Bikini Atoll
| Bikini Atoll Pikinni Atoll | ||
|---|---|---|
| Atoll | ||
|
Bikini Atoll. On the northwest cape of the atoll, adjacent to Nam island, the crater formed by the 15 Mt Castle Bravo nuclear test can be seen, with the smaller 11 Mt Castle Romeo crater adjoining it. | ||
| ||
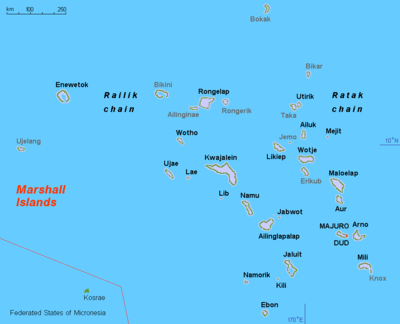 Map of the Marshall Islands showing Bikini | ||
 Map of Bikini Atoll | ||
| Coordinates: 11°35′N 165°23′E / 11.583°N 165.383°ECoordinates: 11°35′N 165°23′E / 11.583°N 165.383°E | ||
| Country | Republic of the Marshall Islands | |
| Area | ||
| • Land | 2.3 sq mi (6 km2) | |
| Population | ||
| • Total | 4-6 caretakers[1] | |
| Native population relocated in 1948. | ||
| Official name | Bikini Atoll Nuclear Test Site | |
| Type | Cultural | |
| Criteria | iv, vi | |
| Designated | 2010 (34th session) | |
| State Party | Marshall Islands | |
| Region | Asia-Pacific | |
Bikini Atoll (pronounced /ˈbɪk.ɨˌniː/ or /bɨˈkiː.ni/; Marshallese: Pikinni, [pʲi͡ɯɡɯ͡inʲːii̯], meaning coconut place)[2] is an atoll in the Marshall Islands. The atoll consists of 23 islands totaling 3.4 square miles (8.8 km2) surrounding a deep 229.4-square-mile (594.1 km2) central lagoon at the northern end of the Ralik Chain (approximately 87 kilometres (54 mi) northwest of Ailinginae Atoll and 850 kilometres (530 mi) northwest of Majuro). Within Bikini Atoll, Bikini, Eneu, Nam and Enidrik islands comprise just over 70% of the land area. Bikini and Eneu are the only islands of the atoll that hosted a permanent population. Bikini Island is the northeastern most and largest islet. Before World War II, the atoll was known by its Baltic German name as Escholtz Atoll.[3]
Between 1946 and 1958, 23 nuclear devices were detonated by the United States at seven test sites located on the reef, inside the atoll, in the air, or underwater.[4] They had a combined fission yield of 42.2 Mt. The testing began with the Operation Crossroads series in July 1946. Prior to nuclear testing, the residents initially accepted resettlement voluntarily to Rongerik Atoll, believing they would be able to return home within a short time. Rongerik Atoll could not produce enough food and the islanders starved for lack of food. When they could not return home, they were relocated to Kwajalein Atoll for six months before choosing to live on Kili Island, a small island one-sixth the size of their home island. Some were able to return to the Bikini Island in 1970 until further testing revealed dangerous levels of strontium-90. The islanders have been the beneficiary of several trust funds created by the United States government which as of 2013 covered medical treatment and other costs and paid about $550 annually to each individual.
In 1998, the Bikini Council authorized diving operations as a means to generate income for Bikini islanders currently and upon their eventual return. The tours, limited to fewer than a dozen experienced divers a week, cost more than US$5000 and include detailed histories of the nuclear tests. The dive operations were managed from a shore-based facility until operations were suspended in 2008 when the Marshall Island airline ceased service due to unresolved mechanical issues. They have since been resumed from a live-aboard ship. While the island may be habitable in the near term, virtually all of the islanders alive today have never lived there. As of 2013, about 4880 Bikini people live on Kili and other Marshall Islands, and some have emigrated to the United States. Bikini Island is currently visited by a few scientists and inhabited by 4-6 caretakers.[1]
The atoll and island gained world-wide attention due to nuclear testing, and because of the remaining direct tangible evidence of the nuclear tests, UNESCO named it a World Heritage Site. Building on this attention, in 1946, French engineer Louis Réard named his new swimsuit design the bikini, in hopes that its revealing style would create an "explosive commercial and cultural reaction" similar to the 1946 nuclear explosion at Bikini Atoll.[5][6][7][8][9]
Etymology
The island's English name is derived from the German colonial name Bikini given to the atoll when it was part of German New Guinea. The German name is transliterated from the Marshallese name for the island, Pikinni, ([pʲi͡ɯɡɯ͡inʲːii̯]), Pik" meaning "surface" and "Ni" meaning "coconut", or surface of coconuts.[2]
Culture

Before the advent of Western influence, the Bikini islanders' sustenance-based lifestyle was based on cultivating native plants and eating shellfish and fish. They were skilled boat builders and navigators, sailing the two-hulled proa to and from islets around the Bikini and other atolls in the Marshall Islands.[10] The islanders were relatively isolated and had developed a well-integrated society bound by close extended family association and tradition.[10]
Clothing and dress
The men wore a fringe skirt of native materials about 25 to 30 inches (60 to 80 cm) long. Women traditionally[11] wore two mats about a yard (metre) square each, made by weaving pandanus and hibiscus leaves together,[10] and belted around the waist.[12] Children were usually naked.[10]
The Christian missionaries who began arriving in the late 19th century influenced the islanders' notions of modesty. In 1919, a visitor reported that Marshall Islands women "are perfect models of prudery. Not one would think of exposing her ankles..." Every lagoon was led by a king and queen and a following of chieftains and chief women who comprised a ruling caste. Some of the leaders maintained Western-style bungalows and maintained servants, including secretaries, maids, and valets. Poverty was non-existent. The islanders worked the copra plantations under the watchful eye of the Japanese, who took a portion of the sales. Chiefs could retain as much as $20,000 per year, and the remainder was distributed to the workers. The Marshall islanders were formerly aggressive, but the influence of the mission churches eliminated most conflict. They took pride in extending hospitality to one another, even distant relatives.[13]
Women in the Marshall Islands today are still very modest. They believe a woman's thighs[14] and shoulders should be covered.[15] Women generally wear cotton muʻumuʻus or similar clothing that covers most of the body. While personal health is never discussed except within the family, and although women are especially private about female-related health issues,[11] they are willing to talk about their breasts.[11]
Marshall island women swim in muʻumuʻus which are made of a fine polyester that quickly dries. In the capital of Majuro, revealing cocktail dresses are inappropriate for both islanders and guests.[15] With the increasing influence of Western media, the younger generation may wear shorts, though the older generation equates shorts with loose morals. T-shirts, jeans, skirts, and makeup are making their way via the media to the islands.[16]
Land-based wealth
The Bikini islanders continue to maintain land rights as the primary measure of wealth.[17]
To all Marshallese, land is gold. If you were an owner of land, you would be held up as a very important figure in our society. Without land you would be viewed as a person of no consequence... But land here on Bikini is now poison land.[18]
Each family is part of a clan (Bwij), which owns all land. The clan owes allegiance to a chief (Iroij). The chiefs oversee the clan heads (Alap), who are supported by laborers (Dri-jerbal). The Iroij control land tenure, resource use and distribution, and settle disputes. The Alap supervise land maintenance and daily activities. The Dri-jerbal work the land including farming, cleaning, and construction.
