Wiley
- Lemonte, A. J.; Cribari-Neto, F.; Vasconcellos, K. L. P. (2007), "Improved statistical inference for the two-parameter Birnbaum–Saunders distribution", Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 51: 4656–4681, doi:10.1016/j.csda.2006.08.016
- Lemonte, A. J.; Simas, A. B.; Cribari-Neto, F. (2008), "Bootstrap-based improved estimators for the two-parameter Birnbaum–Saunders distribution", Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation 78: 37–49, doi:10.1080/10629360600903882
- Cordeiro, G. M.; Lemonte, A. J. (2011), "The β-Birnbaum–Saunders distribution: An improved distribution for fatigue life modeling", Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 55: 1445–1461, doi:10.1016/j.csda.2010.10.007
- Lemonte, A. J. (2013), "A new extension of the Birnbaum–Saunders distribution", Brazilian Journal of Probability and Statistics 27: 133–149, doi:10.1214/11-BJPS160
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
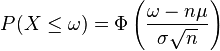
![P( T \le t ) = 1 - \Phi\left( \frac{ \omega - t \mu }{ \sigma \sqrt{ t } } \right)
= \Phi\left( \frac{ t \mu - \omega }{ \sigma \sqrt{ t } } \right)
= \Phi\left( \frac{ \mu \sqrt{ t } }{ \sigma } - \frac{ \omega }{ \sigma \sqrt{t} } \right)
= \Phi\left( \frac{ \sqrt{ \mu \omega } }{ \sigma } \left[ \left( \frac{ t }{ \omega / \mu } \right)^{ 0.5 } - \left( \frac{ \omega / \mu }{ t } \right)^{ 0.5 } \right] \right)](../I/m/0acdca7dd6a0e2044636cd7625532d23.png)
![F( x; \alpha, \beta ) = \Phi\left( \frac{ 1 }{ \alpha } \left[ \left( \frac{ x }{ \beta } \right)^{0.5} - \left( \frac{ \beta }{ x } \right)^{0.5} \right] \right)](../I/m/fa61a95b400b99d0dc02e5d758855ad1.png)
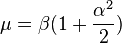
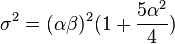
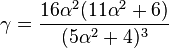
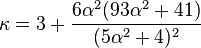
![\left\{\begin{array}{l}
2 \alpha^2 \beta x^2 (\beta+x) f'(x)+f(x) \left(-\beta^3+x^3+
\left(\alpha^2+1\right) \beta x^2+\left(3 \alpha^2-1\right) \beta^2 x\right)=0, \\[12pt]
f(1)=\frac{(\beta +1)
e^{-\frac{(\beta -1)^2}{2 \alpha^2 \beta}}}{2 \sqrt{2 \pi} \alpha \sqrt{\beta }}
\end{array}\right\}](../I/m/5c18e09e77209f2e8e3d1d4c48769bee.png)
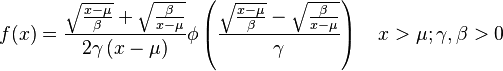
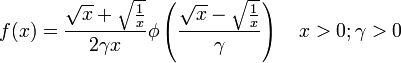
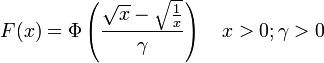
![G(p) = \frac{1}{4}\left[\gamma\Phi^{-1}(p) + \sqrt{4+\left(\gamma\Phi^{-1}(p)\right)^2}\right]^2](../I/m/6c306feb19408a8ac030249efc95689c.png)