Bidirectional associative memory
Bidirectional associative memory (BAM) is a type of recurrent neural network. BAM was introduced by Bart Kosko in 1988.[1] There are two types of associative memory, auto-associative and hetero-associative. BAM is hetero-associative, meaning given a pattern it can return another pattern which is potentially of a different size. It is similar to the Hopfield network in that they are both forms of associative memory. However, Hopfield nets return patterns of the same size.
Topology
A BAM contains two layers of neurons, which we shall denote X and Y. Layers X and Y are fully connected to each other. Once the weights have been established, input into layer X presents the pattern in layer Y, and vice versa.
Procedure
Learning
Imagine we wish to store two associations, A1:B1 and A2:B2.
- A1 = (1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0), B1 = (1, 1, 0, 0)
- A2 = (1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0), B2 = (1, 0, 1, 0)
These are then transformed into the bipolar forms:
- X1 = (1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1), Y1 = (1, 1, -1, -1)
- X2 = (1, 1, 1, -1, -1, -1), Y2 = (1, -1, 1, -1)
From there, we calculate 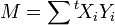 where
where 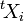 denotes the transpose.
So,
denotes the transpose.
So,
![M = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{10}c}
2 & 0 & 0 & -2 \\
0 & -2 & 2 & 0 \\
2 & 0 & 0 & -2 \\
-2 & 0 & 0 & 2 \\
0 & 2 & -2 & 0 \\
-2 & 0 & 0 & 2 \\
\end{array} } \right]](../I/m/e6d5dec21ad1718ffc99818c21385abb.png)
Recall
To retrieve the association A1, we multiply it by M to get (4, 2, -2, -4), which, when run through a threshold, yields (1, 1, 0, 0), which is B1. To find the reverse association, multiply this by the transpose of M.
See also
- Autoassociative memory
- Self-organizing feature map