The Marshallese society is matrilineal and land is passed down from generation to generation through the mother. Land ownership ties families together into clans. Grandparents, parents, grandchildren, aunts, uncles, and cousins form extended, close-knit family groups. Gatherings tend to become big events. One of the most significant family events is the first birthday of a child (kemem), which relatives and friends celebrate with feasts and song.[10][19]
Payments made in the 20th century as reparations for damage to the Bikini Atoll and the islanders' way of life have elevated their income relative to other Marshall Island residents. It has caused some Bikini islanders to become economically dependent on the payments from the trust fund. This dependency has eroded individual's interest in traditional economic pursuits like taro and copra production. The move also altered traditional patterns of social alliance and political organization. On Bikini, rights to land and land ownership were the major factor in social and political organization and leadership. After relocation and settlement on Kili, a dual system of land tenure evolved. Disbursements from the trust fund was based in part to land ownership on Bikini and based on current land tenure on Kili.[20]
Before the residents were relocated, they were led by a local chief and under the nominal control of the Paramount Chief of the Marshall Islands. Afterward, they had greater interaction with representatives of the trust fund and the U.S. government and began to look to them for support.[20]
Language
Most Marshallese speak both the Marshallese language and at least some English. Government agencies use Marshallese. One important word in Marshallese is "yokwe" which is similar to the Hawaiian "aloha" and means "hello", "goodbye" and "love".[21]
Environment
The Bikini Atoll is part of the Ralik Chain (for "sunset chain") within the Marshall Islands.
Geography
There are 23 islands in the Bikini Atoll; the islands of Bokonijien, Aerokojlol, and Nam were vaporized during the nuclear tests.[22] The islands are composed of low coral limestone аnd sand.[21] The average elevation is only about 7 feet (2.1 m) above low tide level. The total lagoon area is 229.4-square-mile (594.1 km2). The primary home of the islanders was the most northeast and largest islet, Bikini Island, totaling 586 acres (237 ha) and 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) long.
Flora and fauna
The islanders cultivated native foods including coconut, pandanus, papaya, banana, arrowroot, taro, limes, breadfruit, and pumpkin. A wide variety of other trees and plants are also present on the islands.[22]
The islanders were skilled fishermen. They used fishing line made from coconut husk and hooks from sharpened sea shells. They used more than 25 methods of fishing.[10] The islanders raised ducks, pigs, and chickens for food and kept dogs and cats as pets. Animal life in the atoll was severely impacted by the atomic bomb testing. Existing land species include small lizards, hermit crabs, and coconut crabs. The islands are frequented by a wide variety of birds.[22]
To allow vessels with a larger draft to enter the lagoon and to prepare for the atomic bomb testing, the United States used explosives to cut a channel through the reef and to blow up large coral heads in the lagoon. The underwater nuclear explosions carved large holes in the bottom of the lagoon that were partially refilled by blast debris. The explosions distributed vast amounts of irradiated, pulverized coral and mud across wide expanses of the lagoon and surrounding islands. As of 2008, the atoll had recovered nearly 65% of the biodiversity that existed prior to radioactive contamination, but 28 species of coral appear to be locally extinct.[4]
Weather
The islands are hot аnd humid. The temperature on Bikini Atoll is a constant 80 to 85 °F (27 to 29 °C) year round. The water temperature is also 80 to 85 °F (27 to 29 °C) all year. The islands border the Pacific typhoon belt. The wet season is frоm May tо December while the trade winds from January through May produce higher wave action.[22]
Resident and non-resident population
When the United States asked the islanders to relocate in 1946, 19 islanders lived elsewhere. The 167 residents comprising about 40 families[23] who lived on the atoll voluntarily moved to Rongerik Atoll, and then to Kwajalein Atoll, and once again in November 1948 to Kili Island, when the population numbered 184. They were later given public lands on Ejit and a few families initially moved there to grow copra. In 1970, about 160 Bikini islanders returned to live on the atoll after they were reassured that it was safe. They remained for about 10 years until scientists found an 11-fold increase in the cesium-137 body burdens and determined that the island wasn't safe after all. The 178 residents were evacuated in September 1978 once again.[17]
Since then a number of descendants have moved to Majuro (the Marshall Islands' capital), other Marshall Islands, and the United States. In 1999, there were 2600 total individuals; 1000 islanders living on Kiji, 700 in Majuro, 275 on Ejit, 175 on other Marshall Islands or atolls, and 450 in the United States. Of those, 81 were among those who left the atoll in 1946.[24] In 2001, the population of the dispersed islanders was 2800.[25]
As of February 2013, there were 4880 living Bikini islanders: 1250 islanders living on Kili, 2150 on Majuro, 280 on Ejit, 350 on other Marshall Islands, and 850 in the United States and other countries. Of that number, 31 lived on Bikini in 1946.[22] The resident population of the atoll is currently 4-6 caretakers,[1][25] including Edward Maddison. Maddison has lived on Bikini Island since 1985. His grandfather was one of the original residents relocated in 1947.[26] He also helps the U.S. Department of Energy with soil monitoring, testing cleanup methods, mapping the wrecks in the lagoon, and accompanying visitors on dives.[27]
Government
The Bikini islanders were historically loyal to a king, or Irojj. After the Marshall Islands separated from the United States in the Compact of Free Association in 1986, its constitution established a bicameral parliament. The upper house is only a consultative body. It consists of traditional leaders (Iroijlaplap), known as the Council of Irooj, who advise the lower house on traditional, cultural issues.[28] As of 2013, there are four members of the Council.
The lower house or Nitijela consists of 33 senators elected by 24 electoral districts. Universal suffrage is available to all citizens 18 years of age and older. The 24 electoral districts correspond roughly to each Marshall Islands atoll. The lower house elects the president who, with the approval of the Nitijela, selects a cabinet from among members of the Nitijela.[29][30]
Local government
Four district centers in Majuro, Ebeye, Jaluit, and Wotje provide local government. Each district elects a council and mayor and may appoint local officials. The district centers are funded by the national government and by local revenues. There are two political parties. Elections are held every four years. In 2011 Nishma Jamore was elected mayor of the district representing the Bikini people. Council members are elected from two wards on Ejit Island (three seats) and Kili Island (12 seats).[29]
U.S. liaison
The local government works with a U.S. paid Liaison Officer for Bikini Atoll Local Government, Jack Niedenthal, who is acting Bikini/Kili/Majuro Projects Manager. He is also the Tourism Operations Manager and oversees Bikini Atoll Divers.
History
Human beings have inhabited the Bikini Atoll for about 3,600 years.[31] U.S. Army Corps of Engineers archaeologist Charles F. Streck, Jr., found bits of charcoal, fish bones, shells and other artifacts under 3 feet (1 metre) of sand. Carbon-dating placed the age of the artifacts at between 1960-1650, B.C. Other discoveries on Bikini and Eneu island were carbon-dated to between 1,000 B.C. and 1 B.C., and others between 400-1,400 A.D.[32]

The first recorded sighting by Europeans was in September 1529 by the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Saavedra on board his ship La Florida when trying to return to New Spain, and was charted as Buenos Jardines (Good Gardens in Spanish).[33] The Marshalls lacked the wealth to encourage exploitation or mapping. The British captain Samuel Wallis chanced upon Rongerik and Rongelap atolls while sailing from Tahiti to Tinian. The British naval captains John Marshall and Thomas Gilbert partially explored the Marshalls in 1788.[34]
The first Westerner to see the atoll in the mid-1820s was the Baltic German captain and explorer Otto von Kotzebue, sailing in service of the Russian Empire. He visited three times during 1816 and 1817.[35] He named the atoll Eschscholtz Atoll after Johann Friedrich von Eschscholtz, the naturalist of von Kotzebue's ship. The Baltic Germans used the atoll to produce copra oil from coconuts, although contact with the native population was infrequent. The atoll's climate is dryer than the more fertile southern Marshall Islands which produced more copra. Bikini islanders were recruited into developing the copra trade during the German colonial period.[20]
Spanish-German Treaty of 1899
The explosion in Havana Harbor of the battleship USS Maine—sent by the U.S. to protect American commercial interests in Cuba—led to the Spanish–American War in 1898. It resulted in Spain's losing many of its remaining colonies, Cuba became independent while the United States took possession of Puerto Rico and Spain's Pacific colonies of the Philippines and Guam. This left Spain with the remainder of the Spanish East Indies in the Pacific, about 6000 islands that were tiny, sparsely populated. After the loss of the administrative center of Manila, the minor islands became ungovernable and, after the entire loss of two Spanish fleets in 1898, indefensible. The year is still known in Spain as the "Year of the national disaster" or "the loss of the 400 years Empire".
The Spanish government sold the islands to Germany.[29] The treaty was signed on February 12, 1899, by Spanish Prime Minister Francisco Silvela and transferred the Caroline Islands, the Mariana Islands, Palau and other possessions to Germany. The islands were then placed under control of German New Guinea. The first American missionary arrived in 1908.
Japanese occupation
Bikini was captured along with the rest of the Marshall Islands by the Imperial Japanese Navy in 1914 during World War I and mandated to the Empire of Japan by the League of Nations in 1920. The Japanese administered the island under the South Pacific Mandate, but mostly left local affairs in the hands of traditional local leaders until the start of World War II. At the outset of the war, the Marshall Islands suddenly became a strategic outpost for the Japanese. They built and manned a watchtower on the island, an outpost for the Japanese headquarters on Kwajalein Atoll, to guard against an American invasion of the islands.[36]
World War II
The islands remained relatively unscathed by the war until February 1944, when in a terrific bloody battle, the American forces captured Kwajalein Atoll. There were only five Japanese soldiers on Bikini and they committed suicide rather than allow themselves to be captured.[36]
Residents relocated

After World War II, the United States was engaged in a Cold War Nuclear arms race with the Soviet Union to build bigger and better bombs.[36] The nuclear weapons testing at Bikini Atoll program was a series of 23 nuclear devices detonated by the United States between 1946 and 1958 at seven test sites. The test weapons were detonated on the reef itself, on the sea, in the air and underwater[4] with a combined fission yield of 42.2 Mt. The testing began with the Operation Crossroads series in July 1946. Shortly after World War II ended, President Harry S. Truman directed Army and Navy officials to secure a site for testing nuclear weapons on American warships. While the Army had seen the results of a land-based explosion, the Navy wanted to know the effect of a nuclear weapon on ships. They wanted to determine whether ships could be spaced at sea and in ports in a way that would make nuclear weapons ineffective against vessels.[38]
Bikini was distant from both regular sea and air traffic, making it an ideal location. In February 1946, Navy Commodore Ben H. Wyatt, the military governor of the Marshall Islands, asked the 167 Micronesian inhabitants of the atoll to voluntarily and temporarily relocate so the United States government could begin testing atomic bombs for "the good of mankind and to end all world wars." After "confused and sorrowful deliberation" among the Bikinians, their leader, King Juda, agreed to the US relocation request, announcing "We will go believing that everything is in the hands of God."[36] Nine of the eleven family heads, or alaps, chose Rongerik as their new home.[39]
In February, Navy Seabees helped them to disassemble their church and community house and prepare to relocate them to their new home. On March 7, 1946, the residents gathered their personal belongings and saved building supplies. They were transported 125 miles (201 km) eastward on U.S. Navy landing craft 1108 to the uninhabited Rongerik Atoll,[39] which was one-sixth the size of Bikini Atoll.[39] No one lived on Rongerik because it had an inadequate water and food supply and due to deep-rooted traditional beliefs that the island was haunted by the Demon Girls of Ujae. The Navy left them with a few weeks of food and water which soon proved to be inadequate.[36]
Nuclear testing program
The weapons testing began with the Operation Crossroads series in July 1946. The Baker test's radioactive contamination of all the target ships was the first case of immediate, concentrated radioactive fallout from a nuclear explosion. Chemist Glenn T. Seaborg, the longest-serving chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission, called Baker "the world's first nuclear disaster."[40] This was followed by a series of later tests that left the island contaminated with radioactivity, particularly Caesium-137, and uninhabitable.
Strategic Trust Territory
In 1947, the United States convinced the United Nations to designate the islands of Micronesia a United Nations Strategic Trust Territory. This was the only trust ever granted by the U.N.[41] The United States Navy controlled the Trust from a headquarters in Guam until 1951, when the United States Department of the Interior took over control, administering the territory from a base in Saipan.[42] The directive stated that the United States should "promote the economic advancement and self-sufficiency of the inhabitants, and to this end shall... protect the inhabitants against the loss of their lands and resources..."[36]
Despite the promise to "protect the inhabitants," from July 1946 through July of 1947, the residents of Bikini Atoll were left alone on Rongerik Atoll and were starving for lack of food. A team of U.S. investigators concluded in late 1947 that the islanders must be moved immediately. Press from around the world harshly criticized the U.S. Navy for ignoring the people. Harold Ickes, a syndicated columnist, wrote "The natives are actually and literally starving to death."[36]
Move to Kili Island

In January 1948, Dr. Leonard Mason, an anthropologist from the University of Hawaii, visited Rongerik Atoll and was horrified at what he found. One resident of Rongerik commented,[18]
We'd get a few fish, then the entire community would have to share this meager amount... The fish were not fit to eat there. They were poisonous because of what they ate on the reef. We got sick from them, like when your arms and legs fall asleep and you can't feel anything. We'd get up in the morning to go to our canoes and fall over because we were so ill... Then we started asking these men from America [to] bring us food... We were dying, but they didn't listen to us.
Mason requested that food be brought to the islanders on Rongerik immediately along with a medical officer. The Navy then selected Ujelang Atoll for their temporary home and some young men from the Bikini Atoll population went ahead to begin constructing living accommodations. But U.S. Trust Authorities changed their mind. They decided to use Enewetak Atoll as a second nuclear weapons test site and relocated that atoll's residents to Ujelang Atoll instead and to the homes built for the Bikini Islanders.[36]
In March 1948, 184 malnourished Bikini islanders were relocated again to Kwajalein Atoll. They were given tents on a strip of grass alongside the airport runway to live in.[41] In June 1948, the Bikini residents chose Kili Island as a long-term home.[36] The small, 200 acres (81 ha) (.036 square miles (0.093 km2)) island was uninhabited and wasn't ruled by a paramount iroij, or king. In June, the Bikini community chose two dozen men to accompany eight Seabees to Kili to begin construction of a village. In November 1948, the residents, now totaling 184 individuals, moved to Kili Island,[36] at 0.93 square kilometres (0.36 sq mi), one of the smallest islands in the Marshall Island chain. They soon learned they could no longer fish the way they had on Bikini Atoll. Kili lacked the calm, protected, bountiful lagoon.[41] Living on Kili Island effectively destroyed their culture that had been based on fishing and island-hopping canoe voyages to various islets around the Bikini Atoll.[18] Kili does not provide enough food for the transplanted residents.
Failed resettlement
After their relocation to Kili, the Bikini residents continued to suffer from inadequate food supplies. Kili is a small island without a lagoon, and most of the year it is exposed to 10 to 20 feet (3.0 to 6.1 m) waves that make fishing and putting canoes out difficult. Starvation ensued. In 1949, the Trust Territory administration donated a 40 feet (12 m) ship for transporting copra between Kili and Jaluit Atoll, but the ship was wrecked in heavy surf while delivering copra and other fruit.[36] The U.S. Trust Authorities airdropped food onto Kili. The residents were forced to rely on imported USDA rice and canned goods and had to buy food with their supplemental income.[36]
During 1955 and 1956, ships dispatched by the U.S. Trust Territory continually experienced problems unloading food because of the rough seas around the island, leading to additional food shortages once again. The people once again suffered from starvation and food shortages increased in 1956. The U.S. suggested that some of the Bikini Islanders move to Jaluit where food was more readily available. A few people moved.[41]
The United States opened a satellite community for the families on public land on Jaluit Atoll, 30 miles (48 km) north. Three families moved there to produce copra for sale and other families rotated living there later on.[36] Their homes on both Kili and Jaluit were struck by typhoons during 1957 and 1958, sinking their supply ship and damaging crops.
Return to Bikini Island
In June 1968, based on scientific advice that the radiation levels were sufficiently reduced, President Lyndon B. Johnson promised the 540 Bikini Atoll family members living on Kili and other islands that they would be able to return to their home. The Atomic Energy Commission cleared radioactive debris from the island, and the U.S. Trust Territory was in charge of rebuilding structures and replanting crops on the atoll. But shortly afterward the Trust Territory ended regular air flights between Kwajalein Atoll and Bikini Atoll which seriously impeded progress. Coconut trees were finally replanted in 1972, but the AEC learned that the coconut crabs retained high levels of radioactivity and could not be eaten. The Bikini Council voted to delay a return the island as a result.[36]
In 1987, a few Bikini elders returned to the island to reestablish old property lines. Construction crews began building a hotel on Bikini, and installed generators, desalinators, and power lines. A packed coral and sand runway still exists on Enyu Island.
Three extended families, eventually totaling about 100 people, moved back to their home island in 1972 despite the risk. But 10 years later, a team of French scientists performed additional tests on the island and its inhabitants. They found some wells were too radioactive for use and determined that the pandanus and breadfruit were also dangerous for human consumption. Urine samples from the islanders on Bikini Atoll showed low levels of plutonium 239 and 240. As a result, the Bikini community filed a federal lawsuit seeking a complete scientific survey of Bikini and the northern Marshall Islands. Inter-departmental squabbling over responsibility for the costs delayed the work for three years.[36] Then in May 1977 scientists found dangerously high levels of strontium-90 in the well water exceeding the U.S. maximum allowed limits.[43] In June, the Department of Energy stated that "All living patterns involving Bikini Island exceed Federal [radiation] guidelines for thirty year population doses." Later that year scientists discovered an 11-fold increase in the cesium-137 body burdens in all of the people living on the atoll.[36] In May 1978 officials from the U.S. Department of the Interior described the 75% increase in radioactive cesium 137 found as "incredible."[17]
Women were experiencing miscarriages, stillbirths, and genetic abnormalities in their children.[44][45] Researchers learned that the coral soil behaved differently from mainland soil because it contains very little potassium. Plants and trees readily absorb potassium as part of the normal biological process, but since cesium is part of the same group on the periodic table, it is absorbed by plants in a very similar chemical process. The islanders who unknowingly consumed contaminated coconut milk were found to have abnormally high concentrations of cesium in their bodies. The Trust Territory decided that the islanders had to be evacuated from the atoll a second time.[46]
Relocation to Kili Island
As a result of the military use of the island and the failed resettlement, the islands are littered with abandoned concrete bunkers and tons of heavy equipment, vehicles, supplies, machines, and buildings.[47] In September 1978, Trust Territory officials finally arrived to relocate the residents. The radiological survey of the northern Marshalls, compelled by the 1975 lawsuit, began only after the residents were removed[36] and returned to Kili Island.[36]
As of 2013, the tiny 0.93 square kilometres (0.36 sq mi) Kili Island supported about 600 residents who live in cinderblock houses. They must rely on contributions from a settlement trust fund to supplement what they produce locally. Each family receives 1-2 boxes of frozen chicken, 2-4 23 kilograms (51 lb) bags of flour, and 2-4 bags of rice 2-3 times per year. The islanders operate several small stores out of their homes to supply nonperishable food items like salt, Tabasco, candy, and canned items. A generator provides electricity.
Children attend elementary school on Kili through eighth grade. Toward the end of the eighth grade, students must pass a standardized test to gain admission to attend public high school in Jaluit or Majuro.
Trust funds and failed claims
In 1975, when the islanders who had returned to Bikini Atoll learned that it wasn't safe, they sued the United States for the first time, demanding a radiological study of the northern islands.[48]
In 1975, the United States set up The Hawaiian Trust Fund for the People of Bikini, totaling $3 million. When the islanders were removed from the island in 1978, the U.S. added $3 million to the fund. The U.S. created a second trust fund, The Resettlement Trust Fund for the People of Bikini, containing $20 million in 1982. The U.S. added another $90 million to that fund to pay to clean up, reconstruct homes and facilities, and resettle the islanders on Bikini and Eneu islands.[49]
In 1983, the U.S. and the Marshall islanders signed the Compact of Free Association, which gave the Marshall Islands independence. The Compact became effective in 1986 and was subsequently modified by the Amended Compact that became effective in 2004.[50] It also established the Nuclear Claims Tribunal, which was given the task of adjudicating compensation for victims and families affected by the nuclear testing program. Section 177 of the compact provided for reparations to the Bikini islanders and other northern atolls for damages. It included $75 million to be paid over 15 years.[49] On March 5, 2001, the Nuclear Claims Tribunal ruled against the United States for damages done to the islands and its people.[36]
The payments began in 1987 with $2.4 million paid annually to entire Bikini population, while the remaining $2.6 million is paid into The Bikini Claims Trust Fund. This trust is intended to exist in perpetuity and to provide the islanders a 5% payment from the trust annually.[49]
The United States provided $150 million in compensation for damage caused by the nuclear testing program and their displacement from their home island.[51]
By 2001, of the original 167 residents who were relocated, 70 were still alive, and the entire population has grown to 2800.[18] Most of the islanders and their descendents lived on Kili, in Majuro, and in the United States.
The Hawaiian Trust Fund for the People of Bikini was liquidated as required by law in December 2006. The value of The Resettlement Trust Fund for the People of Bikini as of 31 March 2013 was approximately $82 million and The Bikini Claims Trust Fund was worth approximately $60 million. Each member of the trust receives about $550 a year, making them relatively well-off (compared to other Marshall Island residents).[49]
In 2001, the Nuclear Claims Tribunal awarded the islanders a total of $563,315,500 after deducting past awards. However, the U.S. Congress has failed to fund the settlement. The only recourse is for the Bikini people to petition the U.S. Congress to fund the payment and fulfill this award. The United States Supreme Court turned down the islanders' appeal of the United States Court of Appeals decision that refused to compel the government to fund their claim.
Representatives for the Bikini people expect this process to take many years and do not know whether the United States will honor the terms of the Compact of Free Association.[49]
World Heritage Site
Because the site bears direct tangible evidence of the nuclear tests conducted there amid the paradoxical tropical location, UNESCO determined that the atoll symbolizes the dawn of the nuclear age and named it a World Heritage site on 3 August 2010.[52][53]
Bikini Atoll has conserved direct tangible evidence ... conveying the power of ... nuclear tests, i.e. the sunken ships sent to the bottom of the lagoon by the tests in 1946 and the gigantic Bravo crater. Equivalent to 7,000 times the force of the Hiroshima bomb, the tests had major consequences on the geology and natural environment of Bikini Atoll and on the health of those who were exposed to radiation. Through its history, the atoll symbolises the dawn of the nuclear age, despite its paradoxical image of peace and of earthly paradise.[54][52]
Visitor access
Bikini Atoll is open to visitors aboard vessels that are completely self-sufficient if they obtain prior approval. They must also pay for a diver and two local government council representatives to accompany them. The local representation is required to verify that visitors don't remove artifacts from the wrecks in the lagoon.[55]
Bikini Lagoon diving
To provide an economic base for future resettlement of the atoll, the Bikini Council organized the Bikini Atoll Divers to host divers in June 1996.[56] Because the lagoon has remained undisturbed for so long, it contains a larger amount of sea life than usual, including sharks, which increases divers' interest in the area. Visibility depth is over 100 feet (30 m). The lagoon is immensely popular with divers and is regarded as among the top 10 diving locations in the world. The Bikini Council hired Edward Maddison who has lived on Bikini Island since 1985 as head divemaster and resort manager.[27]
Facilities
To accommodate the dive program and anglers, the Bikini Council built new air-conditioned rooms with private bathrooms and showers. They include verandas overlooking the lagoon. There is a dining facility that serves American-style meals. The head chef Mios Maddison also prepares Marshallese dishes featuring fresh seafood. Only 12 visitors can be hosted at one time.[27]
In September 2007, the last of Air Marshall Islands' commuter aircraft ceased operations when spare parts could not be located and the aircraft were no longer airworthy. A half dozen divers and a journalist were stranded for a week on Bikini Island.[41] The Bikini islanders suspended land-based dive operations from August 2008 through 2010, unless the vessel was fully self-contained and only by prior arrangement.[57]
Diving program
The diving program is limited to 11 visitors per week at US$4,000 per diver; the operation brought in more than $500,000 during the season from May to October during 2001.[58] Because of the lingering contamination, all fruits and vegetables used for the Bikini Atoll dive and sport fishing operation were imported.[24]
The visitors receive a history lesson along with the dive experience, including movies and complete briefings about each of the ships, their respective histories, and a tour of the island and the atoll.[58] Divers are able to visit the USS Saratoga.[58] Sport fishing was also opened to visitors.
Sportfishing
Although the atomic blasts obliterated three islands and contaminated much of the atoll, after 50 years the coral reefs had recovered. The reefs attracted reef fish and their predators: 30 pounds (14 kg) dogtooth tuna, 20 pounds (9.1 kg) barracuda, and bluefin trevally as big as 50 pounds (23 kg). Given the long-term absence of humans, the Bikini lagoon offers sportsmen one of the most pristine fishing environments in the world.[25]
Live-aboard program
In October 2010, a live-aboard, self-contained vessel successfully conducted dive operations. In 2011, the local government licensed the live-aboard operator as the sole provider of dive expeditions on the nuclear ghost fleet at Bikini Atoll. The dive season runs from May through October. As of 2013, the 12-day dive trip costs US$5,100 per person.[22] Visitors are still able to land on the island for brief stays.
Shipwrecks
Shipwrecks in the lagoon include:
- USS Saratoga (CV-3) - aircraft carrier
- USS Arkansas (BB-33) - battleship
- USS Gilliam (APA-57) - attack transport
- USS Carlisle (APA-69) - attack transport
- USS Lamson (DD-367) - destroyer
- USS Anderson (DD-411) - destroyer
- USS Apogon (SS-308) - submarine
- USS Pilotfish (SS-386) - submarine
- Japanese battleship Nagato - battleship
- Japanese cruiser Sakawa - light cruiser
Current habitable state
The potential to make the island habitable has substantially improved in recent years. The International Atomic Energy Agency found that cesium-137 levels are dropping considerably faster than anyone expected. Terry Hamilton, scientific director of Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory’s Marshall Islands Dose Assessment and Radioecology Program, reported that “Conditions have really changed on Bikini. They are improving at an accelerated rate. By using the combined option of removing soil and adding potassium, we can get very close to the 15 millirem standard. That has been true for roughly the past 10 years. So now is the time when the Bikinians, if they desired, could go back.”[25][59]
The islanders want the top soil removed, but the money is not there for the cleanup. The opportunity for some Bikini islanders to potentially relocate back to their home island creates a dilemma. Only a few living islanders were born there. Most of the younger generation have never lived there or even visited and do not have a desire to return. As of 2013, unemployment in the Marshall Islands was at about 40 percent. The population is growing at a four-percent growth rate, so increasing numbers are taking advantage of terms in the Marshall Islands’ Compact of Free Association that allow them to obtain jobs in the United States.[25]
After the islanders were relocated in 1946, while the Bikini islanders were experiencing starvation on Rongerik Atoll, Lore Kessibuki wrote an anthem for the island:[25]
No longer can I stay, it’s true
No longer can I live in peace and harmony
No longer can I rest on my sleeping mat and pillow
Because of my island and the life I once knew there
The thought is overwhelming
Rendering me helpless and in great despair.
In popular culture
Swimsuit design
The atoll's name became well-known world-wide as a result of the nuclear tests. On July 5, 1946, five days after the first nuclear device (nicknamed Able) was exploded over the Bikini Atoll during Operation Crossroads,[60] Louis Réard introduced a new swimsuit design named the bikini[61] after the atoll. Réard was a French mechanical engineer by training and manager of his mother's lingerie shop in Paris. He introduced the new garment to the media and public[62] on July 5, 1946[63] at Piscine Molitor, a public pool in Paris.[64] He hired Micheline Bernardini, a 19-year-old nude dancer from the Casino de Paris,[65] to demonstrate his design. It featured a g-string back of 30 square inches (200 cm2) of cloth with newspaper-type print and was an immediate sensation. Bernardini received 50,000 fan letters, many of them from men.[64][66]
Réard said that "like the bomb, the bikini is small and devastating".[67] Fashion writer Diana Vreeland described the bikini as the "atom bomb of fashion".[67] Réard hoped his swimsuit's revealing style would create an explosive commercial and cultural reaction, similar in intensity to society's response to the nuclear test on Bikini Atoll.[6][7][8][9]
The bikini's design violates Marshall Islanders' modern customs of modesty because it exposes a woman's thighs and shoulders.[14][15] However, before contact with Western missionaries, Marshall Island women were traditionally topless and still do not sexually objectify female breasts as is common in much of Western society[11] which the bikini does cover. Marshall Island women swim in their muumuus which are made of a fine polyester that dries quickly.[15] Wearing a bikini in the Marshall Islands is mainly limited to restricted-access beaches and pools like those at private resorts or on United States government facilities on the Kwajalein Atoll within the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site.[68][69]
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Borrett, Lloyd (March 2013). "Diving the Nuclear Ghost Fleet at Bikini Atoll". Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Marshallese-English Dictionary-Place Name Index". Retrieved 8 August 2013.
- ↑ "The Marshall Islands: A Brief History". Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Zoe T. Richards, Maria Beger, Silvia Pinca, and Carden C. Wallace (2008). "Bikini Atoll coral biodiversity resilience five decades after nuclear testing" (PDF). Marine Pollution Bulletin 56 (3): 503–515. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.11.018. PMID 18187160. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ↑ "The History of the Bikini". Time. July 3, 2009. Retrieved August 20, 2013.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Tiny Swimsuit That Rocked the World: A History of the Bikini". Randomhistory.com. May 1, 2007. Retrieved December 3, 2011.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Swimsuit Trivia – The Surprising History of the Bikini". Swimsuit-style.com. Retrieved December 3, 2011.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Brij V. Lal; Kate Fortune (2000). The Pacific Islands: an Encyclopedia. University of Hawaii Press. p. 259. ISBN 978-0-8248-2265-1. Retrieved July 5, 2011.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Ruth Foster (June 2007). Nonfiction Reading Comprehension: Social Studies, Grade 5. Teacher Created Resources. p. 130. ISBN 978-1-4206-8030-0. Retrieved July 5, 2011.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 "Introduction to Marshallese Culture". Retrieved 17 August 2013.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Briand, Greta; Peters, Ruth (2010). "Community Perspectives on Cultural Considerations for Breast and Cervical Cancer Education among Marshallese Women in Orange County, California" (PDF). Californian Journal of Health Promotion (8): 84–89. Retrieved 25 August 2013.
- ↑ Bliss, Edwin Munsell (1891). The Encyclopedia of Missions II. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
- ↑ McMahon, Thomas J. (November 1919). "The Land of the Model Husband". Travel 34 (1).
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Customs". Marshall Islands. FIU College of Business Administration. Retrieved 25 August 2013.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 "Marshall Islands". Encyclopedai.com. Retrieved 25 August 2013.
- ↑ "Republic of the Marshall Islands" (PDF). Culture Grams 2008. Ann Arbor, Michigan: ProQuest. Retrieved 25 August 2013.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 "Bikini History". Archived from the original on 23 June 2007. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 Guyer, Ruth Levy (September 2001). "Radioactivity and Rights". American Journal of Public Health 91 (9, issue 9): 1371–1376. doi:10.2105/AJPH.91.9.1371. PMC 1446783. PMID 11527760.
- ↑ "Marshallese Culture". Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Bikini". Countries and their Cultures. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Destinations / Marshall Islands
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 22.4 22.5 "Bikini Atoll Reference Facts". Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ "Bikini Atoll". Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Bikini Facts". Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 25.4 25.5 Gwynne, S.C. (5 October 2012). "Paradise With an Asterisk". Outside Magazine. Retrieved 9 August 2013.
- ↑ Pena, Tony. "Return To Bikini Atoll". Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Kattenburg, Dave. "After the bombs". New Internationalist Magazine. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ↑ "History of the Nitijela". Republic of the Marshall Islands. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 "The Nitijela (Parliament)". Republic of the Marshall Islands. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- ↑ "The Presidency and Cabinet". Republic of the Marshall Islands. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- ↑ "The Natural History of Enewetak Atoll". 1987. p. 333.
- ↑ Taggart, Stewart. "Bikini Excavation Indicates Early Man in Micronesia". Associated Press. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ Montana, Alberto Descubrimientos, exploraciones y conquistas de españoles y portugueses en América y Oceania, Miguel Salvatella, Barcelona, 1943, p.81
- ↑ "Marshall Islands". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ↑ "Bikini". Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 36.4 36.5 36.6 36.7 36.8 36.9 36.10 36.11 36.12 36.13 36.14 36.15 36.16 36.17 36.18 Niedenthal, Jack. "A Short History of the People of Bikini Atoll". Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- ↑ "he Republic of the Marshall Islands and the United States: A Strategic Partnership". Embassy of the Marshall Islands of the United States. Retrieved 18 August 2013.
- ↑ "Bikini". Newsweek. 1 July 1946. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 "Operation Crossroads - The Official Pictorial Record" (PDF). New York: W. H. Wise and Co. Inc. 1946. p. 21.
- ↑ Weisgall 1994, p. ix.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 41.2 41.3 41.4 Kattenburg, David (December 2012). "Stranded on Bikini". Green Planet Monitor. Retrieved 19 August 2013.
- ↑ "Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands". University of Hawaii.
- ↑ "A Short History of the People of Bikini Atoll". Archived from the original on 25 June 2007. Retrieved 27 June 2007.
- ↑ Chris Hamilton (March 4, 2012). "Survivors of nuke testing seek justice: Marshall Islanders on Maui rally to share nation's story". Maui News.
- ↑ "Victims of the Nuclear Age". Archived from the original on 9 August 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2007.
- ↑ "The Ghost Fleet of Bikini Atoll". August 9, 2010. A&E Television Networks. Military History Channel. Retrieved 4 May 2012. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ "Cruising Bikini Atoll 60 Years after the bomb". July 2006. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ↑ "Despite High Court Denial, Battle Over Bikini Atoll Bombing Endures". Bikini Island Local Government. 26 April 2010. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 49.2 49.3 49.4 "U.S. Reparations for Damages". Bikini Atoll. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ "U.S. Relations With Marshall Island". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 14 August 2013.
- ↑ "Marshall Islands Nuclear Claims Tribunal". Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2007.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "Bikini Atoll, Nuclear Tests Site" (PDF). Thirty-fourth Session. World Heritage Committee. 3 August 2010. Retrieved 6 June 2012.
- ↑ "Bikini Atoll Nuclear Test Site". UNESCO. Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- ↑ Bikini Atoll Nuclear Test Site, unesco.org
- ↑ "Indies Trader". Bikini Atoll Divers. Retrieved 13 August 2013.
- ↑ "Scuba Diving in Bikini Lagoon". diveadventures.com.au. Retrieved 30 October 2009.
- ↑ "Bikini Atoll Dive Tourism Information". bikiniatoll.com. 2008-08-23. Retrieved 4 December 2013.
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 58.2 Niedenthal, Jack (6 August 2002). "Paradise Lost - 'For the Good of Mankind'". The Guardian. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- ↑ "Conditions at Bikini Atoll". International Atomic Energy Agency. Retrieved 12 August 2013.
- ↑ Campbell, Richard H. (2005). The Silverplate Bombers: A History and Registry of the Enola Gay and Other B-29s Configured to Carry Atomic Bombs. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland & Company. ISBN 0-7864-2139-8. OCLC 58554961 pp=18, 186–189.
- ↑ "Swimsuit Trivia History of the Bikini". Swimsuit Style. Retrieved 10 July 2008.
- ↑ Westcott, Kathryn (5 June 2006). "The Bikini: Not a brief affair". BBC News. Retrieved 17 September 2008.
- ↑ David Louis Gold (2009). Studies in Etymology and Etiology: With Emphasis on Germanic, Jewish, Romance and Slavic Languages. Universidad de Alicante. pp. 99–. ISBN 978-84-7908-517-9. Retrieved 9 March 2013.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Bikini Introduced, This Day in History, History Channel
- ↑ Rosebush, Judson. "Michele Bernadini: The First Bikini". Bikini Science. Retrieved 19 September 2007.
- ↑ Hoover, Elizabeth D. (July 5, 2006). "60 Years of Bikinis". American Heritage Inc. Archived from the original on September 9, 2007. Retrieved November 13, 2007.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Judson Rosebush, "1945–1950: The Very First Bikini". Bikini Science. Retrieved November 25, 2012.
- ↑ "Marshallese Culture". Safaritheglobe.com. Retrieved 18 July 2013.
- ↑ "Marshall Islands Facts, information, pictures". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 18 July 2013.
Bibliography
- Niedenthal, Jack, For the Good of Mankind: A History of the People of Bikini and their Islands, Bravo Publishers, (November 2002), ISBN 982-9050-02-5
- Wiesgall, Jonathan M, Operation Crossroads: Atomic Tests at Bikini Atoll, Naval Institute Press (21 April 1994), ISBN 1-55750-919-0
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bikini Atoll. |
- A Short History of the People of Bikini Atoll
- What About Radiation on Bikini Atoll?
- Department of Energy Marshall Islands Program: Chronology of nuclear testing, relocation of islanders and results of radiation tests
- Annotated bibliography for Bikini Atoll from the Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues
- Islanders Want The Truth About Bikini Nuclear Test
- Marshall Islands site
- Entry at Oceandots.com at the Wayback Machine (archived December 23, 2010)
- Everything Marshall Islands
- Lauren R. Donaldson Collection, served as a radiation monitor for Operation Crossroads; the codename for the first atomic bomb tests at Bikini Atoll. - University of Washington Digital Collection
| |||||||||||||||||



